1 Functions of Human-CAV Interaction. 14
2 Reference Architecture of Human-CAV Interaction. 14
3 I/O Data of Human-CAV Interaction. 15
4 Functions of Human-CAV Interaction’s AI Modules. 16
5 I/O Data of Human-CAV Interaction’s AI Modules. 17
1 Functions of Human-CAV Interaction
The Human-CAV Interaction (HCI) Subsystem performs the following high-level functions:
- Authenticates humans e.g., for the purpose of letting them into the CAV.
- Interprets and executes commands provided by humans, possibly after a dialogue, e.g., to go to a Waypoint, issue commands such as turn off air conditioning, open window, call a person, search for information, etc.
- Displays Full Environment Representation to passengers via a viewer and allows passengers to navigate and control the viewing.
- Interprets conversation utterances with the support of the extracted Personal Statuses of the humans, e.g., on the fastest way to reach a Waypoint because of an emergency, or during a casual conversation.
- Displays itself as a Body and Face with a mouth uttering Speech showing a Personal Status comparable to the Personal Status that a human counterpart (e.g., driver, tour guide, interpreter) would display in similar circumstances.
The HCI operation is highly influenced by the notion of Personal Status, the set of internal characteristics of conversing humans and machines. See Annex 0 Section 5.
2 Reference Architecture of Human-CAV Interaction
Figure 3 gives the Reference Model of Human-CAV Interaction (HCI) Subsystem supporting the case of a group of humans approaching the CAV from outside the CAV and sitting inside the CAV.
The HCI operation in the outdoor and indoor scenarios unfolds as follows:
- Audio Scene Description AIM creates the Audio Scene Description in the form of 1) Audio (Speech) Objects corresponding to each speaking human in the Environment (close to the CAV) and 2) Audio Scene Geometry.
- Visual Scene Description creates the Visual Scene Descriptors in the form of Descriptors of 1) Faces and the Bodies corresponding to each human in the Environment (close to the CAV) and 2) Visual Scene Geometry.
- Speech Recognition recognises the speech of each human.
- Spatial Object Alignment Identifies Audio, Visual, and Audio-Visual Objects, from Audio and Visual Scene Geometries.
- Spatial Object Identification produces Object ID from Physical Objects, Body Descriptors, and Visual Scene Geometry.
- The Full Environment Representation (FER) Viewer renders the FER in response to FER navigation Commands.
- Language Understanding produces the Refined Text and extracts the Meaning.
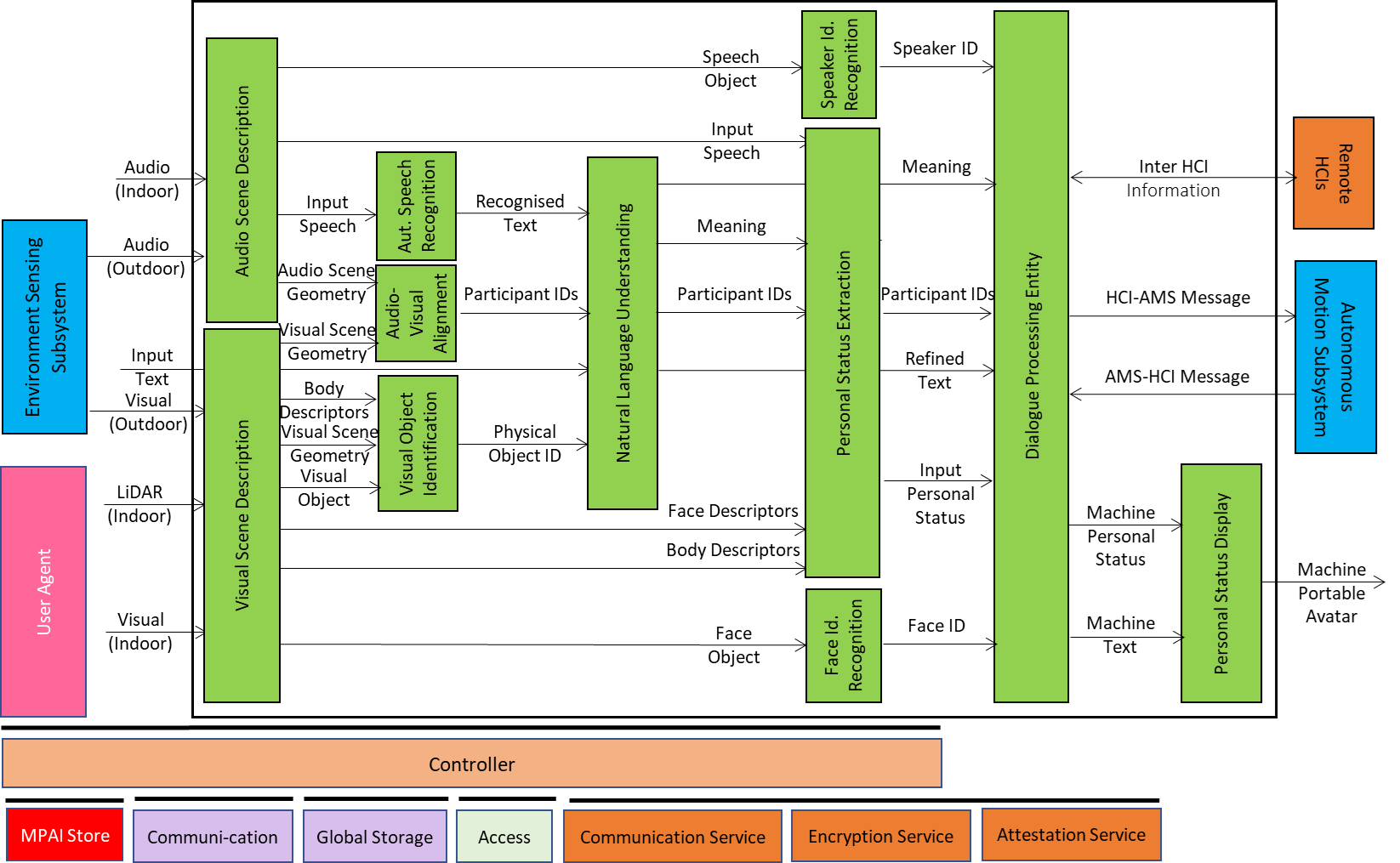
Figure 3 – Human-CAV Interaction Reference Model
- The Speaker Recognition and Face Recognition AIMs authenticate the humans the HCI is interacting with. The processing of these two AIMs may be carried out remotely.
- The Personal Status Extraction AIM extracts the Input Personal Status from Meaning, Speech, Face Descriptors, and Body Descriptors.
- The Dialogue Processing AIM:
- Validates the human Identities.
- Produces Machine Text and Machine Personal Status.
- The Personal Status Display produces the ready-to-render Machine Portable Avatar [8] conveying Machine Speech and Machine Personal Status.
- Issues commands to the Autonomous Motion Subsystem.
- Receives and processes responses from the Autonomous Motion Subsystem.
- Communicates with Remote HCIs.
3 I/O Data of Human-CAV Interaction
Table 3 gives the input/output data of the Human-CAV Interaction Subsystem.
Table 3 – I/O data of Human-CAV Interaction
| Input data | From | Comment |
| Full Environment Representation | Autonomous Motion Subsystem | Rendered by Full Environment Representation Viewers |
| Full Environment Representation Commands | Cabin Passengers | To control rendering of Full Environment Representation |
| Audio (Outdoor)) | Environment Sensing Subsystem | User authentication
User command User conversation |
| Audio (Indoor) | Cabin Passengers | User’s social life
Commands/interaction with HCI |
| Visual (Outdoor) | Environment Sensing Subsystem | Commands/interaction with HCI |
| Visual (Indoor) | Cabin Passengers | User’s social life
Commands/interaction with HCI |
| LiDAR | Cabin Passengers | User’s social life
Commands/interaction with HCI |
| AMS-HCI Response | Autonomous Motion Subsystem | Response to HCI-AMS Command |
| Inter HCI Information | Remote HCI | HCI-to-HCI information |
| Output data | To | Comments |
| Full Environment Representation Audio | Passenger Cabin | For passengers to hear external Environment |
| Full Environment Representation Visual | Passenger Cabin | For passengers to view external Environment |
| Inter HCI Information | Remote HCI | HCI-to-HCI information |
| HCI-AMS Command | Autonomous Motion Subsystem | HCI-to-AMS information |
| Machine Portable Avatar | Cabin Passengers | HCI’s avatar. |
4 Functions of Human-CAV Interaction’s AI Modules
Table 4 gives the functions of all Environment Sensing Subsystem AIMs.
Table 4 – Functions of Human-CAV Interaction’s AI Modules
| AIM | Function |
| Audio Scene Description | Produces the Audio Scene Descriptors using the Audio captured by the appropriate (indoor or outdoor) Microphone Array. |
| Visual Scene Description | Produces the Visual Scene Descriptors using the visual information captured by the appropriate indoor visual sensors (Visual and LiDAR) or outdoor visual sensors. |
| Speech Recognition | Converts speech into Recognised Text. |
| Audio-Visual Alignment | Identifies Audio, Visual, and Audio-Visual Objects. |
| Physical Object Identification | Provides the ID of the class of objects of which the Physical Object is an Instance |
| Full Environment Representation Viewer | Converts the Full Environment Representation produced by the Autonomous Motion Subsystem into Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors that can be perceptibly rendered by the Viewer. |
| Language Understanding | Refines the Recognised Text by using context information (e.g., Instance ID of object). |
| Speaker Recognition | Provides Speaker ID from Speech Object. |
| Personal Status Extraction | Provides the Personal Status of a passenger. |
| Face Recognition | Provides Face ID from Face Object. |
| Dialogue Processing | Provides:
1. Machine Text containing the HCI response. 2. Machine Personal Status. |
| Personal Status Display | Produces Machine Personal Avatar. |
5 I/O Data of Human-CAV Interaction’s AI Modules
Table 5 gives the input/output data of the Human-CAV Interaction AIMs.
Table 5 – I/O Data of Human-CAV Interaction’s AI Modules
| AIM | Input | Output |
| Audio Scene Description | Audio (outdoor)
Audio (indoor) |
Speech Objects
Audio Scene Description |
| Visual Scene Description | Visual (outdoor)
Visual & LiDAR (indoor) |
Face Descriptors
Body Descriptors Physical Objects Visual Scene Description |
| Speech Recognition | Speech Object | Recognised Text |
| Physical Object Identification | Physical Object
Body Descriptors |
Physical Object ID |
| Full Environment Representation Viewer | FER Commands | FER Audio
FER Visual |
| Language Understanding | Recognised Text
Personal Status Physical Object ID |
Meaning
Personal Status Refined Text |
| Speaker Recognition | Speech Descriptors | Speaker ID |
| Personal Status Extraction | Meaning
Speech Object Face Descriptors Human Descriptors |
Personal Status |
| Face Recognition | Face Object | Face ID |
| Dialogue Processing | Speaker ID
Meaning Refined Text Personal Status Face ID AMS-HCI Response |
AMS-HCI Commands
Machine Text Machine Personal Status |
| Personal Status Display | Machine Text
Machine Personal Status |
Machine Personal Avatar |

