1 Version
V2.1
2 Functions
Unidirectional Speech Translation (MMC-UST):
- Receives
- Language Preference – Language of Speech and Target Speech.
- Input Text – Text to be translated
- Input Speech – Speech to be translated
- Input Selector – indicates whether
- Input is Text of Speech
- Speech Features of Input Speech should be preserved in Translated Speech.
- Produces Translated Text or Speech.
3 Reference Model
Figure 1 describes the input/output data, the AIMs and the data exchanged between AIMs.
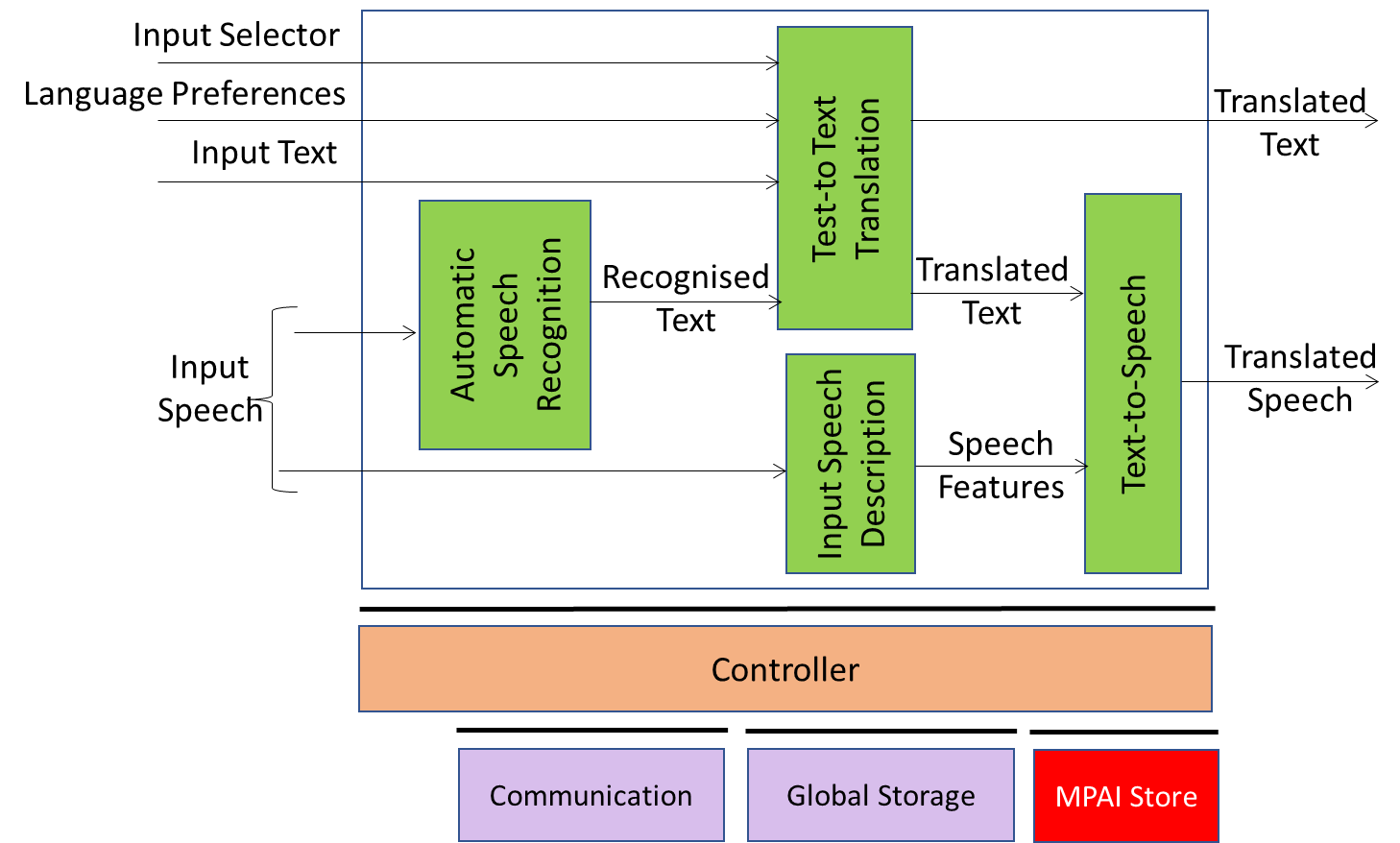
Figure 1 – Reference Model of Unidirectional Speech Translation (UST)
4 I/O Data
The input and output data of the Unidirectional Speech Translation Use Case are:
Table 1 – I/O Data of Unidirectional Speech Translation
| Input | Descriptions |
| Input Selector | Determines whether: 1. The input will be in Text or Speech 2. The Input Speech features are preserved in the Output Speech. |
| Language Preferences | User-specified input Language (A) and output Language (B). |
| Input Speech | Speech produced in Language A by a human desiring translation into language B. |
| Input Text | Alternative textual source information to be translated into and pronounced in language B depending on the value of Input Selector. |
| Output | Descriptions |
| Translated Speech | Input Speech translated into language B preserving the Input Speech features in the Output Speech, depending on the value of Input Selector. |
| Translated Text | Text of Input Speech or Input Text translated into language B, depending on the value of Input Selector. |
5 JSON Metadata
https://schemas.mpai.community/MMC/V2.1/AIWs/UnidirectionalSpeechTranslation.json
6 SubAIMs
| AIMs | Name | JSON | |
| – | MMC-ASR | Audio Scene Description | X |
| – | MMC-TTT | Text-to-Speech | X |
| – | MMC-ISD | Input Speech Description | X |
| – | MMC-TTS | Text-to-Speech | X |

