Abstract
This document, issued by Moving Picture, Audio, and Data Coding by Artificial Intelligence (MPAI), collects Use Cases and Functional Requirements relevant to Technical Specification: Compression and Understanding of Industrial Data (MPAI-CUI) V2.0 that MPAI intends to develop. This document is part of the set of documents comprising MPAI-CUI V2.0 Call for Technologies [4], MPAI-CUI V2.0 Framework Licence [5], and MPAI-CUI V2.0 Template for Responses [6].
MPAI is an international non-profit organisation having the mission to develop standards for Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled data coding and technologies facilitating integration of data coding components into Information and Communication Technology (ICT) systems [1]. The MPAI Patent Policy [2] guides the accomplishment of the mission.
Contents
3 CUI-CPP V2.0 Functional Requirements
5 CUI-CPP V2.0 Input/Output Data.
6 Functional Requirements of AIMs
7 Input/Output Data of AI Modules
1 Introduction
Established in September 2020, MPAI has developed fourteen Technical Specifications relevant to its mission such as execution environment of multi-component AI applications, context-based audio enhancement, connected autonomous vehicle, company performance prediction, governance of the MPAI ecosystem, multimodal human-machine conversation and communication, metaverse, neural network traceability, object and scene description, portable avatar format, AI Module Profiles, and Qualifiers. Eight Technical Specifications have been adopted by IEEE without modification, one is about to be adopted, and more are in the pipeline. A Call for Technologies has been issued for up-sampling filters for video applications [9]. Several other standard projects – such as AI for Health, online gaming and XR Venues – are under way and are expected to deliver specifications in the next few months.
MPAI specifications are the result of a process whose main steps are:
- Development of functional requirements in an open environment.
- Adoption of “commercial requirements” (Framework Licence) by MPAI principal members setting main elements of the future licence to be issued by standard essential patents holders.
- Publication of a Call for Technologies referring the two sets of requirements inviting the submission of contributions by parties who accept to licence their technologies according to the Framework Licence, if their technologies are accepted to be part of the target Technical Specification.
This document is the Use Cases and Functional Requirements related to the planned Technical Specification: Compression and Understanding of Industrial Data (MPAI-CUI) V2.0 which is intended to extend and enhance the capabilities of the previous V1.1 version [7].
As done for most MPAI standards published so far, it is assumed that MPAI-CUI V2.0 is implemented in an AI Framework (AIF), an environment enabling initialisation, dynamic configuration, execution, and control of AI Workflows (AIW) composed of interconnected AI Modules (AIM) [8].
2 Scope
MPAI-CUI V1.1 [7] specifies the Company Performance Prediction Use Case whose Reference Model is depicted in Figure 1 where the following data are processed:
- Governance and Financial Statement Data are pre-processed to produce Governance and Financial Features.
- Governance and Financial Features are processed by AIM to produce Organisational Model Index and Default Probability, both scalar values.
- AIM converts the company-produced Risk Assessments into a Risk Matrix and feeds to a Result AIM
- Default Probability and Risk Matrix are processed to produce the Business Discontinuity Probability, another scalar value.
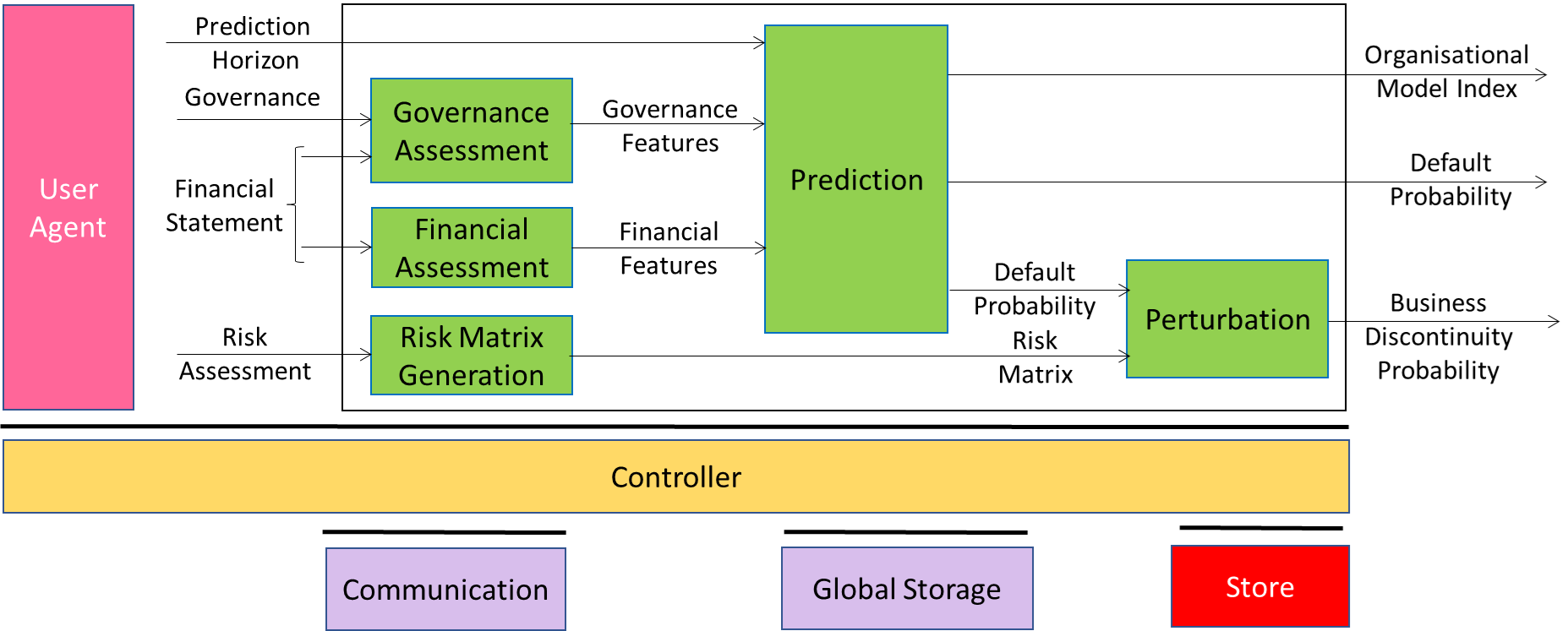
Figure 1 – CUI-CPP V1.1 Reference Model
The Company Performance Prediction Use Case of MPAI-CUI V2.0 (CUI-CPP V2.0) extends V1.1 in the following ways:
- Governance and Financial Data are pre-processed to produce Governance and Financial Descriptors.
- Vertical Risks Data for which the following descriptors available
- Risk name
- Risk type
- Target regulation
- Vector of inputs
- The Organisation, Discontinuity, and Default Prediction AIMs are grouped in the Assessment and Prediction Composite (see Figure 3). It receives Governance and Financial Descriptors and Vertical Risk Descriptors to produce Organisation, Default, and Discontinuity Descriptors. These are data structures composed of Index and Explainability Data.
- Vertical Risks for which the data of point 2. above do not include information about relevant regulations are converted to a Risk Matrix and processed by the AIM. It uses the Risk Matrix to perturb the Default Data and produces Discontinuity Probability. It should be used if the AIM does not provide a specific AIM for the given risk or if the AIM is not compatible with the regulation of the use case.
Figure 2 depicts the Reference Model of CUI-CPP V2.0 AIW. 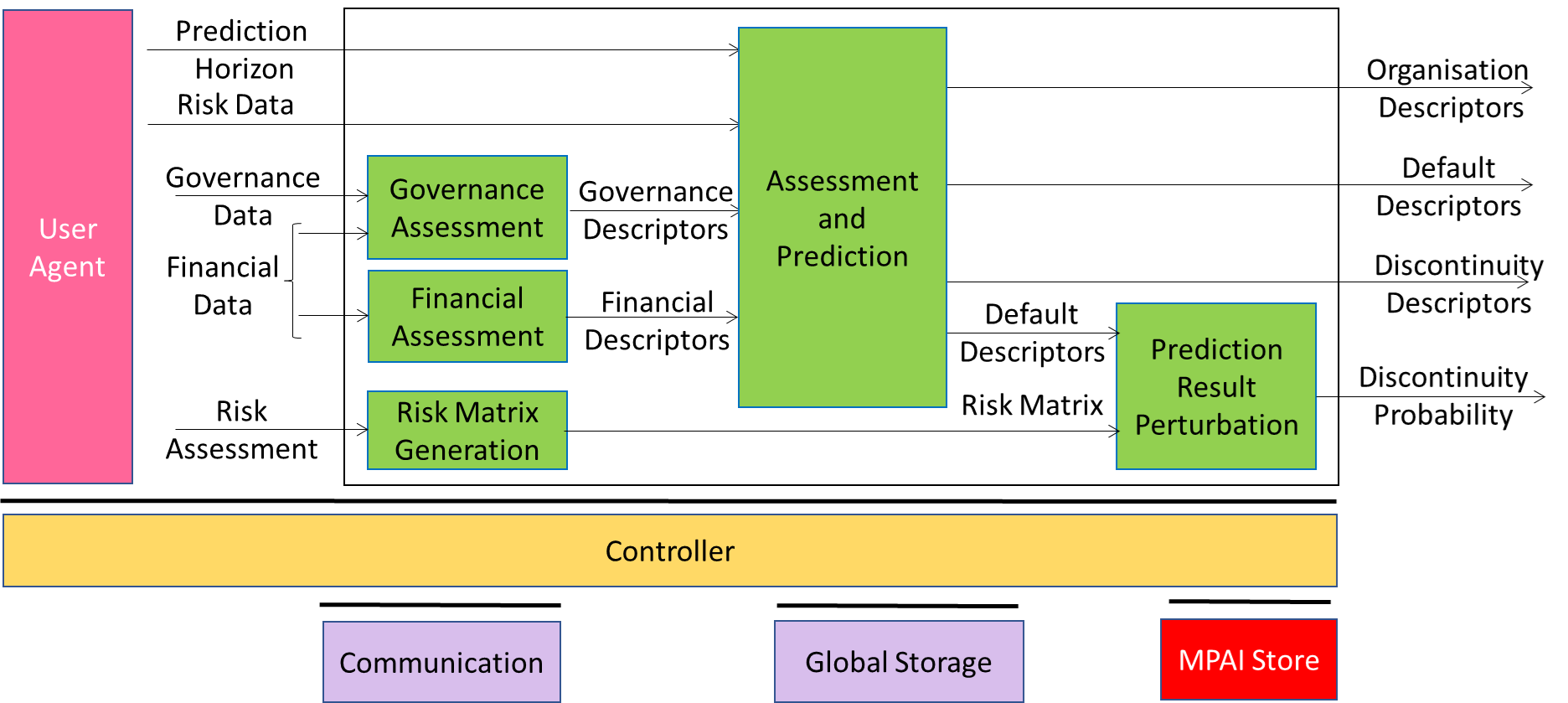
Figure 2 – CUI-CPP V2.0 Reference Model
The AIM is a Composite AIM with two prediction AIMs and one computation AIM.
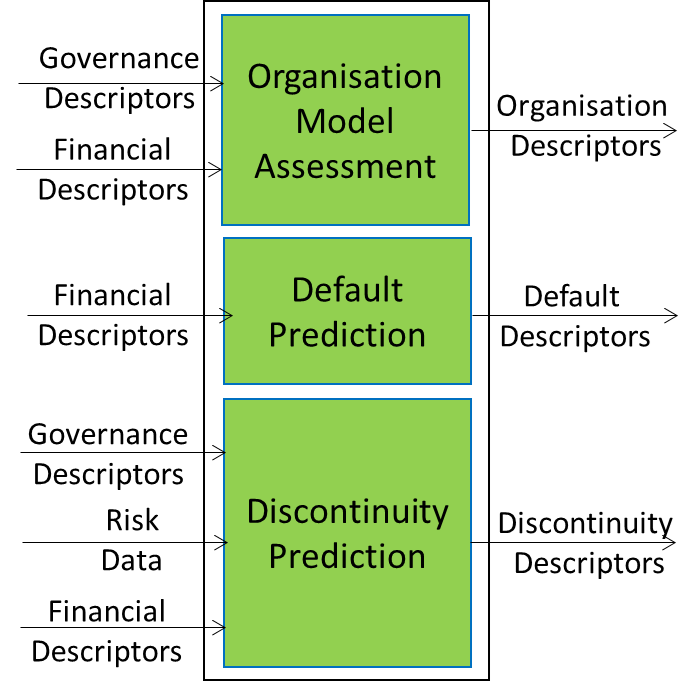
Figure 3 – New Assessment and Prediction AIM in MPAI-CUI V2.0
3 CUI-CPP V2.0 Functional Requirements
The Functional Requirements of MPAI-CUI V2.0 data are the following:
- Governance data:
- Frequency of officer terms in the last 5 years.
- Which and how many roles officers have in other legal entities.
- Extensions to CUI-CPP V1.1
- Financial data:
- Extensions to CUI-CPP V1.1
- Risk assessment
- Risk taxonomy
- Extensions to CUI-CPP V1.1
- Vertical risk data: features for each considered risk, including:
- Risk name
- Risk type: cyber, etc.
- Target regulation
- Vector of inputs, e.g. for cyber:
- Name of input: IP address, Denial of service.
- Time: time the attack was detected.
- Source: provider of input vector.
- Type: (image, text, category, …).
- Value: depends on type.
- Default Descriptors
- Components of explainability.
- Organisation Descriptors
- Components of explainability.
- Discontinuity Descriptors
- Components of explainability.
4 CUI-CPP V2.0 Vertical Risks
The following is an initial list of Risks proposed for support by CUI-CPP V2.0 that can be extended or refined:
- Cyber
- Embedded systems
- IoT
- Data and backup loss
- Credential loss
- Unauthorised access
- Remote access to ICT infrastructure
- Digitisation
- Credential loss
- Software update
- Data and backup loss
- Other unintended or malicious actions
- Climate
- Physical risks
- Transition risks (forced reduction of emissions, forced change of energy creation, impact of climate change on the type of product portfolio to production and market)
- ESG (Environment-Social-Governance)
- Business
- Risk management: The risk generated by inadequate risk management
- Finance: Risks such as: exchange, interest rates, taxation, price fluctuation (raw materials, semi-finished materials, transportation, supply chain)
- Compliance: the risk of inappropriate actions inside the company leading to penalties (personnel, managers, sabotage to others, cartel).
- Operational (suppliers, product failure)
- Strategic (competition, distribution agreement, partnership agreement)
Comments and proposals requested on:
- CUI-CPP V1.1 risk list: extension, reduction, different partitioning of risk classification
- Semantics of the individual risks/proposal of final risk semantics
- Formats of input data
- JSON syntax for each risk requested.
5 CUI-CPP V2.0 Input/Output Data
The following CUI-CPP V2.0 AIW input and output data need formats with the functional requirements identified in Sections 3 and 4.
Table 1 – Input/Output Data of AIW
| Input | Description |
| Prediction Horizon | Number of months of prediction. |
| Risk Data | Proposals. |
| Governance | V1.1 Extensions/proposals. |
| Financial Statement | V1.1 Extensions/proposals. |
| Risk Assessment | V1.1 Extensions/proposals. |
| Output | Description |
| Organisation Descriptors | Proposals. |
| Default Descriptors | Proposals. |
| Discontinuity Descriptors | Proposals. |
6 Functional Requirements of AIMs
Table 2 gives high level functionalities of the CUI-CPP V2.0 AIMs.
Table 2 – Functional Requirements of the AIMs
| AIM | Functional Requirements |
| Governance Assessment | Computes the Governance Descriptors. |
| Financial Assessment | Computes the Financial Descriptors. |
| Risk Matrix Generation | Computes the Risk Matrix. |
| Assessment and Prediction | Computes Organisation, Default, and Discontinuity Descriptors. |
| Prediction Result Perturbation | Computes Discontinuity Probability by perturbing the Default Descriptors. |
7 Input/Output Data of AI Modules
AI Modules receive/produce data which should have a format in CUI-CPP V2.0.
Table 3 – Input/Output Data of AI Modules
| Governance Assessment | Governance Data Financial Data |
Governance Descriptors |
| Financial Assessment | Financial Data | Financial Descriptors |
| Risk Matrix Generation | Risk Assessment | Risk Matrix |
| Assessment and Prediction | Prediction Horizon Risk Data Governance Descriptors Financial Descriptors |
Organisation Descriptors Default Descriptors Discontinuity Descriptors |
| Prediction Result Perturbation | Default Descriptors Risk Matrix |
Discontinuity Probability |
8 References
- MPAI; Statutes
- MPAI; Patent Policy
- MPAI; Technical Specifications
- MPAI; Call for Technologies: Compression and Understanding of Industrial Data (MPAI-CUI); N2130
- MPAI; Framework Licence: Compression and Understanding of Industrial Data (MPAI-CUI); N2131
- MPAI; Template for Responses: Compression and Understanding of Industrial Data (MPAI-CUI); N2132
- MPAI; Technical Specification: Compression and Understanding of Industrial Data (MPAI-CUI) V1.1
- MPAI; Technical Specification: AI Framework (MPAI-AIF) V2.1
- MPAI; Call for Technologies: Up-sampling for Video application (MPAI-UFV) V1.0

