| Function | Reference Model | Input/Output Data |
| SubAIMs | JSON Metadata | Profiles |
1. Function
The Prompt Creation AIM (PGM-PRC) synthesises multimodal input — including Audio and Visual Scene Descriptors, Entity State, and signals from A‑User Control — into a structured representation of user intent, resolved referents, spatial relations, and interaction context.
Prompt Creation makes available an internal set of MCP‑exposed operations, each defined by schema‑validated inputs and outputs. These operations represent the intermediate computational steps (e.g., intent candidate formation, referent resolution, state adaptation) that downstream AIMs, such as Basic Knowledge, may invoke as MCP tools.
These are the specific PGM-PRC Functional requirements
Multimodal Interpretation: Extract, integrate, and refine information from the Token Stream, Audio and Visual Scene Descriptors, Entity State, and contextual inputs.
Intent Candidate Formation: Produce a ranked set of inferred user intents from multimodal analysis.
Spatial and Referent Resolution: Resolve ambiguous referents and spatial primitives derived from contextual descriptors.
User‑State Adaptation: Adjust communicative framing based on the current user state.
Expose PRC Internal Operations as MCP Tools: Provide a set of schema‑validated MCP tool definitions that correspond to PRC’s internal interpretation steps (intent candidates, referent resolution, spatial analysis, state adaptation). These tools must expose inputs, outputs, and functional descriptions via an MCP Server.
Enable Structured Invocation by Basic Knowledge: Allow the Basic Knowledge AIM to call PRC’s MCP‑exposed operations to obtain structured intermediate computations necessary for generating responses.
Produce Structured Output in MCP Format: Produce the Initial Response input for Basic Knowledge and PGM‑AUC in machine‑interpretable structured form via MCP, rather than natural‑language prompts.
The resulting outputs enable A-User Control, Personality Alignment, and Rendering AIMs to operate with full awareness of the User’s communicative intent, supporting expression coherence, goal-driven orchestration, and context-sensitive interaction.
2. Reference Model
Figure 1 gives Reference Model of Prompt Creation (PGM-PRC).
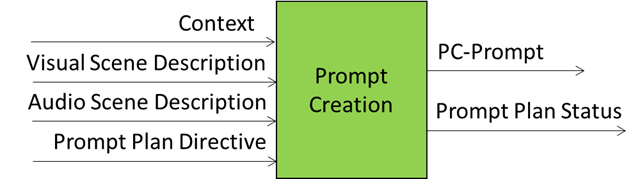
Figure – The Reference Model of Prompt Creation (PGM-PRC)
3. Input/Output Data
Table 1 – Input/Output Data of PGM-PRC
| Input | Description |
| Context | A structured and time-stamped snapshot representing the initial understanding that the A-User achieves of the environment and of the User posture. |
| Audio Scene Descriptors | A Data Type that conveys spatially grounded semantic audio data from the Spatial Reasoning AIM that enables the Prompt Construction AIM to generate context-aware and referentially precise prompts. |
| Visual Scene Descriptors | A Data Type that conveys spatially grounded semantic visual data from the Spatial Reasoning AIM that enables the Prompt Construction AIM to generate context-aware and referentially precise prompts. |
| Prompt Creation Directive | Trigger to initiates prompt generation or refinement from PGM-AUC. |
| Output | Description |
| PC-Input | A machine‑interpretable MCP‑structured object containing PRC’s interpretation of Context, User Intent, referents (objects, people, or scene elements referred to by User’s vague expressions), User State, and Audio and Visual Scene Descriptors. Sent as input to PGM-BKN. |
| Prompt Creation Status |
Structured MCP metadata expressing PRC readiness, alignment, and processing state. Sent to and used by PGM‑AUC for orchestration and control.
|
|
A structured MCP data object enumerating the MCP tools exposed by Prompt Creation, each defined by its name, purpose, input schema, and output schema. This manifest enables PGM‑BKN – and when appropriate, Domain Access – to discover and invoke PRC’s internal computational functions through the MCP Server.
|
4. SubAIMs
Table 2 describes the informative SubAIMs that have been identified for PGM-PRC.
Table 2 – Informative SubAIMs
| SubAIM | Function | Inputs | Outputs | To |
| CIP – Context Integration & Parsing | Assemble multimodal context and Entity State for prompt; select exact referents/relations in prompt scope. | ASD1; VSD1; ASD3; VSD3; Entity State | Item Zone Map; Validation Flags | CVV |
| CVV – Context & Validation Verifier (Prompt‑Scoped) | Final verification of consistency wrt input-text-referenced items/relations; apply policy gates; check zone feasibility. | Item Zone Map; ASD1; VSD1; ASD3; VSD3; Entity State; Validation Flags | Validation Status; Zone Feasibility Tag; Scene Consistency Flag | BSL |
| BSL – Behaviour Selection & Logic | Retrieve and rank candidate behaviours based on validated context and Entity State. | Entity State; Validation Status; Scene Consistency Flag | Behaviour Candidates List | EFR |
| EFR – Execution Feasibility & Recovery | Assess feasibility and produce fallback or adjusted prompt when needed. | Behaviour Candidates List; Validation Status; Zone Feasibility Tag | Execution Feasibility Status; Fallback Action | PCP |
| PCP – Prompt Composition & Planning | Prepare structured PC-Prompt Plan (JSON) integrating validated context, constraints, and behaviours. | Execution Feasibility Status; Behaviour Candidates List; Scene/Entity Tags | PC-Prompt Plan | PFT |
| PFT – Prompt Formatter (new) | Convert PC-Prompt Plan (JSON) into natural language PC-Prompt for BKN. | PC-Prompt Plan | PC-Prompt | BKN |
| LTM – Lifecycle Trace Metadata | Record provenance and traceability for audit/lifecycle management. | ASD1 ID; ASD3 ID; VSD1 ID; VSD3 ID; Execution Feasibility Status | Trace Log | AUC |
Table 3 defines the terms used.
Table 3 – Terminology used in this AIM
| Term | Definition |
| ASD1 / VSD1 | Audio Scene Descriptor (ASD1) and Visual Scene Descriptor (VSD1) generated by Context Capture. These represent the initial scene understanding before refinement. |
| ASD3 / VSD3 | Audio Scene Descriptor (ASD3) and Visual Scene Descriptor (VSD3) produced by ASR/VSR after their final interaction cycle with DAC. These are the most refined descriptors available to PRC. |
| Entity State | A structured representation of the current state of relevant entities (e.g., position, orientation, status flags) in the scene. Replaces the older concept of “User State.” |
| Item Zone Map | A mapping of referenced items (from the input text) to their spatial zones and relationships in the scene, derived from ASD1/VSD1 and ASD3/VSD3. Used to ground prompt content. |
| Validation Flags | Indicators generated by CIP to highlight potential ambiguities or risks (e.g., unresolved referents, missing zone info) for CVV to resolve. |
| Validation Status | The result of CVV’s checks (OK / WARN / FAIL) including reasons and confidence scores for multimodal consistency and policy compliance. |
| Zone Feasibility Tag | A tag indicating whether the spatial zone referenced in the prompt is physically/logically feasible for the intended action. |
| Scene Consistency Flag | A graded indicator confirming that the scene context assumed by the prompt matches the actual scene descriptors. |
| Behaviour Candidates List | A ranked list of possible behaviours/actions retrieved by BSL based on validated context and Entity State. |
| Execution Feasibility Status | A status object indicating whether the selected behaviour(s) can be executed under current constraints (e.g., zone reachability, operational limits). |
| Fallback Action | An alternative behaviour or adjusted prompt generated by EFR when execution feasibility fails. |
| PC-Prompt Plan | A structured JSON plan integrating validated context, constraints, and behaviours for natural language generation. Used internally by PRC to produce the PC-Prompt. |
| PC-Prompt | The natural-language prompt assembled by PRC and sent to BKN (LLM). |
| Trace Log | Provenance and lifecycle metadata recorded by LTM for audit and orchestration purposes. |
Table 4 maps PRC Inputs/Outputs to Unified Messages.
Table 4 — PRC Inputs/Outputs mapped to Unified Messages
| PRC Data Name | Role | Origin / Destination | Unified Schema Mapping |
| Context | Input | From Context Capture (CXC) | Consumed by PRC as contextual basis for prompt generation; carried in Context; referenced via Envelope.CorrelationId; MUST include Trace.Origin and Trace.Timestamp. |
| Prompt Creation Directive | Input | From A‑User Control (AUC) | Directive → TargetAIM=PRC; includes generation parameters (style, constraints, modality); correlation maintained via Envelope.CorrelationId. |
| Entity State (optional) | Input | From Context Capture (CXC) | If used by PRC: carried in Context; referenced for personalization or posture-aware prompt adaptation. |
| Prompt Object | Output | To BKN | Status → Result (generated prompt text or multimodal structure); maintain Envelope.CorrelationId; MUST include Trace.Origin and Trace.Timestamp. |
| Prompt Creation Status | Output | To A‑User Control (AUC) | Status → State/Progress/Summary/Result; includes confidence, generation steps, and any fallback logic; MUST include Trace.Origin and Trace.Timestamp. |
5. JSON Metadata
https://schemas.mpai.community/PGM1/V1.0/AIMs/PromptInput.json
6. Profiles
No Profiles.

