<– Notices and Disclaimers Go to ToC
With reference to Figure 7, MPAI issues and maintains a standard – called MPAI-AIF – whose components are:
- An environment called AI Framework (AIF) running AI Workflows (AIW) composed of interconnected AI Modules (AIM) exposing standard interfaces.
- A distribution system of AIW and AIM Implementation called MPAI Store from which an AIF Implementation can download AIWs and AIMs.
A Level 1 Implementation shall be an Implementation of the MPAI-AIF Technical Specification executing AIWs composed of AIMs able to call the MPAI-AIF APIs.
| Implementers’ benefits | Upload to the MPAI Store and have globally distributed Implementations of
– AIFs conforming to MPAI-AIF. – AIWs and AIMs performing proprietary functions executable in AIF. |
| Users’ benefits | Rely on Implementations that have been tested for security. |
| MPAI Store | – Tests the Conformance of Implementations to MPAI-AIF.
– Verifies Implementations’ security, e.g., absence of malware. – Indicates unambiguously that Implementations are Level 1. |
Level 2 Interoperability
In a Level 2 Implementation, the AIW must be an Implementation of an MPAI Use Case and the AIMs must conform with an MPAI Application Standard.
| Implementers’ benefits | Upload to the MPAI Store and have globally distributed Implementations of
– AIFs conforming to MPAI-AIF. – AIWs and AIMs conforming to MPAI Application Standards. |
| Users’ benefits | – Rely on Implementations of AIWs and AIMs whose Functions have been reviewed during standardisation.
– Have a degree of Explainability of the AIW operation because the AIM Functions and the data Formats are known. |
| Market’s benefits | – Open AIW and AIM markets foster competition leading to better products.
– Competition of AIW and AIM Implementations fosters AI innovation. |
| MPAI Store’s role | – Tests Conformance of Implementations with the relevant MPAI Standard.
– Verifies Implementations’ security. – Indicates unambiguously that Implementations are Level 2. |
Level 3 Interoperability
MPAI does not generally set standards on how and with what data an AIM should be trained. This is an important differentiator that promotes competition leading to better solutions. However, the performance of an AIM is typically higher if the data used for training are in greater quantity and more in tune with the scope. Training data that have large variety and cover the spectrum of all cases of interest in breadth and depth typically lead to Implementations of higher “quality”.
For Level 3, MPAI normatively specifies the process, the tools and the data or the characteristics of the data to be used to Assess the Grade of Performance of an AIM or an AIW.
| Implementers’ benefits | May claim their Implementations have passed Performance Assessment. |
| Users’ benefits | Get assurance that the Implementation being used performs correctly, e.g., it has been properly trained. |
| Market’s benefits | Implementations’ Performance Grades stimulate the development of more Performing AIM and AIW Implementations. |
| MPAI Store’s role | – Verifies the Implementations’ security
– Indicates unambiguously that Implementations are Level 3. |
The MPAI ecosystem
The following Figure 8 is a high-level description of the MPAI ecosystem operation applicable to fully conforming MPAI implementations as specified in the Governance of the MPAI Ecosystem Specification [1]:
- MPAI establishes and controls the not-for-profit MPAI Store.
- MPAI appoints Performance Assessors.
- MPAI publishes Standards.
- Implementers submit Implementations to Performance Assessors.
- If the Implementation Performance is acceptable, Performance Assessors inform Implementers and MPAI Store.
- Implementers submit Implementations to the MPAI Store
- MPAI Store verifies security and Tests Conformance of Implementation.
- Users download Implementations and report their experience to MPAI.
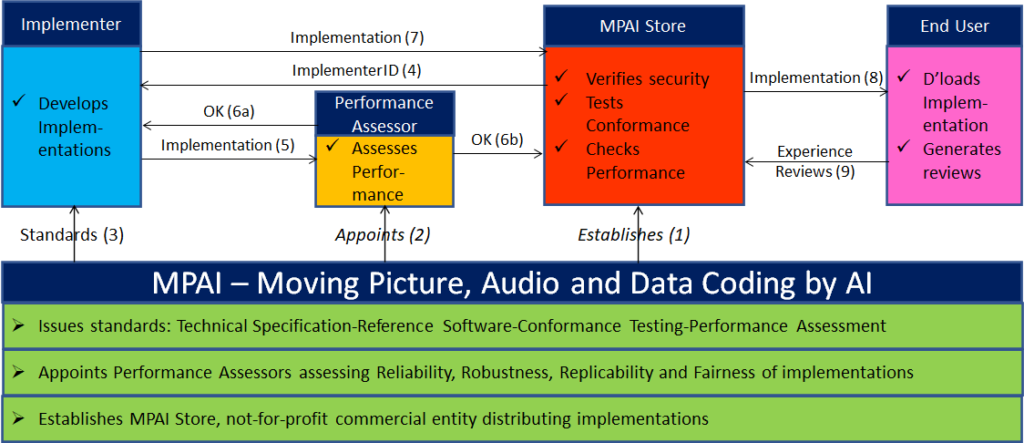
Figure 8 – The MPAI ecosystem operation

