The international, unaffiliated, non-profit Moving Picture, Audio, and Data Coding by Artificial Intelligence (MPAI) organisation was established in September 2020 in the context of:
- Increasing use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies applied to a broad range of domains affecting millions of people
- Marginal reliance on standards in the development of those AI applications
- Unprecedented impact exerted by standards on the digital media industry affecting billions of people
believing that AI-based data coding standards will have a similar positive impact on the Information and Communication Technology industry.
The design principles of the MPAI organisation as established by the MPAI Statutes are the development of AI-based Data Coding standards in pursuit of the following policies:
- Publish upfront clear Intellectual Property Rights licensing frameworks.
- Adhere to a rigorous standard development process.
- Be friendly to the AI context but, to the extent possible, remain agnostic to the technology thus allowing developers freedom in the selection of the more appropriate – AI or Data Processing – technologies for their needs.
- Be attractive to different industries, end users, and regulators.
- Address five standardisation areas:
- Data Type, a particular type of Data, e.g., Audio, Visual, Object, Scenes, and Descriptors with as clear semantics as possible.
- Qualifier, specialised Metadata conveying information on Sub-Types, Formats, and Attributes of a Data Type.
- AI Module (AIM), processing elements with identified functions and input/output Data Types.
- AI Workflow (AIW), MPAI-specified configurations of AIMs with identified functions and input/output Data Types.
- AI Framework (AIF), an environment enabling dynamic configuration, initialisation, execution, and control of AIWs.
- Provide appropriate Governance of the ecosystem created by MPAI Technical Specifications enabling users to:
- Operate Reference Software Implementations of MPAI Technical Specifications provided together with Reference Software Specifications
- Test the conformance of an implementation with a Technical Specification using the Conformance Testing Specification.
- Assess the performance of an implementation of a Technical Specification using the Performance Assessment Specification.
- Obtain conforming implementations possibly with a performance assessment report from a trusted source through the MPAI Store.
MPAI operates on four solid pillars:
- The MPAI Patent Policy specifies the MPAI standard development process and the Framework Licence development guidelines.
- Technical Specification: Artificial Intelligence Framework (MPAI-AIF) V2.1 specifies an environment enabling initialisation, dynamic configuration, and control of AI applications in the standard AI Framework environment depicted in Figure 1. An AI Framework can execute AI applications called AI Workflows (AIW) typically including interconnected AI Modules (AIM). MPAI-AIF supports small- and large-scale high-performance components and promotes solutions with improved explainability.
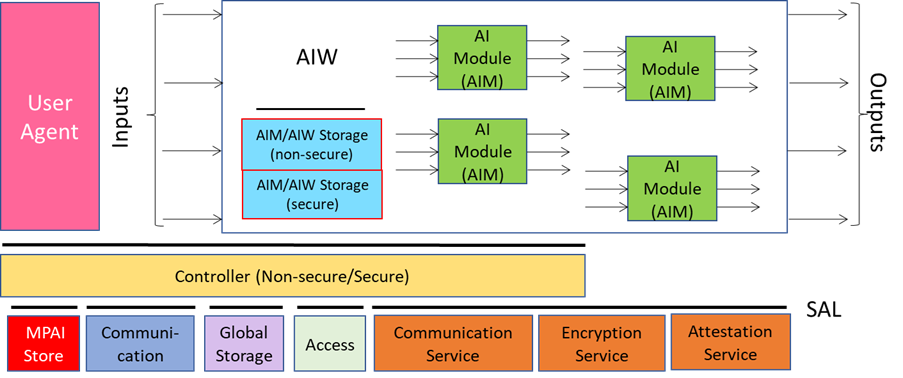
Figure 1 – The AI Framework (MPAI-AIF) V2 Reference Model
- Technical Specification: Data Types, Formats, and Attributes (MPAI-TFA) V1.4 specifies Qualifiers, a type of metadata supporting the operation of AIMs receiving data from other AIMs or from input data. Qualifiers convey information on Sub-Types (e.g., the type of colour), Formats (e.g., the type of compression and transport), and Attributes (e.g., semantic information in the Content). Although Qualifiers are human-readable, they are only intended to be used by AIMs. Therefore, Text, Speech, Audio, Visual, and other Data received by or exchanged between AIWs and AIMs should be interpreted as being composed of Content (Text, Speech, Audio, and Visual as appropriate) and associated Qualifiers. For instance, a Text Object is composed of Text Data and Text Qualifier. The specification of most MPAI Data Types reflects this point.
- Technical Specification: Governance of the MPAI Ecosystem (MPAI-GME) V2.0 defines the following elements:
- Standards, i.e., the ensemble of Technical Specifications, Reference Software, Conformance Testing, and Performance Assessment.
- Developers of MPAI-specified AIMs and Integrators of MPAI-specified AIWS (Implementers).
- MPAI Store in charge of making AIMs and AIWs submitted by Implementers available to Integrators and End Users.
- Performance Assessors, independent entities assessing the performance of implementations in terms of Reliability, Replicability, Robustness, and Fairness.
- End Users.
The interaction between and among actors of the MPAI Ecosystem are depicted in Figure 2.
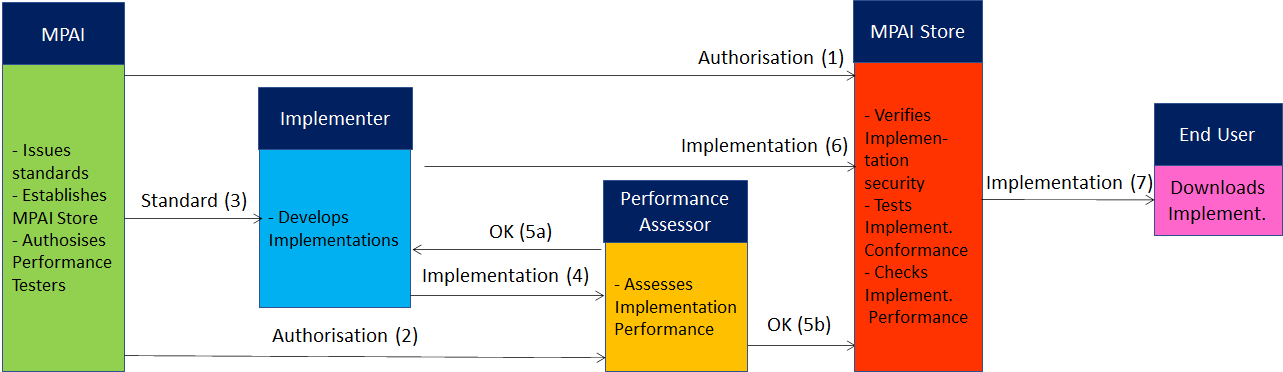
Figure 2 – The MPAI Ecosystem

