<–Use Cases Go to ToC Functional Requirements->
This Chapter introduces the Functionalities of the MPAI Metaverse Model (MPAI-MMM) making use of the Terms defined in Table 3 (also available online)
| 3.1 | Disclaimer | 3.5 | Items |
| 3.2 | Basic Functionalities | 3.6 | Data Types |
| 3.3 | Processes | 3.7 | Interoperability support |
| 3.4 | Actions performed by Processes |
3.1 Disclaimer
The MPAI-MMM – Architecture does not assume:
- A specific type of architecture (the model should be applicable to centralised, decentralised, or blockchain-based architectures).
- A specific identification technology (the model only assumes that identification is possible, it does not make assumptions on how identification is achieved).
- A specific security technology (the model only assumes that the environment in which the operation takes place is secure, it does not make assumptions on how security is achieved).
- A specific data formats (the model only identifies the functionalities that the data format should provide, it does not make assumptions on any specific data format).
- A specific network (the model only assumes that the network has the required capabilities, it does not make assumptions on how they can be provided).
3.2 Basic Functionalities
Main definitions:
- A Process is Program and Metadata that can be executed in the M-Instance to perform Actions on Items.
- An Action is a supported Functionality that is performed in an M-Instance. The currently identified Actions are introduced in 3.
- An Item is Data and Metadata supported by the M-Instance where the Item exists. The currently identified Items are introduced in 3.
- Metadata may include Rights.
- Rights define:
- The ability of a Process to perform Actions on Items.
- The possibility that an Item be subjected to an Action by a Process.
- An Item may include Rights held by User and Rights that it may be possible to acquire on the Item.
- Data Types are data referenced by Actions and Items and are introduced in 5.
An M-Instance is a set of Processes providing some or all the following functions:
- Senses data from U-Location.
- Produces Items autonomously or by processing the sensed data.
- Hosts one or more M-Environments populated by Objects that can be either digitised or virtual, the latter with or without autonomy.
- Processes Objects from the M-Instance or potentially from other M-Instances to affect U- and/or M-Environments using Objects in ways that are:
- Consistent with the goals set for the M-Instance.
- Effected within the capabilities and Rules of the M-Instance, and in accordance with applicable laws and regulations.
- Identifies Processes and Items with one or more than one Identifier that uniquely refers to one Process or Item and includes an Identifier.
- May contain one or more M-Environments each of which:
- Includes an Identifier.
- May include M-Locations with space and time attributes.
- May require a Registration specific to the M-Environment.
- May make available information regarding its Capabilities.
- May require Registration for use:
- A human can request to deploy one or more Users and one or more Personae in an M-Instance.
- An M-Instance may request a subset of the Personal Profile of the Registering human.
- Establishes Rules that human’s Users in the M-Instance shall comply with.
- May penalise a User for lack of compliance with the Rules.
3.3 Processes
MPAI-MMM – Architecture identifies the following types of Process performing Actions on Items in an M-Instance (see Figure 1):
- User represents a human rendered as:
- A Model (Persona) animated by a stream generated by the human or by an autonomous agent. A User may be rendered by one or more Personae.
- An Object rendering the human.
- Device connects User with a human or a U-Location:
- From Universe to Metaverse: captures a scene as Media and Provides Media as Data and Metadata:
- From Metaverse to Universe: receives an Entity and renders the Entity as Media with a Spatial Attitude.
- Service provides Functionalities.
- App is a Program executed on a Device.
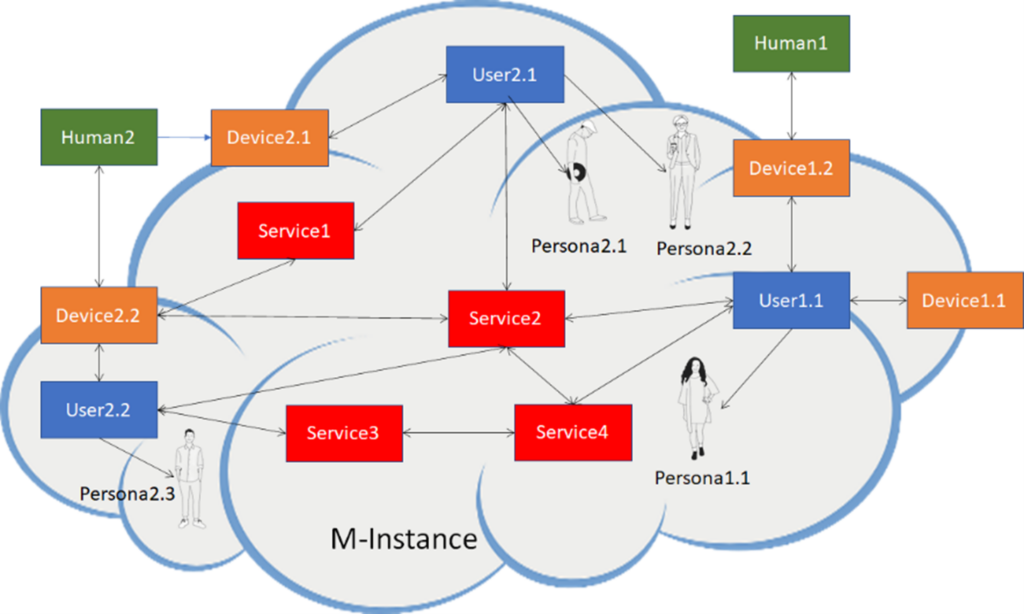
Figure 1 – Relationship of Human-Device-User-Service-Persona
A Process has the following general features:
- Performs an Action on an Item if it has the Rights to do that.
- Can make available information about its Capabilities.
- Items on which the Actions can be performed.
- The time during which they can be performed.
- The M-Locations where they can be performed.
- Can request another Process to perform Actions on Items by transmitting to it a Request-Action Item.
- Can be requested to perform an Action and it does so if:
- The requesting Process has the Rights required to perform that request.
- The requested Process has the Rights to perform the requested Action on the Item.
- Can respond to another Process requesting an Action with a Response-Action Item.
- Uses a supported format:
- To request another Process to perform Actions on Items (Request-Action).
- To respond to another Process that has requested an Action (Respond-Action).
- May perform, or to request other Processes to perform, Actions on Items even in the absence of Rights, if the Rules so allow.
- May need to be certified by the M-Instance Manager for use in an M-Instance.
- The currently identified Processes are introduced in 2.
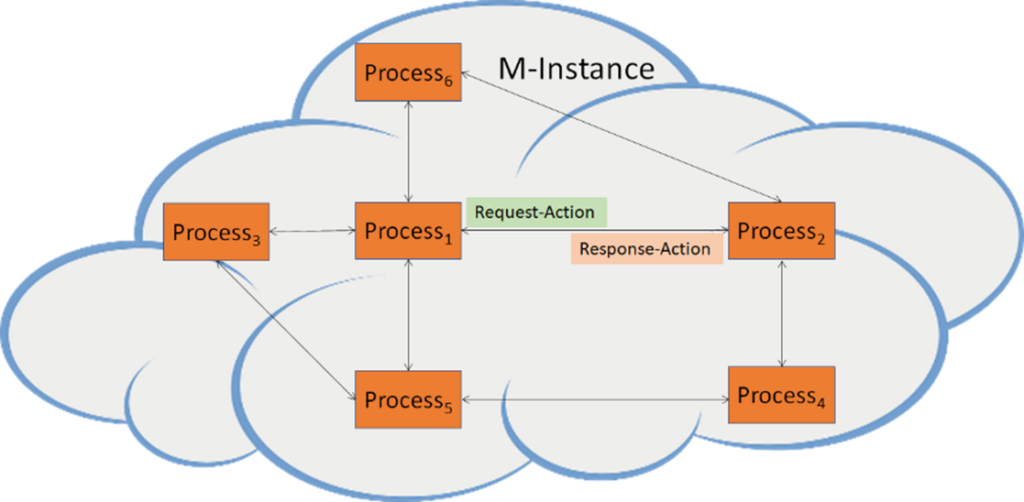
Figure 2 – Processes in an M-Instance
3.4 Actions performed by Processes
A Process may request that the following Actions be performed (in bracket the initially assigned name):
- Modify the Rights of a User (Change).
Comments: A User not complying with the Rules may have its Rights diminished or additional Rights may be granted to a User.
- Authenticate an Item (Authenticate).
Comments: A Process can confirm that the speech of a human imported into an M-Instance is from a specific human.
- Make an Item unavailable (Hide).
Comments: A certain Item may be made no longer accessible. Depending on the Rights of the User, the Item may be made accessible again.
- Create an Item using Data and Metadata (Identify).
Comments: A Device may capture Media as Data subject to certain Rights for use in an M-Instance. The Data and Metadata shall be converted to an Item for them to be usable in the M-Instance.
- Create a new Item by modifying an original Item with Data and Metadata (Modify).
Comments: A User with Rights on the Item may clone and then modify the components of an existing Item.
- Create an Item by providing it with Data and Metadata (Author).
Comments: An M-Instance can provide a Service, internal or external to the M-Instance, that Users can call to create Items for use in the M-Instance.
- Request to find Items by giving a description of the Items (Discover).
Comments: An M-Instance can provide a Service, internal or external to the M-Instance, that Users can call to find Items or Processes they need.
- Request to provide information about an Item (Inform).
Comments: A User may wish to know more about an Item, starting from its Metadata.
- Request it to provide interpretations of an Item (Interpret).
Comments: A User may need to have an Item interpreted, e.g., to have the speech of a User translated.
- Request to display an Item on a Service (Post).
Comments: A User can make known its intention to surrender its Rights on an Asset by posting it to a marketplace.
- Request Rights to perform Actions on Items (Transact).
The User acquiring Rights on an Item is typically required to make a Transaction to the original Rights holder of the Item.
- Place an Entity at an M-Location not perceived by other Users/humans (MM-Add).
- Make an Entity perceptible that was not (MM-Enable).
- Place an Entity at an M-Location perceived by other Users (MM-Embed).
- Stop making an Entity perceptible (MM-Disable).
Comments: A User can place an Entity at an M-Location with different modalities:
- By placing it but not making it perceptible by other User (MM-Add) and making it perceptible at another time (MM-Enable), or
- By Placing and making it perceptible in one stroke (MM-Embed).
- When the User no longer wishes to let other Users perceive the Entity it will MM-Disable it.
- Transmit Items to a Process (MM-Send).
Comments: This general function enables Right-holding Users to have available and make Actions on Items.
- Activate a Contract (Execute).
Comments: Contracts may be Executed by an underlying Blockchain.
- Animate a Model (MM-Animate).
Comments: A Process autonomously animates a Model without using Streams from a U-Location.
- Animate a Model using an Animation Stream (UM-Animate)
Comments: A Process receives a Stream from a U-Location and animates a Model.
- Present Media available at a Device to a U-Location as a scene with an associated Spatial Attitude (MU-Actuate).
Comments: A User may request that a Device present the Media is has received as an Entity via an MM-Send Action. The presentation of is made with a specified Spatial Attitude.
- Present an Entity that is at an M-Location to a U-Location as a scene with an associated Spatial Attitude (MU-Render).
Comments: A User may request that an Entity at an M-Location be presented as Media at a U-Location with a Spatial Attitude. This operation is performed in two steps: MM-Send the Entity to a Device and MU-Actuate the Media from the Device.
- Present a scene that is at a U-Location to an M-Location as an Entity with an associated Spatial Attitude (UM-Render).
Comments: The presentation of a scene captured at a U-Location as an Entity is performed by a Device using the captured Media, converting Data and Metadata to an Entity and them MM-Embedding the Entity.
- Capture a scene at a U-Location as Media (UM-Capture).
Comments: The first step of the process above is represented by the capture of a scene ay a U-Location as Media.
- Transmit Data and Metadata to a Process (UM-Send).
Comments: The second step of the process above is the transmission of Data corresponding to the Media and Metadata added by the Device to a Process.
- Store an Item at an Address (MU-Send).
Comments: Make available to a Process Data and Metadata or an Item stored at an Address (UM-Send).
- Place a Model at an M-Location, animate it with a Stream, and present the animated Model at a U-Location with an associated Spatial Attitude (Track).
Comments: With Track a two-way connection between Universe and Metaverse is established.
- Verify that a Process has Rights to make an Action on an Item (Validate).
Comments: This is a basic Functionality preserving integrity of M-Instance operation.
- Convert one or more Items of a Request-Action or Response-Action to another Format (Convert).
Comments: As for other Services, Convert can be a Service offered by the M-Instance or available outside of the M-Instance.
- Transmit a Request-Action to a Resolution Service to communicate to a different M-Instance.
Comments: As for other Services, Resolution can be a Service offered by the M-Instance or available outside of the M-Instance.
- Register with an M-Instance or M-Environment.
Comments: This Action involves a human, not a User
3.5 Items
The Metaverse requires the following Items:
- For general use
- Contract: Program activated by an external entity, e.g., a User or another activated Contract.
- Identifier: An Item that uniquely references an Item. The Item can have more than one Identifier.
- Program: Data that can be executed.
- Rights: the ability of a Process to perform an Action on an Item at an M-Location until a Time.
- For Environments
- M-Environment: A portion of an M-Instance covered by an Account including an Identifier.
- M-Instance: An identifiable portion of an M-Instance covered by an Account.
- For Process-to-Process communication
- Message: An Item containing application-specific Data MM-Sent by a Source to a Destination.
- Request-Action: An Item containing the request to a Service to perform an Action.
- Response-Action: An Item containing the response of a Service to a Request-Action.
- For the Register Action
- Account: An Item that uniquely references a human who has Registered. A human may have more than one Account with one or more Services.
- Activity Data: The record of the Actions of a User.
- Personal Profile: An Item containing the Data about the human represented by User.
- Rules: The terms and conditions under which a User operates in an M-Instance/Environment.
- Social Graph: A representation of a User’s network of connections with Items, Processes, and Services.
- User Data: An Item containing Activity Data, Personae, Social Graph, and Personal Profile of a User.
- For the Transact Action
- Asset: An Item placed at an M-Location or Posted to a Service that may be subject to a Transaction.
- Ledger: The list of Transactions involving Assets.
- Provenance: The Ledger associated with a specific Asset.
- Transaction: Item representing the changed state of the Accounts and the Rights of a seller User and a buyer User on an Asset and optionally of the Service facilitating/enabling the Transaction.
- Value: An Amount and the Currency with which the Amount is expressed.
- Wallet: A container of Currency units. In general, a Wallet is implemented outside of the Environment.
- For requesting Actions by Services
- AuthenticateIn: The description of the Item to be Authenticated.
- AuthenticateOut: The description of the Authentication of the Item.
- DiscoverIn: The description of the Items or Processes to be Discovered.
- DiscoverOut: The description of the Items or Processes Discovered.
- InformIn: The description of the Items or Process about which information is sought.
- InformOut: The information about the Item or Process.
- InterpretIn: The description of the Item to be Interpreted.
- InterpretOut: The Interpretation of the Item.
- For user experience
- Entity: An Item that can be rendered.
- Event: The combination of an M-Location, its Entities and their Animations starting from Start Time until End Time.
- Experience: An Event as MM-Sent to a User and the User Interactions with the Entities of the Event.
- Model: An Object representing an object with its features ready to be animated.
- Object: An Entity representing an object.
- Persona: A Model of a human.
- Scene: A possibly hierarchical Composition of Objects each having a Spatial Attitude.
- Stream: A continuous flow of Data.
- Interaction: The list of Actions made by a User on the Entities at an M-Location and the corresponding Times.
- Map: A structure establishing a correspondence between U-Locations with M-Locations.
- Entity: An Item that can be rendered.
- For spatial information
- M-Location: A delimited portion of an M-Environment with an Identifier.
- U-Location: A delimited portion of the Universe with an Identifier.
3.6 Data Types
The Metaverse requires the following Data Types:
- For general use
- Address: A URL.
- For Transactions
- Currency: A medium of exchange enabling Transactions in an M-Instance.
- Amount: A number expressing a Value in a Currency.
- For internal status
- Cognitive State: A User’s Personal Status that reflects the way it understands the Environment, such as “Confused”, “Dubious”, “Convinced”.
- Emotion: A User’s Personal Status that results from its interaction with an Environment, such as “Angry”, “Sad”, “Determined”.
- Personal Status: The information internal to a User characterising its behaviour.
- Social Attitude: The representation of a User’s Personal Status related to the way it in-tends to position vis-à-vis an M-Environment, e.g., “Respectful”, “Confrontational”, “Soothing”.
- For spatial information
- Coordinates: A set of numbers representing a Position in a Metaverse Environment using a coordinate system.
- Orientation: The set of the 3 roll, pitch, yaw angles indicating the rotation around the principal axis (x) of an Object, its y axis having an angle of 90˚ counterclockwise (right-to-left) with the x axis and its z axis (pointing up toward a viewer from above).
- Point of View: The Spatial Attitude of a User watching the Environment.
- Position: The coordinates of an Object with respect to a coordinate set in a Metaverse Environment.
- Spatial Attitude: The Position and Orientation of an Entity, and their velocities and accelerations.
- For time information
- Time: A measure of time.
3.7 Interoperability support
When ProcessA in MetaverseA requests ProcessB in MetaverseB to perform Action on an ItemA.1, the following workflow enables interoperability between MetaverseA and MetaverseB (RS=Resolution Service, CS=Conversion Service).
- ProcessA transmits Request-Action1 to RSA.
- RSA transmits Request-Action1 to RSB.
- RSB transmits Item1 to CS.
- CS produces and transmit Item2 containing Converted Data to RSB.
- RSB transmits the new Request-Action2 to ProcessB.
- ProcessB
- Performs the Action specified in Request-Action2 using ItemA.2.
- Produces Response-Action2.
- Requests RSB to transmit to RSA Response-Action2 containing ItemA.3 (result of performing Request-ActionA.2).
- RSB transmits Response-Action2 to RSA.
- RSA transmits Item3 to CS.
- CS produces and transmits to RSA Item4, corresponding to ItemA.3 with converted Data.
- RSA produces and transmits to ProcessA a new Response-Action4 that references ItemA.4.
An M-Instance may allow Processes to communicate directly with Processes in other M-Instances without calling ResolutionServiceA.
The Call for Technologies requests comments on, proposed revisions of, or justified proposals for MPAI-MMM Functional Requirements.

Figure 3 – Processes communicating across M-Instances

