MPAI has been established on 30 September 2020 as a not-for-profit unaffiliated organisation with the mission: 1) to develop data coding standards based on Artificial Intelligence and 2) to bridge the gap between standards and their practical use through Framework Licences.
MPAI develops its standards through a rigorous process depicted in Figure 1.
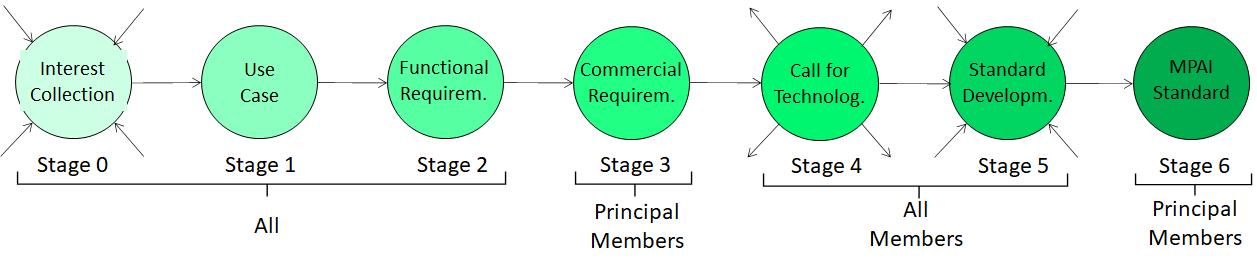
Figure 1 – Process to develop MPAI standards
An MPAI standard passes though 6+1 stages. Anybody can contribute to the first 3 stages. The General Assembly approves the progression of a standard to the next stage.
MPAI defines standard interfaces of AI Modules (AIM) combined and executed in an MPAI-specified AI-Framework (AIF). AIMs receive data with standard formats and produce output data with standard formats.
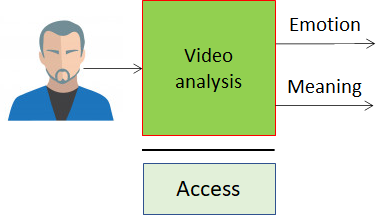 |
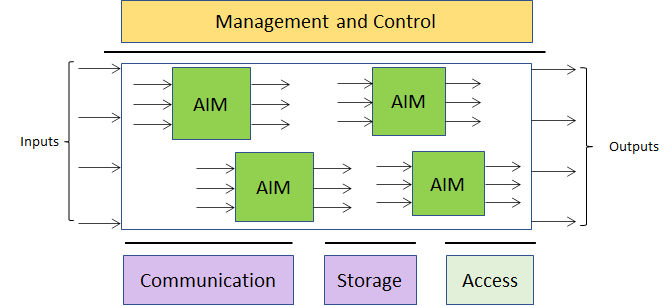 |
| Figure 1 – The MPAI AI Module (AIM) | Figure 2 – The MPAI AI Framework (AIF) |
MPAI is currently engaged in the development of 10 technical specifications. The table below gives the current stage, the MPAI name, the title and the scope of each standard. The first 4 standards will be approved within 2021
Table 1 – MPAI standards under development
| # | MPAI name | Title | Scope |
| 5 | MPAI-AIF | AI Framework | Specifies 6 elements: Management and Control, AIM, Execution, Communication, Storage and Access to enable creation and automation of mixed ML-AI-DP processing and inference workflows. |
| 5 | MPAI-CAE | Context-based Audio Enhancement | Improves the user experience in audio applications, e.g., entertainment, communication, teleconferencing, gaming, post-production, restoration etc. for different contexts, e.g., in the home, in the car, on-the-go, in the studio etc. |
| 5 | MPAI-MMC | Multimodal Conversation | Enables human-machine conversation that emulates human-human conversation in completeness and intensity |
| 5 | MPAI-CUI | Compression and understanding of industrial data | Enables AI-based filtering and extraction of governance, financial and risk data to predict company performance. |
| 3 | MPAI-SPG | Server-based Predictive Multiplayer Gaming | Minimises the audio-visual discontinuities caused by network disruption during an online real-time game and provides a response to the need to detect who amongst the players is cheating. |
| 3 | MPAI-GSA | Integrative Genomic/Sensor Analysis | Understands and compresses the result of high-throughput experiments combining genomic/proteomic and other data, e.g., from video, motion, location, weather, medical sensors. |
| 3 | MPAI-EVC | AI-Enhanced Video Coding | Substantially enhances the performance of a traditional video codec by improving or replacing traditional tools with AI-based tools. |
| 3 | MPAI-CAV | Connected Autonomous Vehicles | Uses AI to enable a Connected Autonomous Vehicle with 3 subsystems: Human-CAV interaction, Autonomous Motion Subsystem and CAV-Environment interaction |
| 2 | MPAI-OSD | Visual object and scene description | A collection of Use Cases sharing the goal of describing visual object and locating them in the space. Scene description includes the usual description of objects and their attributes in a scene and the semantics of the objects. |
| 1 | MPAI-MCS | Mixed-Reality Collaborative Spaces | Enables mixed-reality collaborative space scenarios where biomedical, scientific, and industrial sensor streams and recordings are to be viewed where AI can be utilised for immersive presence, spatial map rendering, multiuser synchronisation etc. |
Additionally, MPAI is engaged in the development of a standard titled “Governance of the MPAI ecosystem”. This standard will specify how:
- Implementers can get certification of the adherence of an implementation to an MPAI standard from the technical (Conformance) and ethical (Performance) viewpoint.
- End users can reliably execute AI workflows on their devices.
Any legal entity supporting the mission of MPAI, if able to contribute to the development of standards for the efficient use of Data may apply for MPAI membership. Additionally, individuals representing technical departments of academic institutions may apply for Associate Membership.

