<-Items Go to ToC Process Actions ->
The activities of an M-Instance involve Processes performing Actions on Items. For instance:
- “Device UM-Captures Media At U-Location” means that a Device captures Media at a U-Location.
- “Device MM-Sends Data With Qualifier to Process” means that a Device sends Data, Qualifier, and Rights resulting from the previous Action to a Process in the M-Instance.
- “User MM-Embeds Persona At M-Location and User MM-Animates Persona With Stream” means, respectively, that User places a Persona (an avatar) at an M-Location and User animates it with a data stream.
An activity in an M-Instance may involve Process1 who requests Process2 to perform an Action. For instance:
- MM-Send may rely on a Communication Service to make available Data, Qualifier, and Items of a Process to another Process. Note, however, that communication in an M-Instance may be peer-to-peer)
- MM-Embed relies on a Location Service instantiating an Item (e.g., Persona) at an M-Location.
Process1 may coincide with Process2 when a Destination Process is not required, i.e., when a Process possesses the necessary functionalities.
MMM-TEC V2.0 enables a ProcessA in an M-InstanceA to request a ProcessB in a different M-InstanceB to perform Actions on Items in M-InstanceB. The two Processes can communicate if a Resolution session is opened by ProcessA calling its Resolution ServiceA.
MMM-TEC does not provide support to the establishment of business agreements based on which communication between M-Instances become possible.
Inter-Process Protocol (IPP) is the protocol enabling two Processes to communicate by sending IPP messages that can be PA Request or PA Response (PA stands for Process Action). IPP Messages include the following elements, some of which are optional. Any Time information is assumed to be added by the communication infrastructure.
| IPP Message Elements | Description |
| Message ID | ID of PA Request or PA Response. |
| Response ID | Absent/Present when the Message is a PA Request/PA Response. |
| Source Process ID | ID of Process issuing Message. |
| Process Action | Combination of Action, Items/Processes and Complement (see Process Action). |
| Resolution Service ID | Service that
(Absent if the two Processes are in the same M-Instance). |
| Destination Process ID | ID of Process to which the Message is intended to be sent. |
| Acknowledgement | Acknowledgement, if successful, or Error, if failure. |
Figure 1 depicts the IPP steps when the two interacting Processes are in the same M-Instance.
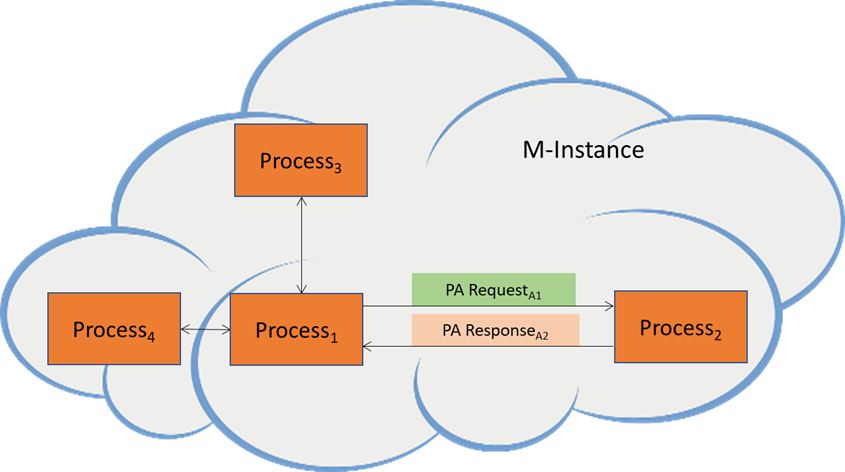
Figure 1 – The Inter-Process Protocol when the two Processes are in the same M-Instance.
The process unfolds through the following steps:
- Process1 sends a PA Request to Process2.
- Process2 analyses the PA Request.
- If the analysis yields an error, Process2 sends a PA Response with an error to Process1.
- Else, Process2 performs the PA Request.
- If the execution of the PA Request fails, Process2 sends a PA Response with an error to Process1.
- Else, Process2 sends a PA Response to Process1.
Figure 2 depicts the IPP steps when the two Processes are in different M-Instances. Here, the Process suffixes are prefixed by the letter A or B indicating the M-Instances they belong to.
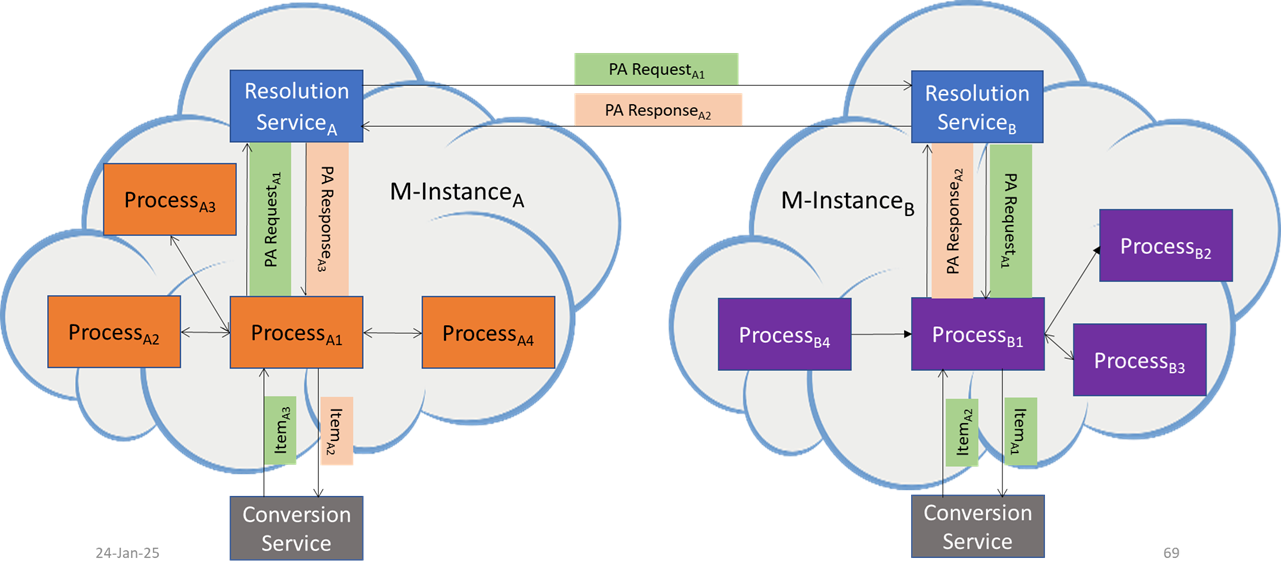 Figure 2 – The Inter-Process Protocol when the two Processes are in different M-Instances.
Figure 2 – The Inter-Process Protocol when the two Processes are in different M-Instances.
The process unfolds through the following steps:
- ProcessA1 sends a PA Request to Resolution ServiceA.
- Resolution ServiceA determines the Resolution ServiceB it should forward the PA Request to.
- If the determination is not reached it send an error to ProcessA1.
- Else it forwards the request to Resolution ServiceB1.
- Resolution ServiceB1 determines the Process it should send the PA Request to.
- If the determination is not reached, it send an error to Resolution ServiceA1.
- Else it forwards the PA Request to ProcessB1
- ProcessB1 analyses the PA Request.
- If the analysis of the request fails, it sends an error to Resolution ServiceB.
- Else, ProcessB1
- May request a Conversion ServiceB to make appropriate conversion of the Formats of the Data in the Items it received.
- Performs the request.
- If the execution of the PA Request fails, it sends an error to Resolution ServiceB.
- Else it sends a PA Response to Resolution ServiceB1.
- Resolution ServiceB sends error or PA Response to Resolution ServiceA.
- Resolution ServiceA sends error or PA Response to ProcessA1.
- ProcessA1 may request a Conversion ServiceA to make appropriate conversion of the Formats of the Data in the Items it received.
The Error Messages generated by either Resolution Service may be “No Rights to request Process Action to this M-Instance” or “No such ProcessID”
The Error Message generated by a receiving Process may be one of three types:
- “Unable to perform request”.
- “Transaction of Value required” (actual value provided).
- “Conversion Service failure”.
- Process Action-specific error.
An Inter-Process Protocol session is set up by the IPP Session Setup whereby:
- ProcessA1 requests Resolution ServiceA to open a session with the M-Instances that host at least one invited Process.
- Resolution ServiceA forwards the request to all relevant Resolution Services.
- A Resolution ServiceB forwards the request to each invited ProcessB‘s of its M-Instance.
- An invited ProcessB1 responds to Resolution ServiceB accepting or rejecting the invitation.
- A Resolution ServiceB forwards the response to Resolution ServiceA.
- Resolution ServiceA forwards the responses to ProcessA1.
- If at least one invited Process accepts the invitation, the session starts.
The process unfolds through the following steps:
- ProcessA1 sends a PA Request to Resolution ServiceA1.
- Resolution ServiceA1 determines the Resolution ServiceB1 it should forward the PA Request to.
- If the determination is not reached it send an error to ProcessA1.
- Else it forwards the request to Resolution ServiceB1.
- Resolution ServiceB1 determines the Process it should send the PA Request to.
- If the determination is not reached, it sends an error to Resolution ServiceA1.
- Else it forwards the PA Request to ProcessB1
- ProcessB1 analyses the PA Request.
- If the analysis of the request fails, it sends an error to Resolution ServiceB.
- Else, ProcessB1
- May request a Conversion ServiceB1 to make appropriate conversion of the Formats of the Data in the Items it received.
- Performs the request.
- If the execution of the PA Request fails, it sends an error to Resolution ServiceB1.
- Else it sends a PA Response to Resolution ServiceB1.
- Resolution ServiceB1 sends error or PA Response to Resolution ServiceA1.
- Resolution ServiceA1 sends error or PA Response to ProcessA1.
- ProcessA1 may request a Conversion ServiceA1 to make appropriate conversion of the Formats of the Data in the Items it received.
The Error Messages generated by either Resolution Service may be “No Rights to request Process Action to this M-Instance” or “No such ProcessID”.
The Error Message generated by a receiving Process may be one of three types:
- “Unable to perform request”.
- “Transaction of Value required” (actual value provided).
- “Conversion Service failure”.
- Process Action-specific error.
An Inter-Process Protocol session is set up by the IPP Session Setup whereby:
- ProcessA1 requests Resolution ServiceA1 to open a session with the M-Instances that host at least one invited Process.
- Resolution ServiceA1 forwards the request to all relevant Resolution Services.
- A Resolution ServiceB1 forwards the request to each invited ProcessB‘s of its M-Instance.
- An invited ProcessB1 responds to Resolution ServiceB1 accepting or rejecting the invitation.
- A Resolution ServiceB1 forwards the response to Resolution ServiceA1.
- Resolution ServiceA1 forwards the responses to ProcessA1.
- If at least one invited Process accepts the invitation, the session is opened.

