| 1 Function | 2 Reference Model | 3 Input/Output Data |
| 4 SubAIMs | 5 JSON Metadata | 6 Profiles |
| 7 Reference Software | 8 Conformance Texting | 9 Performance Assessment |
1 Functions
Natural Language Understanding (MMC-NLU):
| Receives | Text Object directly input by the Entity. |
| Recognised Text from an Automatic Speech Recognition AIM. | |
| The ID of an Instance. | |
| The Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors containing the Instance ID. | |
| Refines | Input Text if coming from an Automatic Speech Recognition AIM |
| Extracts | Meaning (Text Descriptors) from Recognised Text or Entity’s Text Object. |
| Produces | Refined Text. |
| Text Descriptors (Meaning). | |
| Enables | Personal Stats Display to produce a Portable Avatar. |
2 Reference Model
Figure 1 specifies the Reference Model of the Natural Language Understanding (MMC-NLU) AIM.
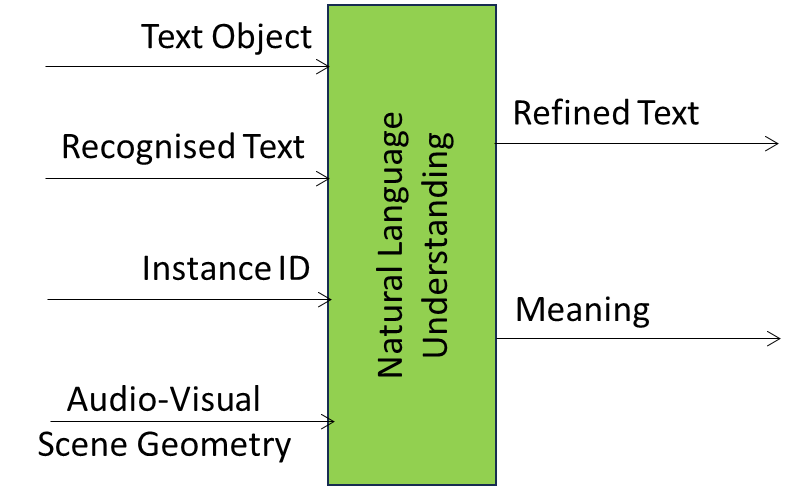
Figure 1 – The Natural Language Understanding (MMC-NLU) AIM Reference Model
3 Input/Output Data
Table 1 specifies the Input and Output Data of the Natural Language Understanding (MMC-NLU) AIM.
Table 1 – I/O Data of the Natural Language Understanding (MMC-NLU) AIM
| Input | Description |
| Text Object | Input Text. |
| Recognised Text | Text from the Automatic Speech Recognition AIM. |
| Instance ID | The Identifier of the specific Audio or Visual Object belonging to a level in the taxonomy. |
| Audio-Visual Scene Geometry | The digital representation of the spatial arrangement of the Visual Objects of the Scene. |
| Visual Instance ID | The Identifier of the specific Visual Object belonging to a level in the taxonomy. |
| Output | Description |
| Meaning | Descriptors of the Refined Text. |
| Refined Text | The refined version of the Recognised Text from the NLU AIM. |
4 SubAIMs
No SubAIMs.
5 JSON Metadata
https://schemas.mpai.community/MMC/V2.3/AIMs/NaturalLanguageUnderstanding.json
6 Profiles
The Profiles of the Natural Language Understanding (MMC-NLU) AIM are specified.
7 Reference Software
8 Conformance Testing
Table 2 provides the Conformance Testing Method for MMC-NLU AIM.
If a schema contains references to other schemas, conformance of data for the primary schema implies that any data referencing a secondary schema shall also validate against the relevant schema, if present and conform with the Qualifier, if present.
Table 2 – Conformance Testing Method for MMC-NLU AIM
| Input | Text Object | Shall validate against Text Object schema. Text Data shall conform with Text Qualifier. |
| Recognised Text | Shall validate against Text Object schema. Text Data shall conform with Text Qualifier. |
|
| Instance ID | Shall validate against Instance ID schema. | |
| Audio-Visual Scene Geometry | Shall validate against AV Scene Descriptors schema. | |
| Output | Refined Text | Shall validate against Text Object schema. Text Data shall conform with Text Qualifier. |
| Meaning | Shall validate against Meaning schema. |
Table 3 provides an example of MMC-NLU AIM conformance testing.
Table 3 – An example MMC-NLU AIM conformance testing
| Input Data | Data Type | Input Conformance Testing Data |
| Input Selector | Binary data | All Input Selectors shall conform with Selector. |
| Text Object | Unicode | All input Text files to be drawn from Text files. |
| Recognised Text | Unicode | All input Text files to be drawn from Text files. |
| Output Data | Data Type | Output Conformance Testing Criteria |
| Meaning | JSON | All JSON files shall validate against Meaning Schema |
| Refined Text | Unicode | All Text files produced shall conform with Text. |
The four taggings: POS_tagging, NE_tagging, dependency_tagging, and SRL_tagging must be present in the output JSON file of Meaning. Any of the four tagging values may be null.

