The Prompt Creation module is the storyteller and translator in the Autonomous User’s “brain”. It takes raw sensory input – audio and visual spatial data of Context (as objects in a scene with their position, orientation and velocity) and the User State (rich description of the A‑User’s understanding of the “internal state” of the User) – and turns it into a well‑formed prompt that Basic Knowledge can actually understand and respond to.
We have already presented the system diagram of the Autonomous User (A-User), an autonomous agent able to move and interact (walk, converse, do things, etc.) with another User in a metaverse. The latter User may be an A-User or be under the direct control of a human and is thus called a Human-User (H-User). The A-User acts as a “conversation partner in a metaverse interaction” with the User.
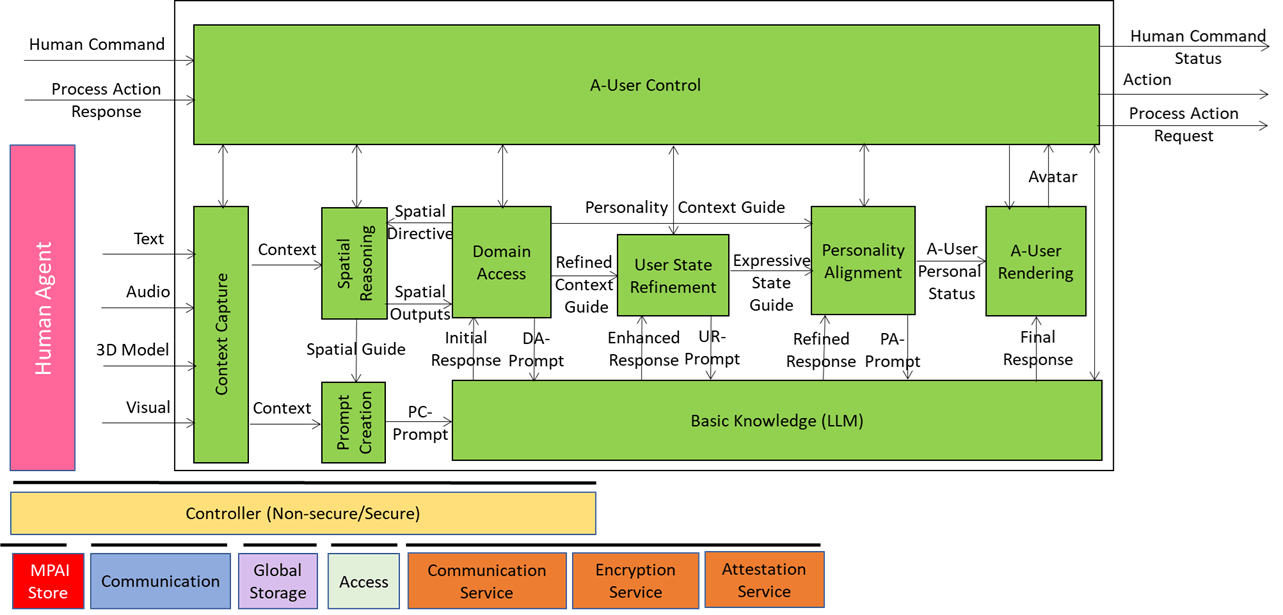
This is the fifth of a sequence of posts aiming at illustrating more in depth the architecture of an A-User and provide an easy entry point for those who wish to respond to the MPAI Call for Technology on Autonomous User Architecture. The first four dealt with 1) the Control performed by the A-User Control AI Module on the other components of the A-User; 2) how the A-User captures the external metaverse environment using the Context Capture AI Module; 3) listens, localises, and interprets sound not just as data, but as data having a spatially anchored meaning; and 4) makes sense of what the Autonomous User sees by understanding objects’ geometry, relationships, and salience.
Prompt Creation is the storyteller and translator in the Autonomous User’s “brain.” It takes raw sensory input – audio and visual spatial data of Context and User State – and turns it into a well‑formed prompt that Basic Knowledge can sensibly understand and respond to.
The audio and visual components of Spatial Reasoning provide the information on things around the User such as “who’s in the room,” “what’s being said,” “what objects are present,” and “what’s the User doing”. Context Capture provides User State as a rich description of the A‑User’s understanding of the “internal state” of the User – which may be biologically real, if the User is a representation of a human, or simulated when the User is the representation of an agent. The task of Prompt Creation is to synthesise these sources of information into a PC‑Prompt Plan. This plan starts from what the User said, adds intent (e.g., “User wants help” or “User is asking a question”), includes the context around the User (e.g., “User is in a virtual kitchen”), and embeds User State (e.g., “User seems confused”).
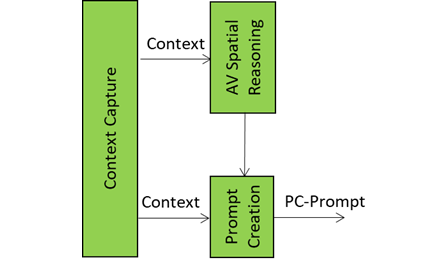
This information is conveniently represented as a JSON object, converted into natural language, and passed to Basic Knowledge. Basic Knowledge then produces a natural language response called the Initial Response – initial because there are more processing elements in the A‑User pipeline that will refine and improve the answer before it is rendered in the metaverse.
Prompt Creation gives the AI a sense of narrative, so the A-User can:
- Ask the right clarifying question.
- Respond with relevance to the situation.
- Adapt to the environment and User mood.
- Maintain continuity across interactions.
If the User says: “Can you help me cook?”
- Spatial Reasoning notes the User is in a virtual kitchen with utensils and ingredients.
- User State suggests the User looks uncertain.
- Prompt Creation combines these into: “User is asking for cooking help, is in a kitchen, seems unsure.”
This Initial Response is then passed to Domain Access, which may elaborate a new prompt enriched with domain-specific information (in this case “cooking”, when Basic Knowledge is not well informed about cooking).
Prompt Creation turns raw multimodal input and spatial information into meaningful prompts so the AI can think, speak, and act with purpose. It is the scriptwriter that ensures the A‑User’s dialogue is not only coherent but also contextually aware, emotionally attuned, and situationally precise.
What you can take away about Prompt Creation
- Translates user speech into Language Model understandable prompts
- Synthesises spatial data and User State
- Detects User intent (e.g., help request, question)
- Embeds environmental context (e.g., virtual kitchen)
- Captures emotional cues (e.g., confusion, excitement)
- Builds a structured PC-Prompt Plan as a JSON object to facilitate prompt creation
- Converts PC-Prompt Plan into a natural language prompt
- Passes the prompt to Basic Knowledge for response generation
- Bridges perception and cognition for purposeful Language Model action

