| CAE | CAV | HMC | MMC | OSD | PAF |
| AI Workflows | AI Modules |
1 AI Workflows
| MMC-AMQ | Answer to Multimodal Question | MMC-HCI | Human-CAV Interaction |
| MMC-CAS | Conversation About a Scene | MMC-MQA | Multimodal Question Answering |
| MMC-CPS | Conversation with Personal Status | MMC-TST | Text and Speech Translation |
| MMC-CWE | Conversation with Emotion | MMC-VMS | Virtual Meeting Secretary |
1.1 Answer to Multimodal Question
MMC-AMQ is a PAAI that provides a Text and/or Speech response to a Text or Speech question related to an image.
It is composed of the following collaborating PAAIs:
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Converts a Speech Object into a Text Object. |
| Text and Image Query | Receives a Text Object and a Visual Object. Produces a Text Object of the response to the input Text or Speech Object. |
| Text-To-Speech | Converting the Text Object into a Speech Object. |
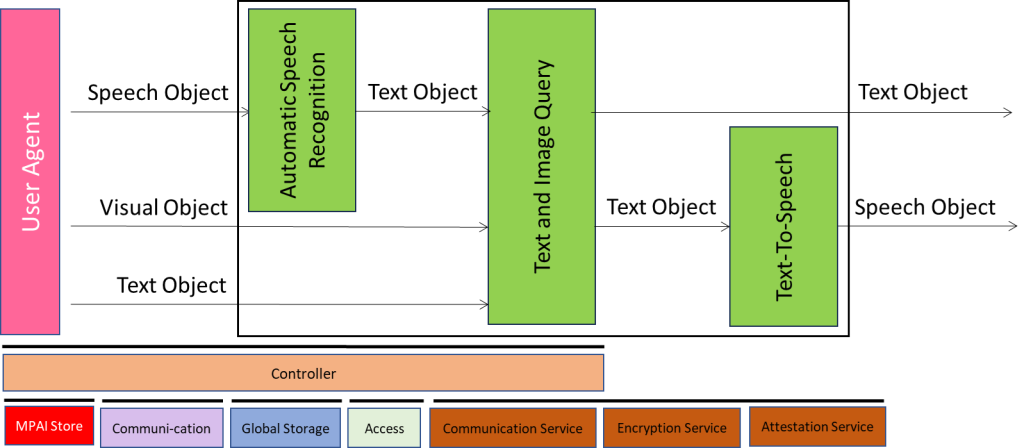 Figure 14 – Reference Model of MMC-AMQ
Figure 14 – Reference Model of MMC-AMQ
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
MMC-AMQ performs Interpretation-Reasoning Operations.
1.2 Conversation About a Scene
MMC-CAS is a PAAI that:engages in a conversation with an Entity about objects in a scene, e.g., a shop full of objects where the salesclerk is a Machine.
It is composed of the following collaborating PAAIs:
| Visual Scene Description | Provides the Visual Scene Descriptors. |
| Visual Object Identification | Provides the ID of a Visual Object. |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Converts input the Speech Object into a Text Object. |
| Natural Language Understanding | Refines the Text providing Refined Text and Meaning. |
| Personal Status Extraction | Extracts the Entity’s Personal Status. |
| Entity Dialogue Processing | Responds to the input from the Entity. |
| Personal Status Display | Provides the Machine’s Portable Avatar. |
| Audio-Visual Scene Rendering | Displays the Scene as seen by the Avatar and the Avatar from an Entity-selected Point of View. |
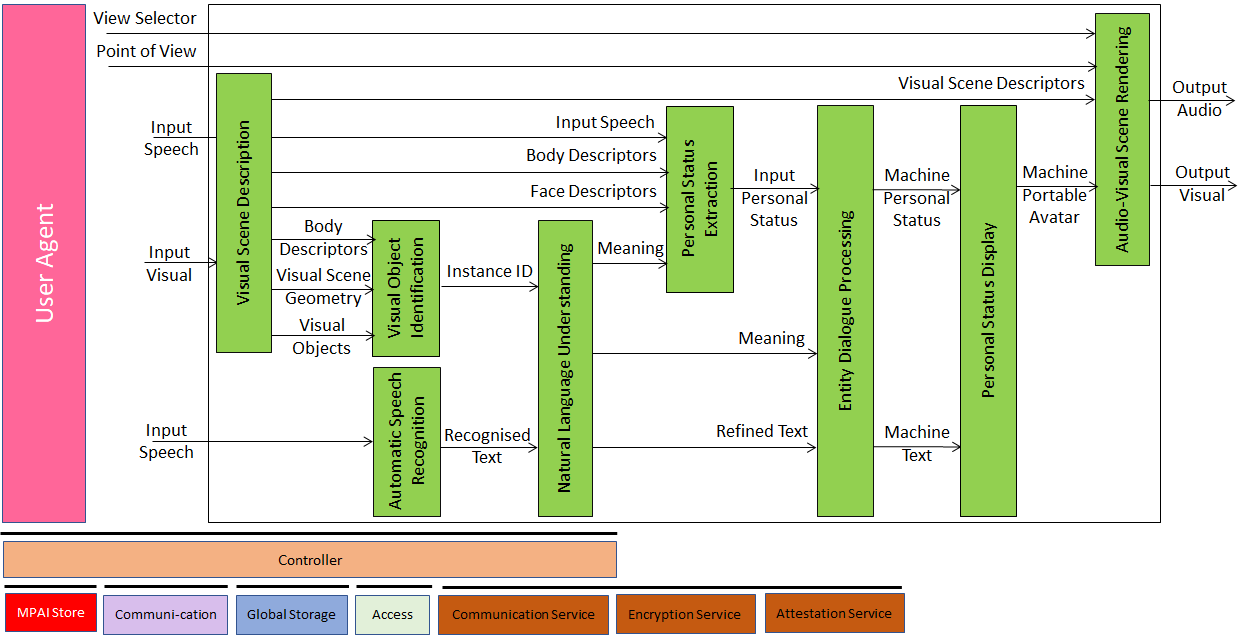 Figure 15 – Reference Model of MMC-CAS
Figure 15 – Reference Model of MMC-CAS
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
- Visual Scene Description
- Visual Object Identification
- Automatic Speech Recognition
- Natural Language Understanding
- Personal Status Extraction
- Entity Dialogue Processing
- Personal Status Display
- Audio-Visual Scene Rendering
MMC-CAS performs Descriptors-Interpretation-Reasoning Operations.
1.3 Conversation with Emotion
MMC-CWE is a PAAI that converses with an Entity in natural language Shows itself as a speaking avatar displaying an Emotion congruent with the Emotion displayed by the Entity.
It is composed of the following collaborating PAAIs:
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Converts the input Speech Object into a Text Object. |
| Entity Speech Description | Extracts the Entity’s Speech Descriptors. |
| Entity Face Description | Extracts the Entity’s Face Descriptors. |
| Natural Language Understanding | Provides Refined Text and Meaning. |
| PS-Speech Interpretation | Provides the Entity’s Emotion in Speech. |
| PS-Face Interpretation | Provides the Entity’s Emotion in Face. |
| PS-Text Interpretation | Provides the Entity’s Emotion in Text. |
| Multimodal Emotion Fusion | Provides a single Entity Emotion. |
| Entity Dialogue Processing | Responds to the input from the Entity providing Machine Text and Machine Emotion. |
| Text-To-Speech | Provides Machine Speech that conveys Machine’s Emotion. |
| Video Lip Animation | Displays the Avatar’s Face. |
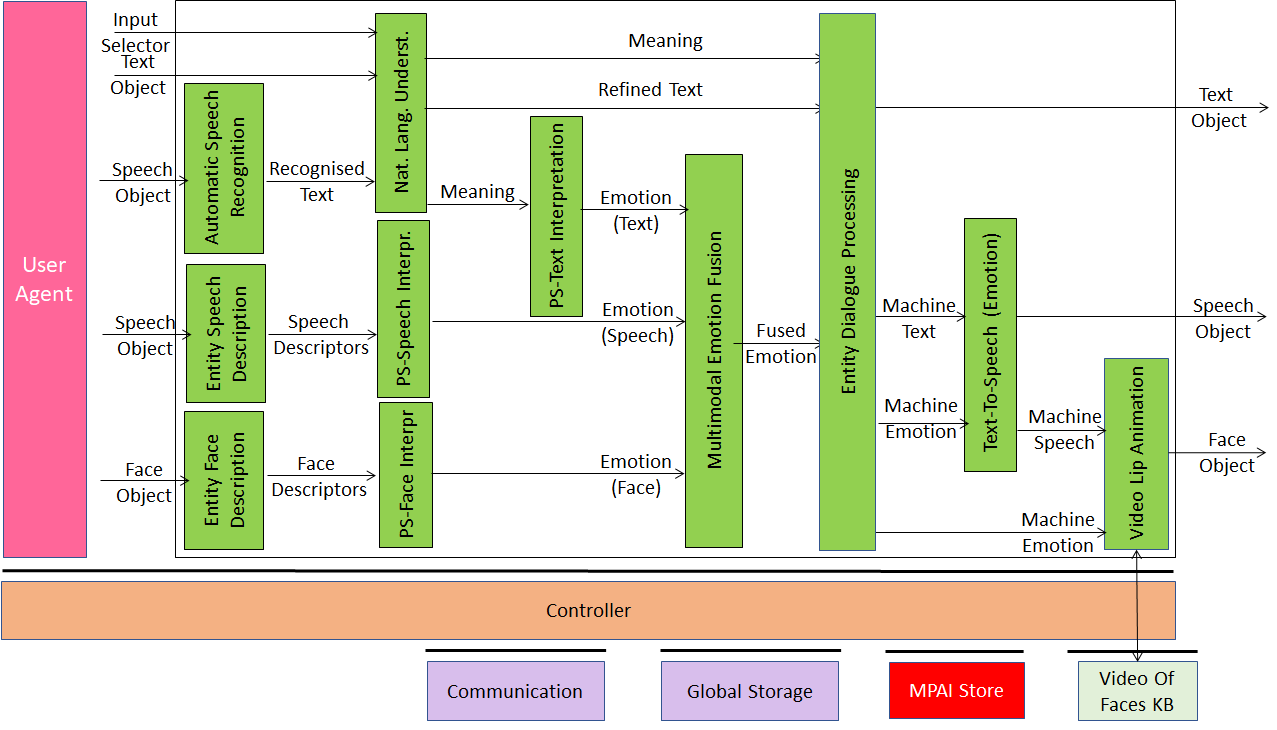 Figure 16 – Reference Model of MMC-CWE
Figure 16 – Reference Model of MMC-CWE
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
- Automatic Speech Recognition
- Entity Speech Description
- Entity Face Description
- Natural Language Understanding
- PS-Text Interpretation
- PS-Speech Interpretation
- PS-Face Interpretation
- Multimodal Emotion Fusion
- Entity Dialogue Processing
- Text-to-Speech
- Video Lip Animation
MMC-CWE performs Descriptors-Interpretation-Reasoning Operations.
1.4 Conversation with Personal Status
MMC-CPS is a PAAI that Converses with an Entity indicating visual objects and displaying a Personal Status while displaying itself a Personal Status that is congruent with that of the Entity’s.
It is composed of the following collaborating PAAIs:
| Visual Scene Description | Describes the Visual Scene. |
| Speech Scene Description | Describes the Speech Scene. |
| Visual Object Identification | Identifies Visual Objects. |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Recognises the Entity’s Speech. |
| Natural Language Understanding | Refines the Recognised Speech and extracts the Meaning from Text |
| Personal Status Extraction | Extracts the Personal Status. |
| Entity Dialogue Processing | Responds to the Entity with a Personal Status congruent with that of the Entity. |
| Personal Status Display | Produces the Personal Status. |
| Audio-Visual Scene Rendering | Renders the Audio-Visual Scene as seen by the MMC-CPS PAAI. |
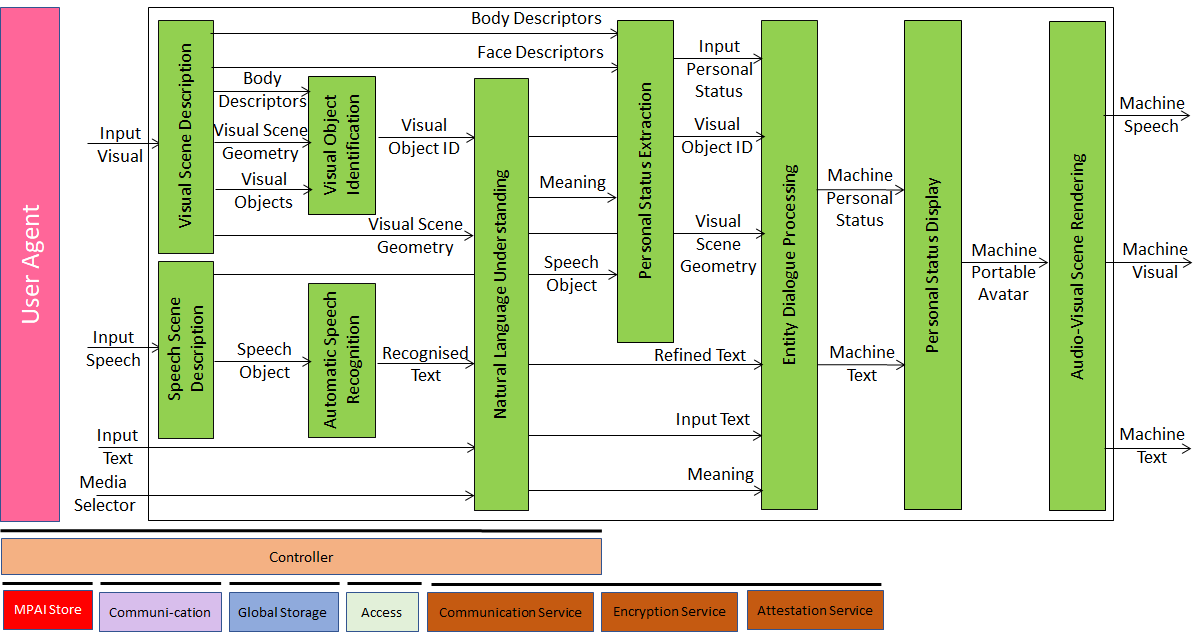
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
- Audio-Visual Scene Rendering
- Automatic Speech Recognition
- Entity Dialogue Processing
- Natural Language Understanding
- Personal Status Display
- Personal Status Extraction
- Speech Scene Description
- Visual Object Identification
- Visual Scene Description
MMC-CPS performs Descriptors-Interpretation-Reasoning Operations.
1.5 Human-CAV Interaction
Human-CAV interaction (HCI) is a PAAI that
- Responds to human utterances expressed by text, speech, face, and gesture.
- Executes requests that are in the scope of a human close to or inside a CAV:
- Recognise the identity of human owner or renter (face and speech).
- Respond to humans’ commands and queries.
- Converse with humans.
- Manifest itself as an audio-visual entity.
- Exchange information with the Autonomous Motion Subsystem in response to humans’ requests.
- Communicate with a Process or Remote HCIs.
It is composed of the following collaborating PAAIs:
| Audio-Visual Scene Description | Produces Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors. |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Produces Recognised Text. |
| Visual Object Identification | Provides the Instance IDs of indicated Visual Objectd. |
| Natural Language Understanding | Produces Refined Text and Meaning. |
| Speaker Identity Recognition | Produces the human’s Speaker ID. |
| Personal Status Extraction | Produces the human’s Personal Status. |
| Face Identity Recognition | Produces the human’s Face ID. |
| Entity Dialogue Processing | Produces MMC-CAV PAAI’s Text Object and Personal Status and AMS-HCI Messages and Ego-Remote HCI Messages. |
| Personal Status Display | Produces MMC-CAV PAAI’s Portable Avatar. |
| Audio-Visual Scene Rendering | 2. Produces MMC-CAV PAAI’s Output Speech, Output Audio, and Output Visual. |
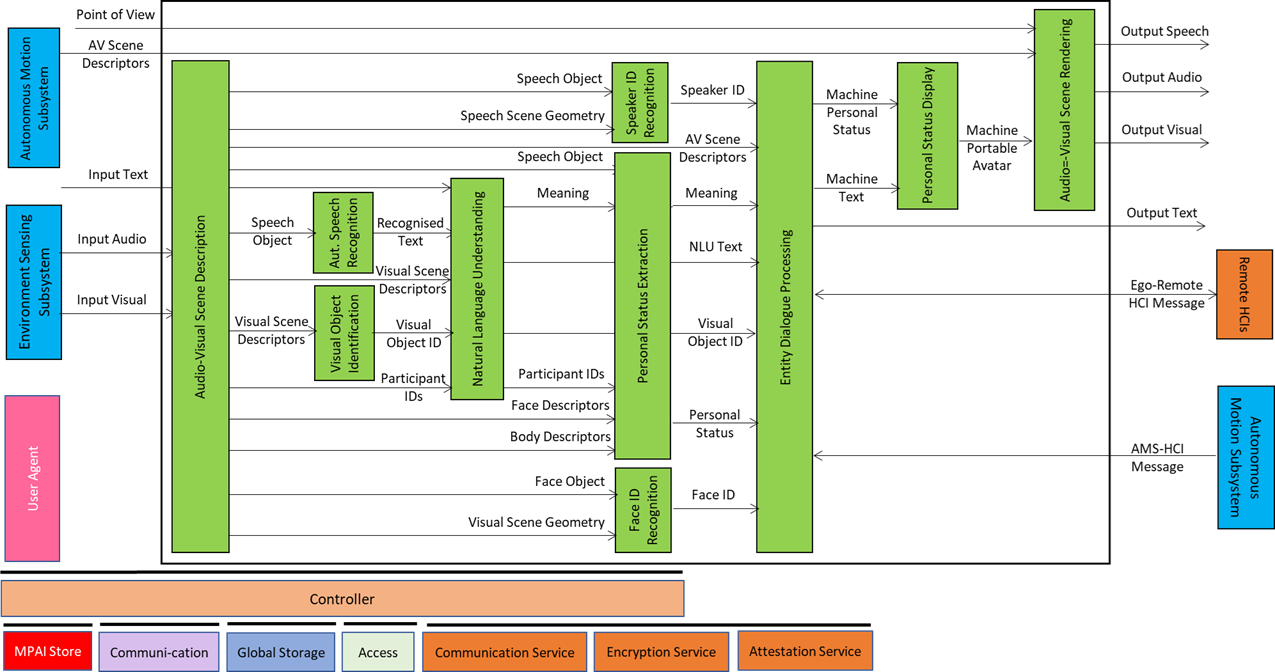 Figure 17 – Reference Model of MMC-HCI
Figure 17 – Reference Model of MMC-HCI
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
Audio-Visual Scene Description
Natural Language Understanding
1.6 Multimodal Question Answering
MMC-MQA is a PAAI that implements the Text and Image Query PAAIs of the Answer to Multimodal Question (MMC-AMQ) PAAI with the following PAAIs:
| Visual Object Identification | Provides the ID of a Visual Object. |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Recognises the Text in the Speech. |
| Natural Language Understanding | Refines Recognised Text and extracts Meaning |
| Question Analysis Module | Provides the Intention. |
| Answer to Question Module | Produces a response to the question. |
| Text-To-Speech | Synthesises Speech from Text. |
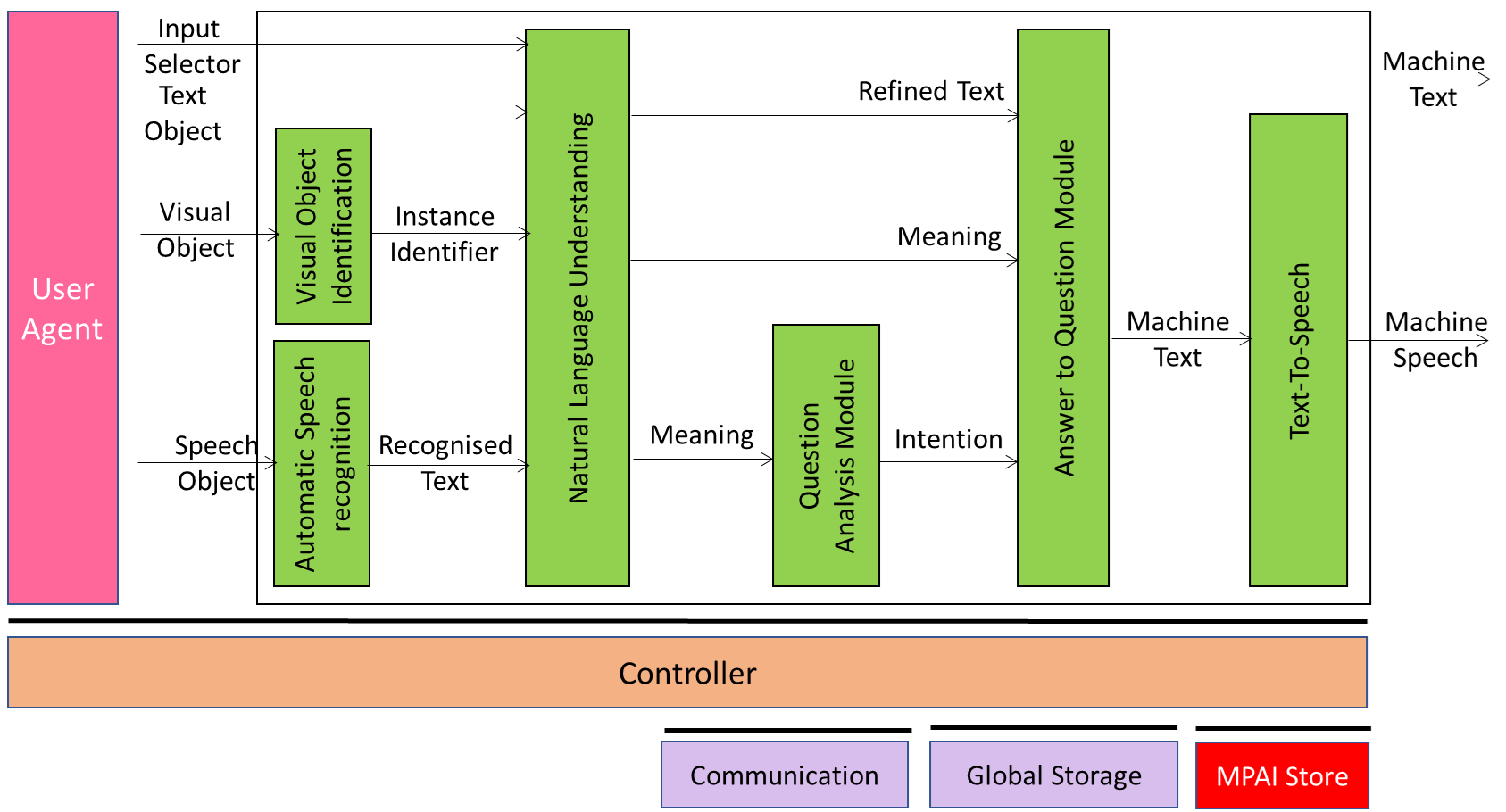 Figure 18 – Reference Model of MMC-MQA
Figure 18 – Reference Model of MMC-MQA
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
- Visual Object Identification
- Automatic Speech Recognition
- Natural Language Understanding
- Question Analysis Module
- Answer to Question Module
- Text-to-Speech
1.7 Text and Speech Translation
MMC-TST is a PAAI that translates a Text Object or a Speech Object into a Text Object and/or a Speech Object in a different language. MMC-TST may optionally retain the features of the input Speech Object in the translated Speech Object.
It is composed of the following PAAIs:
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Extracts Text from Speech |
| Text-to-Text Translation | Translates Text in a language into Text in another language |
| Entity Speech Description | Extracts Speech Descriptors from Speech/ |
| Text-to-Text with Descriptors | Synthesises Speech adding Speech Descriptors. |
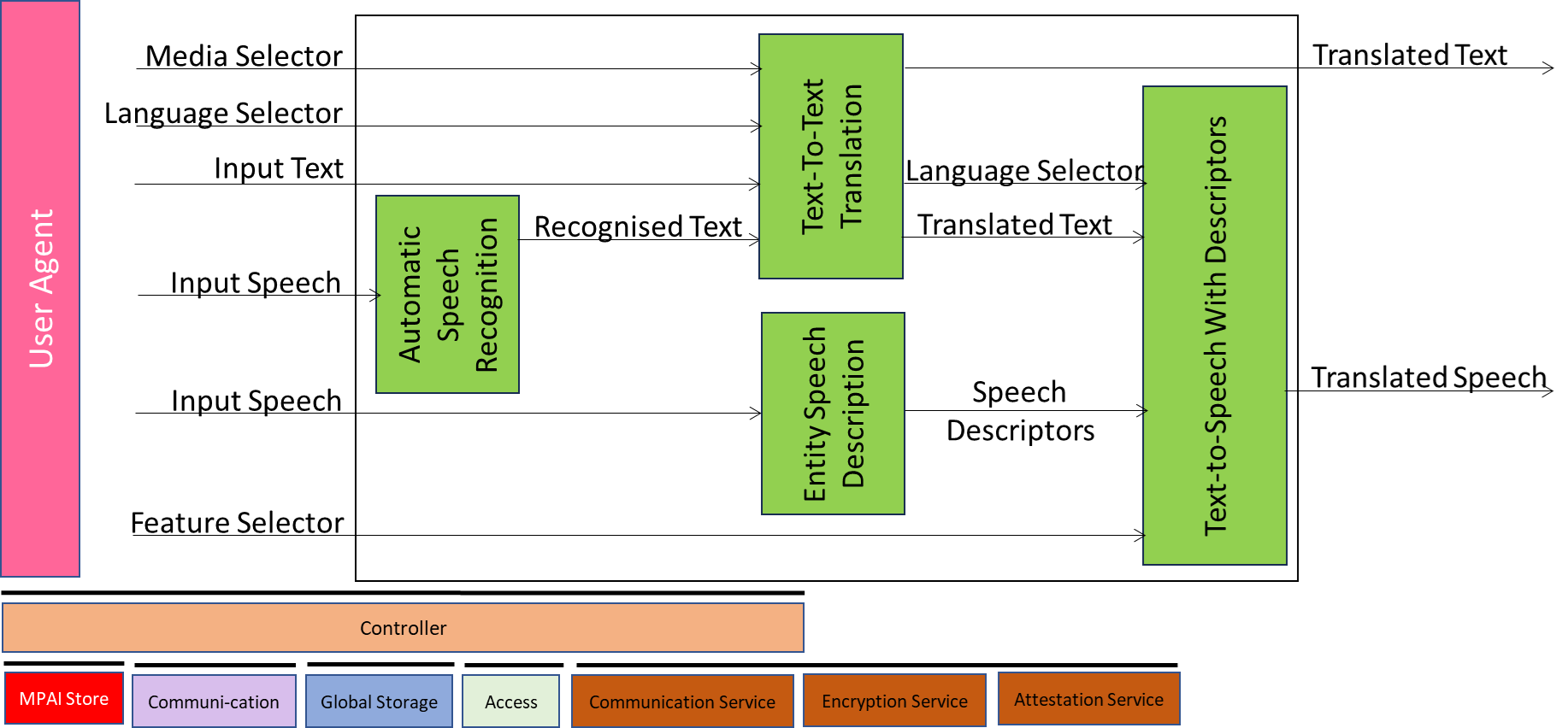
Figure 19 – Reference Model of MM-TST
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
- Automatic Speech Recognition
- Text and Speech Translation
- Text-to-Text Translation
- Entity Speech Description
- Text-to-Speech with Descriptors
1.8 Virtual Meeting Secretary
MMC-VMS is a PAAI
- Describing avatars attending a meeting in terms of Space-Time.
- Interpreting Text provided and Speech uttered by avatars attending a meeting.
- Extracting the avatars’ Personal Status.
- Producing a Summary of what is being said.
- Producing Text and Personal Status of its responses.
- Producing a Portable Avatar of itself.
It is composed of the following PAAIs:
| Portable Avatar Demultiplexing | Provides the Data required by Virtual Secretary’s AIMs. |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Provides Recognised Text. |
| Natural Language Understanding | Extracts Meaning. |
| Personal Status Extraction | Extracts Personal Status. |
| Summary Creation Module | Produces and refines Summary using Edited Summary. |
| Entity Dialogue Processing | Produces Text, Virtual Secretary Personal Status, and Edited Summary. |
| Personal Status Display | Shows Virtual Secretary as Virtual Secretary Portable Avatar. |
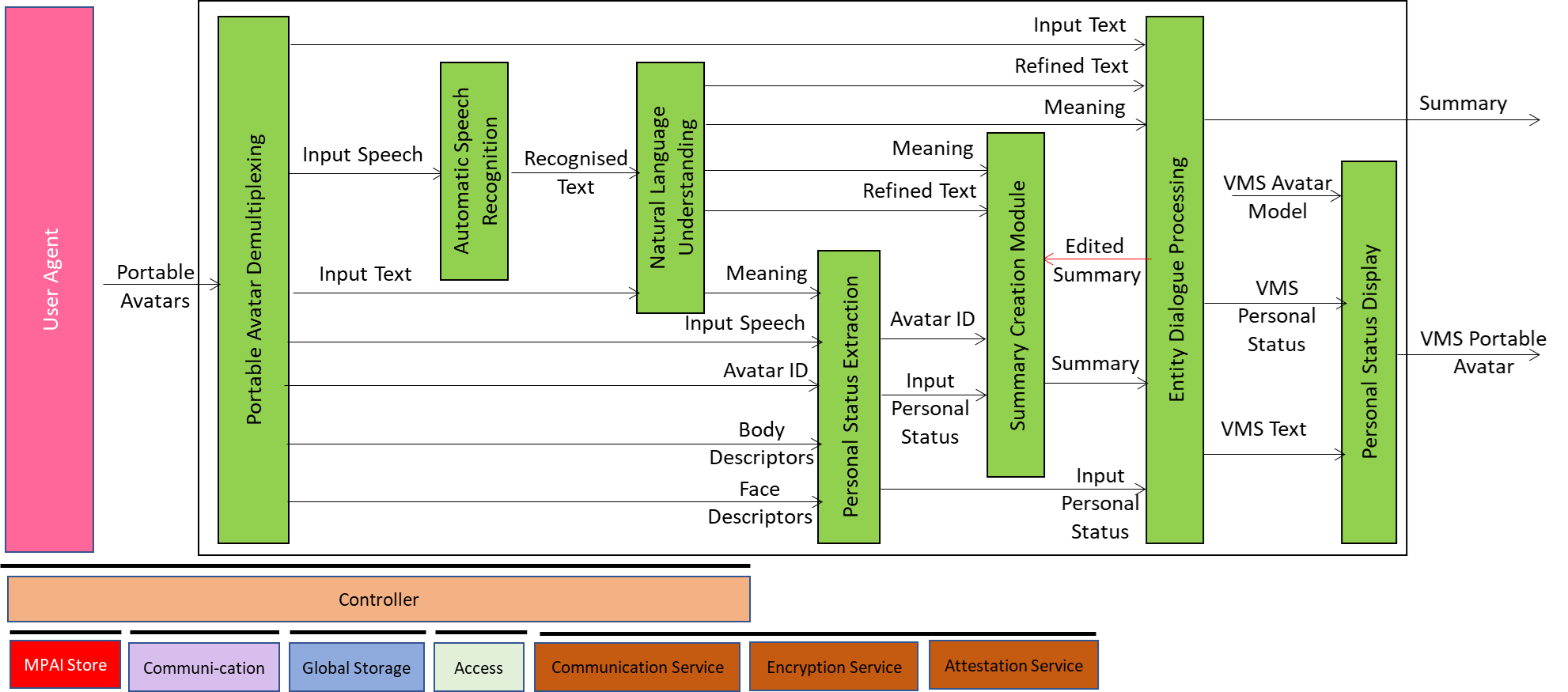 Figure 20 – Reference Model of MMC-VMS
Figure 20 – Reference Model of MMC-VMS
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
- Portable Avatar Demultiplexing
- Automatic Speech Recognition
- Natural Language Understanding
- Personal Status Extraction
- Summary Creation Module
- Entity Dialogue Processing
- Personal Status Display
2 AI Modules
2.1 Automatic Speech Recognition
MMC-ASR is a PAAI that:
| Receives | Language Selector | Signalling the language of the speech. |
| Auxiliary Text | Text that may be used to provide context information. | |
| Speech Object | Speech to be recognised. | |
| Speaker ID | ID of speaker uttering speech. | |
| Speech Overlap | Data type providing information of speech overlap. | |
| Speaker Time | Time during which the speech is to be recognised. | |
| Produces | Recognised Text | (Also called text Transcript). |
MMC-ASR PAAI can receive various types of data that may be used to help it do a better job:
- Just Speech Data to be recognised.
- Qualifier providing Speech-related information , such as language of the Speech.
- Auxiliary Text providing the context of the Speech.
- Speaker ID identifying the speaker-dependent.
- Speech Overlap telling OSD-ASR that there may be more than one speech in all or part of the Speech.
- Speaker Time indicating when the Speech is to be recognised.
MMC-ASR performs Description-Interpretation-level Operations.
2.2 Entity Dialogue Processing
MMC-EDP is a PAAI that:
| Receives | Text Object | Text of the entity upstream to be processed. |
| Object Instance ID | of an object in a scene. | |
| Personal Status | of the entity upstream. | |
| Text Descriptors | Descriptors of input Text Object. | |
| AV Scene Geometry | Geometry of the AV scene containing object whose ID is provided. | |
| Speaker ID | ID of speaker uttering the speech that contains the Text Object. | |
| Face ID | ID of the face of the speaker uttering the speech that contains the Text Object. | |
| Summary | A summary of the discussions being held in the environment. | |
| Handles | Text Object | from an entity upstream. |
| Recognises | The identity | of entity upstream using speech and/or face. |
| Takes into account | Past Text Objects | and their spatial arrangement. |
| Produces | Summary | Edited summary based on input data. |
| Text Object | of Machine. | |
| Personal Status | of Machine. |
The MMC-EDP PAAI can receive various types of data that may be used to help it provide a better or richer response:
- Text to which it responds with:
- Text that is a response to
- A finite set of questions.
- An indefinite set of questions to which a response is provided by a general-purpose or purpose-built Large Language Model (LLM) or Small Language Model (SLM).
- A Personal Status obtained by inferring, from the input Text, the internal state of the Entity that has generated the Text and creating a fictitious Machine Personal Status that is congruent with the Personal Status of the Entity-provided Text.
- Text that is a response to
- Entity ID helping to access previously stored PAAI Experiences with the same Entity.
- Meaning provided by a Natural Language Understanding (NLU) that produces Refined Text and Meaning from Recognised Text to help the MMC-EDP produce a better response.
- Personal Status provided by a Personal Status Extraction PAAI that can act on Text and, if available other Factors – Speech, Face, and Gesture. As for Text and depending on the capability of the communication system incorporating the MMC-EDP, The EDP can produce an extended Personal Status including Speech, Face, and Gesture.
- Audio-Visual Scene Geometry provided by an Audio-Visual Scene Description PAAI because the spatial context in which the information-providing Entity operates helps focus the MMC-EDP’s response.
- Audio-Visual Object IDs provided by an Audio Object Identification (CAE-AOI) or Visual Object Identification (OSD-VOI) because the identity of one or more Audio or Visual or Audio-Visual Objects present in the spatial environment where the Entity operates helps focus the MMC-EDP’s response.
Therefore, an MMC-EDP could provide the following prompt to its LLM:
Please respond to the following Text provided by an Entity with the following Entity ID which is believed to hold the following Personal Status and is located in a scene populated by the following audio objects identified by their Audio Object IDs and visual objects identified by their Visual Object IDs that are located at the following Points of Views of the scene, respectively.
The data referred to by the underlined words are provided by the data of the EDP.
MMC-EDP performs Reasoning Level Operations.
2.3 Natural Language Understanding
MMC-NLU is a PAAI that:
| Receives | Text Object | Provided by the Entity. |
| Recognised Text | Provided by an MMC-ASR. | |
| ID | of an Object Instance. | |
| AV Scene Descriptors | Including the object of which an ID is provided. | |
| Refines | Input Text | if coming from an MMC-ASR. |
| Extracts | Meaning | from Recognised Text or Entity’s Text Object. |
| Produces | Refined Text | Text that corrects/refines the Recognised Text. |
| Meaning | Meaning of the input Text. |
Instance ID and Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors may help the NLU reason about incorrectly recognised word(s) and identify the correct Meaning of the Text.
MMC-NLU performs Interpretation or Reasoning Level Operations.
2.4 Personal Status Extraction
MMC-PSE is a PAAI that includes a plurality of PAAIs producing the Personal Status of an Entity that produces text, utters speech, and displays face and gesture.
| Receives | Selector | Indicating whether each Factor is given as Media or Descriptors |
| Text | Text data | |
| Speech | Speech data | |
| Face | Face data | |
| Gesture | Gesture data | |
| Text Descriptors | Text Descriptors | |
| Speech Descriptors | Speech Descriptors | |
| Face Descriptors | Face Descriptors | |
| Gesture Descriptors | Gesture Descriptors | |
| Produces | Personal Status | Combining or Factor Personal Statuses. |
MMC-PSE can be implemented data processing or neural network technologies as:
- A single component receiving the four Factor data.
- Four components receiving and interpreting the four Factor data, and a multiplexer.
- Four components receiving and describing the four Factor data, four components interpreting the descriptors, and a multiplexer.
- A variety of combination where each of the input data may be directly interpreted or first described and then interpreted.
MMC-PSE performs Descriptors-Interpretation Level Operations.
2.5 Speaker Identity Recognition
MMC-SIR is a PAAI that produce an estimation of the ID of the Entity that uttered speech by acting on a plurality of data sources:
| Receives | Speech Object | Speech of which the Speaker is requested. |
| Auxiliary Text | Text related to the Speech. | |
| Speech Time | Time during whose duration Speaker ID is requested. | |
| Speech Overlap | Data signalling which parts of the Speech Data have overlapping speech. | |
| Speech Scene Geometry | Disposition of Speech Data in the scene where the Speech whose speaker is to be identified is located. | |
| Produces | Speaker Identifier | ID of speaker referencing a Taxonomy. |
Various technologies can be used to implement an MMC-SIR: Hidden Markov model (HMM), Dynamic time warping (DTW), Neural Networks[3], Deep Forward and Recurrent Neural Networks, End-to-End ASR.
MMC-SIR may perform Descriptors-Interpretation Level Operations.
2.6 Summary Creation Module
MMC-SCM is a PAAI that:
| Receives | Entity ID | ID of Entity of which a report is made. |
| Text Object | Text Object whose Data is reported Text. | |
| Space-Time | Entity’s space-time information. | |
| Personal Status | Entity’s Personal Status | |
| Summary | Summary produced | |
| Produces | Summary | Summary revised by MMC-EDP sent back to the Entity making the summary. |
MMC-SCM
- Can be implemented with a Neural Network.
- Unlike most summarisers, MMC-SCM
- Adds information on ID, space-time and Personal Status of the Entity producing the Text.
- Receives a proposed revised Summary that it should review.
MMC-TIQ performs Descriptors-Interpretation-Reasoning Level Operation.
2.7 Text and Image Query
MMC-TIQ is a PAAI that:
| Receives | Text Object | Textual part of query. |
| Image Visual Object | Image part of query. | |
| Produces | Text Object | In response to Text and Image provided as input. |
An MMC-TIQ can operate with various levels of complexity, e.g.,:
- It interprets the text from a limited repertory of questions – e.g., What is this object? Which objects are there in this picture? – related to a specific image.
- It accepts generic questions on generic visual information.
An MMC-TIQ can be implemented as a Large Language Model.
MMC-TIQ performs Descriptors-Interpretation-Reasoning Level Operation.
2.8 Text and Speech Translation
MMC-TST is a PAAI composed of a set of collaborating PAAIs – MMC-ASR, MMC-TTT, MMC-ESD, and MMC-TSD – that:
| Receives | Selector | To choose between output Text/Speech; if Speech, retain or not input Speech features |
| Language Preferences | Signalling requested input and output language. | |
| Text | Text to be translated. | |
| Speech | Speech to be translated. | |
| Performs | Some or all of: | |
| Speech Conversion | Into Text if input is Speech. | |
| Text Translation | To the target language. | |
| Descriptor Extraction | From Speech. | |
| Text Conversion | Into Speech adding the Input Speech’s Features, if output is Speech.. | |
| Produces | Translated Text | Depending on Selector. |
| Translated Speech | Depending on Selector. |
MMC-TST performs Data Processing (MMC-TSD), Descriptors (MMC-ESD), and Interpretation (MMC-ASR Level Operation.
2.9 Text-To-Speech
MMC-TTS is a PAAI that:
| Receives | Text Object | to be converted to speech. |
| Personal Status | to be contained in the Synthesised Speech Object. | |
| Speech Model | to be used synthesise speech. | |
| Feeds | Text Object and Personal Status | to Speech Model. |
| Produces | Synthesised Speech Object |
MMC-RRS can be implemented as a Neural Network. Common models are:
- WaveNet: generates raw audio waveforms.
- Tacotron Series: produces mel-spectrograms from text that is converted to speech by by a vocoder (e.g., WaveNet). Uses using an autoregressive approach.
- FastSpeech Series: produces mel-spectrograms with a non-autoregressive approach
MMC-TTS performs Data Processing Level Operations.
2.10 Text-to-Speech with Descriptors
MMC-TSD is a PAAI that
| Receives | Text Object | to be translated with the colour of the input Speech Descriptors. |
| Speech Descriptors | to be used to produce synthetic Speech. | |
| Produces | Synthesised Speech Object | having the Descriptors of the input Speech Object. |
MMC-TSD adds speech colour information provided by the Descriptors to the synthesised speech. If it is implemented as a neural network, it requires knowledge of the semantics of descriptors.
MMC-TSD performs Data Processing Level Operations.

