In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and related technologies, applied to a broad range of applications, have started affecting the life of millions of people and they are expected to do so even more in the future. As digital media standards have positively influenced industry and billions of people, so AI-based data coding standards are expected to have a similar positive impact. Indeed, research has shown that data coding with AI-based technologies is generally more efficient than with existing technologies for, e.g., compression and feature-based description.
However, some AI technologies may carry inherent risks, e.g., in terms of bias toward some classes of users. Therefore, the need for standardisation is more important and urgent than ever.
The international, unaffiliated, not-for-profit MPAI – Moving Picture, Audio and Data Coding by Artificial Intelligence Standards Developing Organisation has the mission to develop AI-enabled data coding standards. MPAI Application Standards enable the development of AI-based products, applications, and services.
As a part of its mission, MPAI has developed standards operating procedures to enable a user of MPAI implementations to make informed decision about their applicability. Central to this is the notion of Performance, defined as a set of attributes characterising a reliable and trustworthy implementation.
Therefore, to fully achieve the MPAI mission, technical standards must be complemented by the creation and management of an ecosystem designed to underpin the life cycle of MPAI standards through the steps of specification, technical testing, assessment of product safety and security, and distribution.
In the following, Terms beginning with a capital letter are defined in Table 1 if they are specific to this Standard and in Table 32 if they are common to all MPAI Standards.
As specified by Technical Specification: Governance of the MPAI Ecosystem (MPAI-GME) V1.1. the MPAI Ecosystem is composed of:
- MPAI as provider of Technical, Conformance and Performance Specifications.
- Implementers of MPAI standards.
- MPAI-appointed Performance Assessors.
- The MPAI Store which assigns Implementer identifiers (ImplementerID’s) and distributes validated Implementations.
The common infrastructure enabling the implementation of MPAI Application Standards is the AI Framework (AIF) Standard (MPAI-AIF).
Figure 1 depicts the MPAI-AIF Reference Model under which Implementations of MPAI Application Standards and user-defined MPAI-AIF conforming applications operate.
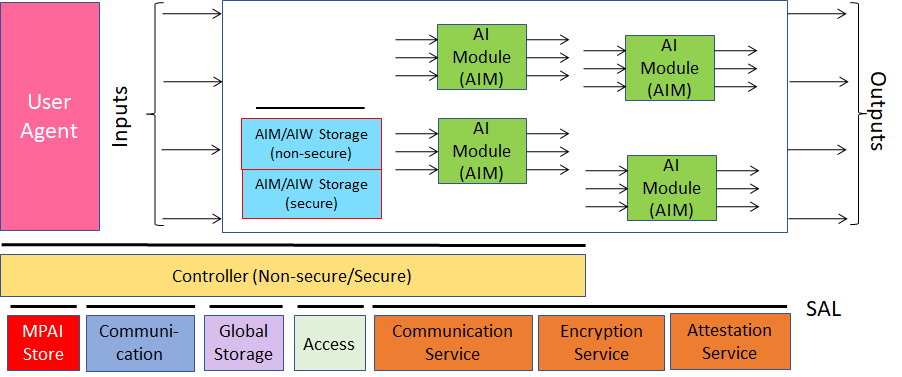
Figure 1 – The AI Framework (AIF) Reference Model and its Components
An AIF Implementation allows execution of AI Workflows (AIW), composed by basic processing elements called AI Modules (AIM).
MPAI Application Standards normatively specify Semantics and Syntax of the input and output data and the Function of the AIW and the AIMs, and the Connections between and among the AIMs of an AIW.
In particular, an AIM is defined by its Function and Data, but not by its internal architecture, which may be based on AI or data processing, and implemented in software, hardware or hybrid software and hardware technologies.
MPAI defines Interoperability as the ability to replace an AIW or an AIM Implementation with a functionally equivalent Implementation. MPAI also defines 3 Interoperability Levels of an AIW that executes an AIW. The AIW may have 3 Levels:
Level 1 – Implementer-specific and satisfying the MPAI-AIF Standard.
Level 2 – Specified by an MPAI Application Standard.
Level 3 – Specified by an MPAI Application Standard and certified by a Performance Assessor.
MPAI offers Users access to the promised benefits of AI with a guarantee of increased transparency, trust and reliability as the Interoperability Level of an Implementation moves from 1 to 3. Additional information on Interoperability Levels is provided in Annex 3.
The Chapters and Annexes of this Technical Specification: Context-based Audio Enhancement (MPAI-CAE) V2.1 are Normative unless they are labelled as Informative.

