1 Functions
Preservation of audio assets recorded on analogue media is an important activity for a variety of application domains, in particular cultural heritage. Preservation goes beyond mere A/D conversion. For instance, the magnetic tape of an open reel may hold important information: it can carry annotations (by the composer or by the technicians) or it can include multiple splices and/or display several types of Irregularities (e.g., corruptions of the carrier, tape of different colour or chemical composition). This information shall be preserved for a correct playback. Nevertheless, some errors can occur during the digitisation as well as the digitisation could be partial because of the corruption of the carrier. These errors shall be restored to make the content listenable. The ARP Use Case (see 5.1.5) concerns the creation of a digital copy of the digitized audio of open reel magnetic tapes for long-term preservation and of an access copy (restored, if necessary) for correct playback of the digitized recording.
In this Audio Recording Preservation Use Case, two files are fed into a preservation system:
The following is not required:
The output of the restoration process is composed by:
- Preservation Master Files.
- Access Copy Files.
2 Reference Architecture
Figure 1 depicts the Audio Recording Preservation Reference Model.
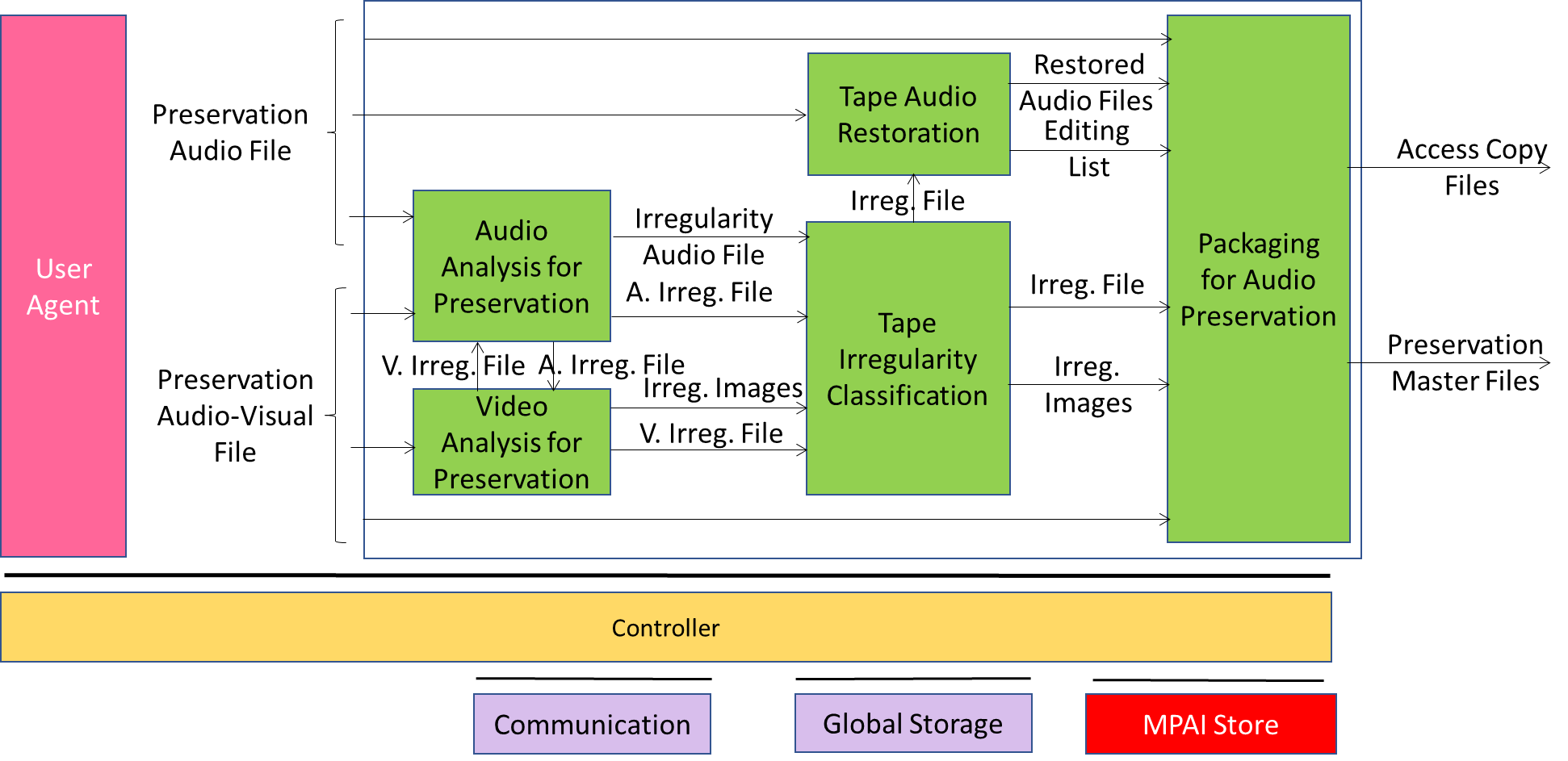
Figure 1 – Audio Recording Preservation Reference Model
The sequence of operations of the Audio Recording Preservation unfolds as follows:
- The sequence of operations of the Audio Recording Preservation unfolds as follows:
1. The analogue audio signal from the open-reel tape recorder is digitised as Preservation Audio File. - Preservation Audio-Visual File is the combination of:
- The video camera pointed at the playback head of the open-reel tape recorder.
- The analogue audio signal digitised with the same video clock.
- Audio Analysis for Preservation:
- Detects Irregularities.
- Assigns IDs to them that are unique to the analysed open-reel tape.
- Receives an Irregularity File from the Video Analysis for Recording
- Extracts the Audio Files corresponding to each Irregularity received or detected.
- Sends the Audio Files and the Irregularity File related to all Irregularities to the Tape Irregularity Classification.
- Video Analysis for Preservation:
- Detects Irregularities.
- Assigns IDs to them that are unique to the analysed open-reel tape.
- Receives an Irregularity File from the Audio Analysis for Recording and the offset between Preservation Audio File and the Preservation Audio-Visual File.
- Extracts the Irregularity Images corresponding to each Irregularity received or detected.
- Sends the Irregularity Images and the Irregularity File related to all Irregularities to the Tape Irregularity Classification.
- 5. Tape Irregularity Classification:
- Receives an Irregularity File with the corresponding Images and Audio Files.
- Classifies and selects the ones considered relevant.
- If the Irregularity was detected by the Video Analysis for Recording, the selected Irregularity File and the corresponding Irregularity Images are sent to the Packaging for Audio Recording.
- The Tape Audio Restoration uses the Irregularity File to identify and restore portions of the Preservation Audio File.
- The Packaging for Audio Preservation collects the Preservation Audio File, Restored Audio Files, the Editing List, the Irregularity File and corresponding Irregularity Images if detected by the Video Analyser, and the Preservation Audio-Visual File and then it produces the Preservation Master Files and Access Copy Files.
3 I/O data of AI Workflow
Table 1 gives the input and output data of Audio Recording Preservation.
Table 1 – I/O data of Audio Recording Preservation
| Input data | Comments |
| Preservation Audio File | A Preservation Audio File obtained by digitising the analogue tape audio recording composed of music, soundscape or speech read from a magnetic tape. |
| Preservation Audio-Visual File | A Preservation Audio-Visual File produced by a camera pointed to the playback head of the magnetic tape recorder. |
| Output data | Comments |
| Preservation Master File | Set of files providing the information stored in an audio tape recording without any restoration. As soon as the original analogue recordings is no more accessible, it becomes the new item for long-term preservation. |
| Access Copy File | Set of Audio Files derived from the Preservation Audio File, where potential speed, equalisation or reading backwards errors that occurred in the digitisation process have been corrected. |
4 Functions of AI Modules
The AIMs required by this Use Case are described in Table 2.
Table 2 – Functions of AI Modules of Audio Recording Preservation
| AIM | Function |
| Audio Analysis for Preservation |
|
| Video Analysis for Preservation |
|
| Tape Irregularity Classification |
|
| Tape Audio Restoration |
|
| Packaging for Audio Preservation | Produces Preservation Master Files and Access Copy Files. |
5 I/O Data of AI Modules
Table 3 – CAE-ARP AIMs and their data
6 Specification of Audio Recording Preservation AIMs and JSON Metadata
Table 4 – Acronyms and URs of JSON Metadata
| AIW | AIMs | Name | JSON |
| CAE-ARP | Audio Recording Preservation | File | |
| CAE-AAP | Audio Analysis for Preservation | File | |
| CAE-VAP | Video Analysis for Preservation | File | |
| CAE-TIC | Tape Irregularity Classification | File | |
| CAE-TAR | Tape Audio Restoration | File | |
| CAE-PAP | Packaging for Audio Preservation | File |

