| 1 Function | 2 Reference Model | 3 Input/Output Data |
| 4 SubAIMs | 5 JSON Metadata | 6 Profiles |
| 7 Reference Software | 8 Conformance Texting | 9 Performance Assessment |
1 Functions
Visual Change Detection (OSD-VCD):
| Receives | Visual Object | Input Video Visual Object. |
| Detects | Scene cuts/transitions | In the input video at a time a video frame is sufficiently different from preceding ones to signal a change. |
| Produces | Video frames | Per scene set by external parameters. |
| Time | Including: 1. Time of changed video frame 2. Time of last video frame before a new change is detected. |
2 Reference Model
The Reference Model of the Visual Change Detection (OSD-BCD) AIM is specified in Figure 1.
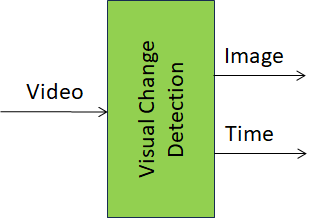
Figure 1 – The Visual Change Detection AIM Reference Model
3 Input/Output Data
Table 1 specifies the Input and Output Data of the Visual Scene Description AIM. Links are to the Data Type specifications.
Table 1 – I/O Data of the Visual Scene Description AIM
| Input | Description |
| Video | Input video file. |
| Output | Description |
| Image | The Image that has been detected as changed. |
| Time | The when a change has been detected (and the time before a new change). |
4 SubAIMs
No SubAIMs
5 JSON Metadata
https://schemas.mpai.community/OSD/V1.3/AIMs/VisualChangeDetection.json
6 Profiles
No Profiles
7 Reference Software
7.1 Disclaimers
- This OSD-VCD Reference Software Implementation is released with the BSD-3-Clause licence.
- The purpose of this OSD-VCD Reference Software is to show a working Implementation of OSD-VCD, not to provide a ready-to-use product.
- MPAI disclaims the suitability of the Software for any other purposes and does not guarantee that it is secure.
- Use of this Reference Software may require acceptance of licences from the respective repositories. Users shall verify that they have the right to use any third-party software required by this Reference Software.
7.2 Guide to the OSD-VCD code
OSD-VCD detects scene cuts/transitions in the input video and saves a given number of frames per scene, according to parameter “images_per_scene” in the input message. If parameter “scenedet_check” in the input message is set to “true”, a helper video will be saved to the output folder. This video helps to visually check whether scene cuts/transitions are detected correctly.
The OSD-VCD Reference Software is found at the MPAI gitlab site. It contains:
- src: a folder with the Python code implementing the AIM
- Dockerfile: a Docker file containing only the libraries required to build the Docker image and run the container
- requirements.txt: dependencies installed in the Docker image
Library: https://github.com/Breakthrough/PySceneDetect
7.3 Acknowledgements
This version of the OSD-VCD Reference Software has been developed by the MPAI AI Framework Development Committee (AIF-DC).
8 Conformance Testing
Table 2 provides the Conformance Testing Method for OSD-VCD AIM.
If a schema contains references to other schemas, conformance of data for the primary schema implies that any data referencing a secondary schema shall also validate against the relevant schema, if present and conform with the Qualifier, if present.
Table 2 – Conformance Testing Method for OSD-VCD AIM
| Receives | Visual Object | Shall validate against Visual Object schema. Visual Data shall conform with Qualifier. |
| Produces | Video frames | Shall validate against Visual Object (images) schema. Visual Data shall conform with Qualifier. |
| Time | Shall validate against Time schema. |
9 Performance Assessment
Performance Assessment of an OSD-VCD AIM Implementation shall be performed using a dataset of video sequences for which scene changes have been identified. The video sequences may include none, one, or more than one scene change.
The Performance Assessment Report of an OSD-VCD AIM Implementation shall include:
- The Identifier of the OSD-VCD AIM.
- The Identifier of the video sequence dataset.
- The classification of the video sequence according to an identified Taxonomy,
- The Performance of the OSD-VCD AIM expressed by the following three numbers:
- The number of times a scene change was correctly identified divided by the total number of scene changes in the dataset (true positives).
- The number of times a scene change was incorrectly identified divided by the total number of scene changes (false positives).
- The number of times a scene change was incorrectly not identified when there was a scene change (false negatives).

