<-Go to AI Workflows Go to ToC
| 1 Functions | 2 Reference Model | 3 I/O Data |
| 4 Functions of AI Modules | 5 I/O Data of AI Modules | 6 AIW, AIM, and JSON Metadata |
| 7 Reference Software | 8 Conformance Texting | 9 Performance Assessment |
1 Functions
The Function of the Receiving Client is to:
| Create | Local Visual Scene by placing and animating the Avatar Models with their Spatial Attitudes. |
| Local Audio-Visual Scene by adding Speech to Avatars’ Mouths. | |
| Render | Audio-Visual Scene as seen from the Participant-selected Point of View. |
2 Reference Model
Figure 1 depicts the Reference Model of the Videoconference Client Receiver. Red Text for Data received at the start. This is the operation:
- At the start
- Receives Portable Avatars containing:
- Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors
- Avatar Models
- Spatial Attitudes
- Creates the initial Audio-Visual Scene.
- Receives Portable Avatars containing:
- During the Videoconference:
- Receives the Avatar Models containing:
- Speech
- Body Descriptors
- Face Descriptors
- Creates the running Audio-Visual Scene using each Avatar’s:
- Body and Face Descriptors.
- Speech Objects.
- Receives the Avatar Models containing:
- Renders the Audio-Visual Scene based on the selected Point of View.
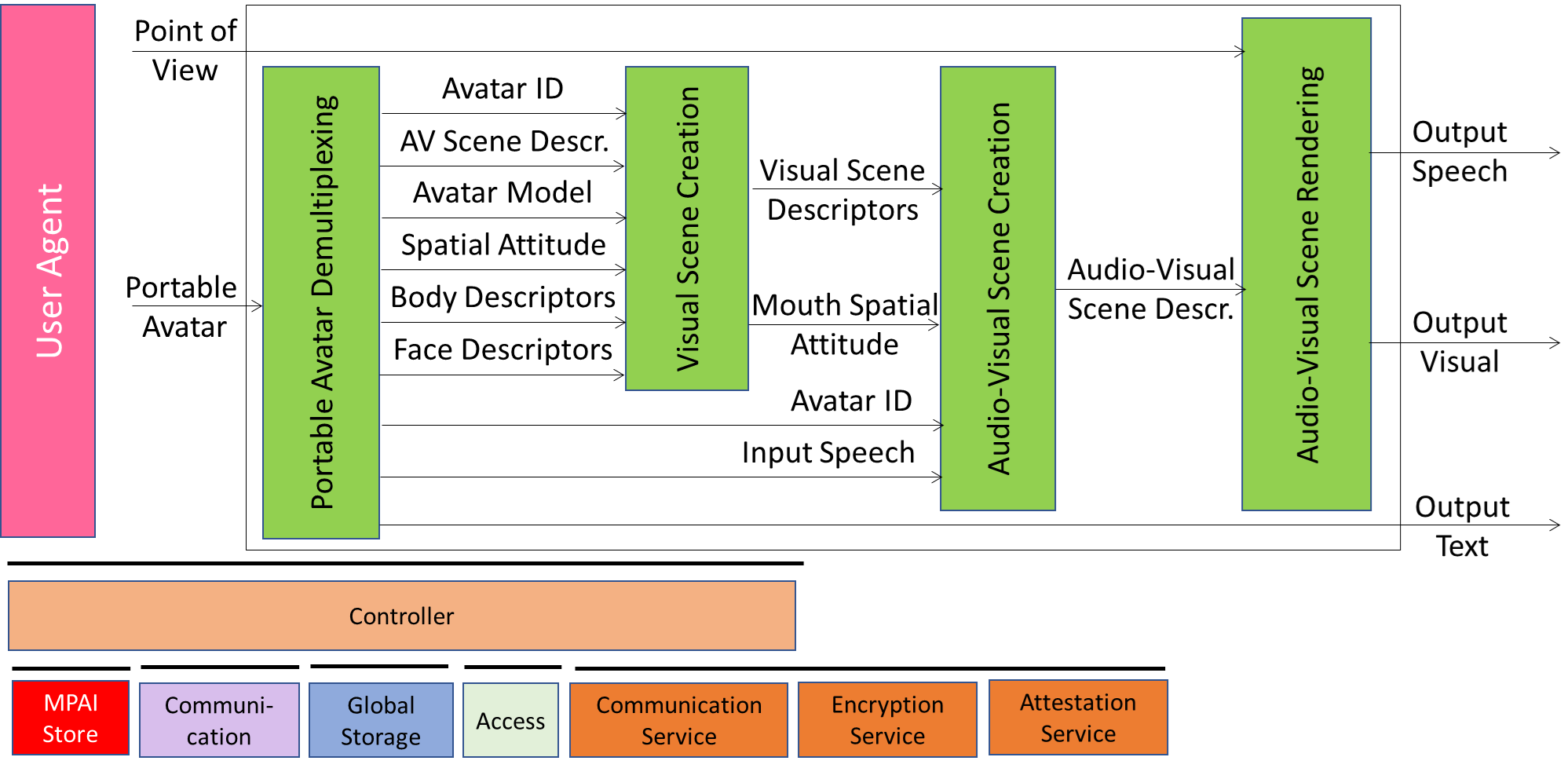
Figure 1 – Reference Model of Videoconference Client Receiver
3 I/O Data
Table 1 gives the input and output data of Videoconference Client Receiver.
Table 1 – Input and Output Data of Videoconference Client Receiver AIW
| Input | Description |
| Point of View | Avatar-selected Position to see the Audio-Visual Scene. |
| Portable Avatars | Portable Avatars from Videoconference Avatar Server. |
| Output | Description |
| Output Speech | Rendered by Audio-Visual Scene Rendering. |
| Output Visual | Rendered by Audio-Visual Scene Rendering. |
4 Functions of AI Modules
Table 2 gives the AI Modules of Videoconference Client Receiver AIW.
Table 2 – Functions of Videoconference Client Receivers’ AI Modules
| AIM | Input |
| Portable Avatar Demultiplexing | Extracts Avatar ID, Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors, Avatar Model, Spatial Attitude, Body Descriptors, Face Descriptors, and Input Speech from Portable Avatars. |
| Visual Scene Creation | Creates the Visual Scene and provides the Spatial Attitudes of the Mouths of all Avatars. |
| Audio-Visual Scene Creation | Creates the Audio Scene. |
| Audio-Visual Scene Rendering | Provides a ready-to-rendered Audio-Visual Scene. |
5 I/O Data of AI Modules
Table 2 gives the AI Modules of Videoconference Receiving Client AIW.
Table 3 – I/O Data of Videoconference Client Receivers’ AI Modules
| AIM | Input | Output |
| Portable Avatar Demultiplexing | Portable Avatars | 1. Avatar ID 2. Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors 3. Avatar Model 4. Spatial Attitude 5. Body Descriptors 6. Face Descriptors 7. Input Speech 8. Output Text |
| Visual Scene Creation | 1. Avatar ID 2. Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors 3. Avatar Model 4. Spatial Attitude 5. Body Descriptors 6. Face Descriptors |
1. Visual Scene Descriptors 2. Mouth Spatial Attitudes |
| Audio-Visual Scene Creation | 1. Avatar ID 2. Input Speech 3. Mouth Spatial Attitudes |
1. Audio Scene Descriptors |
| Audio-Visual Scene Rendering | 1. Audio Scene Descriptors 2. Visual Scene Descriptors 3. Point of View |
1. Output Speech 2. Output Visual |
6 AIW, AIM, and JSON Metadata of Videoconference Client Receiver
Table 4 – AIMs and JSON Metadata
| AIW | AIMs | Name | JSON |
| PAF-CRX | Videoconference Client Receiver | X | |
| – | PAF-PDX | Portable Avatar Demultiplexing | X |
| – | PAF-VSC | Visual Scene Creation | X |
| – | PAF-AVC | Audio-Visual Scene Creation | X |
| – | PAF-AVR | Audio-Visual Scene Rendering | X |
7 Reference Software
8 Conformance Testing
9 Performance Assessment

