<-Process Actions Go to ToC Profiles->
1. Inter-Process Protocol (same M-Instance)
As depicted in Figure 1, Process1 uses the simple form of the Inter-Process Protocol (IP Protocol or IPP) to request Process2 in the same M-Instance to perform a Process Action.
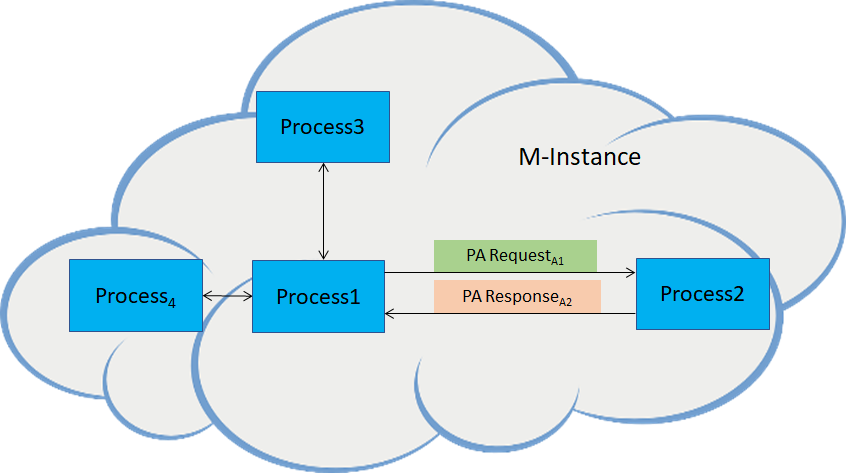
Figure 1 – Process1 requests Process2 to perform a Process Action (same M-Instance).
- Process1 sends a PA Request to Process2.
- If Process2 finds that the PA Request can be performed,
- Then Process2 performs the PA Request and sends a PA Response to Process1.
- Else, Process2, sends a PA Response with an error code to Process1.
2. Inter-Process Protocol (different M-Instances)
Figure 2 depicts the case of a ProcessA in an M-InstanceA requesting a ProcessB in a different M-InstanceB to perform a Process Action in M-InstanceB.
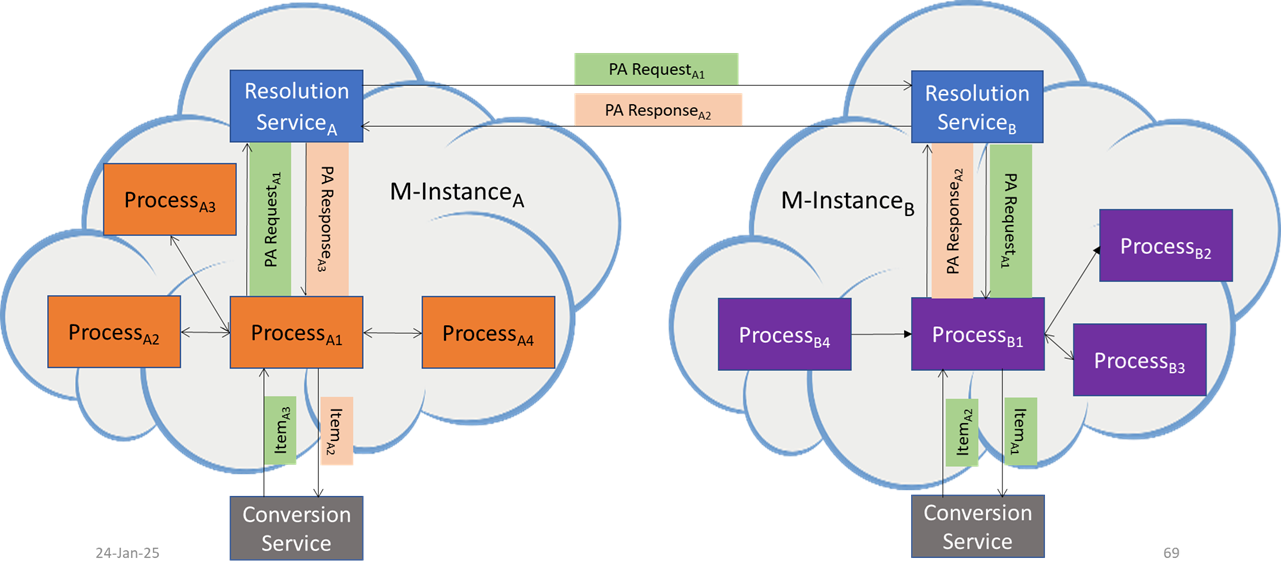 Figure 2 – ProcessA requests ProcessB to perform a Process Action (different M-Instances).
Figure 2 – ProcessA requests ProcessB to perform a Process Action (different M-Instances).
- ProcessA1 sends a PA Request to Resolution ServiceA.
- Resolution ServiceA determines the Resolution ServiceB it should forward the PA Request to.
- If the determination is not reached it sends an error to ProcessA1.
- Else it forwards the request to Resolution ServiceB1.
- Resolution ServiceB1 determines the Process it should send the PA Request to.
- If the determination is not reached, it send an error to Resolution ServiceA1.
- Else it forwards the PA Request to ProcessB1
- ProcessB1 analyses the PA Request and may find that the PA Request may be performed,
- Then
- May request a Conversion ServiceB to make appropriate conversion of the Formats of the Data in the Items it received.
- Performs the request.
- Else, ProcessB1 sends an error to Resolution ServiceB.
- Then
- If the execution of the PA Request fails, it sends an error to Resolution ServiceB.
- Resolution ServiceB sends error or PA Response to Resolution ServiceA.
- Resolution ServiceA sends error or PA Response to ProcessA1.
- ProcessA1 may request a Conversion ServiceA to make appropriate conversion of the Formats of the Data in the Items it received.
The Error Message generated by a receiving Process may be one of three types:
- “Unable to perform request”.
- “Transaction of Value required” (actual value provided).
- “Conversion Service failure”.
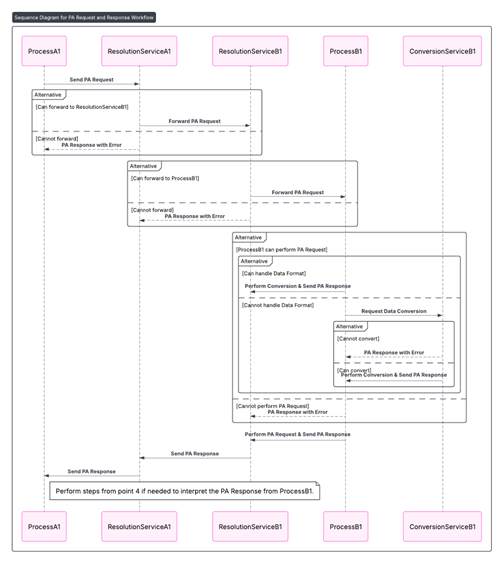
Figure 3 – IP Protocol Sequence Diagram when Processes are in different M-Instances
Note: MMM-TEC does not provide support to the establishment of business agreements based on which communication between different M-Instances become possible.
3. Inter-Process Protocol (multiple M-Instances)
In the case of a multi-M-Instance session (more than 2 M-Instances), an IPP session is set up in the following way:
- ProcessA1 requests Resolution ServiceA1 to open a session with the M-Instances that host at least one invited Process.
- Resolution ServiceA1 forwards the request to all relevant Resolution Services.
- A Resolution ServiceB1 forwards the request to each invited ProcessB‘s of its M-Instance.
- An invited ProcessB1 responds to Resolution ServiceB1 accepting or rejecting the invitation.
- A Resolution ServiceB1 forwards the response to Resolution ServiceA1.
- Resolution ServiceA1 forwards the responses to ProcessA1.
- If at least one invited Process accepts the invitation, the session is opened.
4. Inter-Process Protocol elements
Table 1 provides the elements of the IP Protocol (IPP).
Table 1 – IPP Message elements
| IPP Message Elements | Description |
| Time | Provided by communication infrastructure. |
| Message ID | ID of PA Request or PA Response. |
| Response ID | Absent/Present when the Message is a PA Request/PA Response. |
| Source Process ID | ID of Process issuing Message. |
| Process Action | Combination of Action, Items/Processes and Complement (see Process Action). |
| Resolution Service ID | Service that: 1. Receives a Message from a Process in its M-Instance and forwarding it to a peer Process in a different M-Instance, or 2. Sends a Message received from a peer Process in a different M-Instance to a Process in its M-Instance. (Absent if the two Processes are in the same M-Instance). |
| Destination Process ID | ID of Process to which the Message is intended to be sent. |
| Message Status | “Ack”, if delivery of payload successful, if delivery fails, Error. |
In case of multiple Destination Processes, the Source Process receives the Message Status for each Destination Process.
The JSON Schema of the Inter-Process Protocol is here.
5. Posting Protocol
To request a Service Provider (marketplace) to Post an Item, a Process (User1) invokes the Posting Protocol:
- User1 MM-Sends Model Simple Contract To Service Provider.
- Service Provider MM-Sends Response To User1.
- If response=No, goto End
- Else User1
- Transacts SenderPreValue (Service Provider’s request to Post the Item) To Service Provider.
- Licenses Nil Service Provider With Service Provider Licence (giving Rights to Post Item)
- Service Provider operates per Service Provider Licence.
- When Time=Time2 (End Time of Licence)
- Service Provider stops operating per Service Provider Licence.
- User1 recovers full Rights on Item.
- End
6. Licensing Protocol
The Licensing Protocol assumes that a Process (User1) has Posted an Item at Service Provider and that User2 wishes to obtain a Licence to the Posted Item per the Model Basic Contract:
- User2 MM-Sends Nil Model Basic Contract with its own data To Service Provider.
- Service Provider MM-Sends Nil “Ack” (the characters Ack) To User2.
- User2 Transacts (ReceiverPostValue, the Value that Service Provider requests to User2 for its Service) To Service Provider.
- User2 Transacts (ValueToSender, the Value in the Model Basic Contract) To User1.
- User1 Transacts (SenderPostValue, the Value that Service Provider requests to User1 for its Service) To Service Provider.
- User1 MM-Sends Model Licence to Licence Service.
- Licence Service MM-Sends Nil Model Licence to User2.
- User MM-Sends “Ack” (the characters Ack) to Licence Service.
- Licence Service MM-Sends Licence To User1.
- Licence Service MM-Sends Licence To User2.
<-Process Actions Go to ToC Profiles->

