(Tentative)
| Function | Reference Model | Input/Output Data |
| SubAIMs | JSON Metadata | Profiles |
Function
The Visual Spatial Reasoning AIM (PGM‑VSR) AIM acts as a bridge between raw visual scene descriptors and higher-level reasoning modules by interpreting and refining spatial visual context to support reasoning and action execution.
AIM-VSR
- Receives
- Visual Action Directive (PGM‑VAD) from A-User Control.
- Context (PGM-CXT) from Context Capture that includes Entity State, Visual Scene Descriptors (VSD0), and Audio Scene Descriptors (ASD0).
- Refines and aligns Visual Scene Descriptors through an iterative loop with Doman Access (PGM‑DAC) with the following steps:
- VSR processes VSD0 to obtain an enriched description (VSD1).
- VSR sends VSD1, an enriched version of VSD0 to DAC.
- DAC further enriches VSD1 using Domain Knowledge (VSD2)
- DAC sends VSD2 to VSR.
- VSR further enhances VSD2 (VSD3).
- VSD3 may be sent to DAC again.
- VSR sends the final version of VSD3 to Prompt Creation (PGM-PRC)..
Table 1 describes this iterative loop. Note that User State is not explicitly mentioned in the iterative loop.
Table 1 – Iterative loop of Visual Scene Descriptors
| Phase | Inputs | Operation | Outputs | To |
| Directive intake | PGM‑VAD (Visual Action Directive) | Conform pipeline: select required spatial operations, constraints, and priorities. | Conformance plan (internal) | — |
| Initial refinement | VSD0 (from OSD‑VSD), conformance plan | Produce VSD1 aligned to directive: descriptor parsing, normalisation, preliminary localisation. | VSD1 | PGM‑DAC |
| Domain enrichment | VSD1 | Apply domain‑specific knowledge, resolve ambiguities, add semantic attributes. | VSD2 | PGM‑VSR |
| Directive‑aligned reasoning | VSD2, conformance plan | Execute directive‑scoped spatial reasoning: refined localisation, depth/occlusion, affordance inference, salience mapping. | VSD3 | PGM‑DAC |
| Potential refinement loop | VSD3 | Domain Access may be called for additional Domain Knowledge | VSD3‘ | PGM-VSR |
| Transmission to OGM-PRC | VSD3‘ | VSD3‘ | PGM-PRC | |
| Status reporting | Conformance plan, execution results | Summarise compliance, coverage, uncertainties, and residual constraints | PGM‑VSR (Visual Action Status) | PGM‑AUC |
Reference Model
Figure 1 gives the Reference Model of the Visual Spatial Reasoning (PGM-VSR) AIM.

Figure 1 – The Reference Model of the Visual Spatial Reasoning (PGM-VSR) AIM
Input/Output Data
Table 2 gives the Input and Output Data of PGM-VSR.
Table 2 – Input/Output Data of PGM-VSR
| Input | Description |
| Context | A structured and time-stamped snapshot representing the initial understanding that the A-User achieves of the environment and of the User posture. |
| Visual Scene Descriptors | A modification of the input Visual Scene Descriptors provided by the Domain Access AIM to help the interpretation of the Visual Scene by injecting constraints, priorities, and refinement logic. |
| Visual Action Directive | Visual-related actions and process sequences from PGM-AUC. |
| Output | Description |
| Visual Scene Descriptors | A structured, analytical representation of the Visual Scene with object geometry, 3D positions, depth, occlusion, and affordance data. It highlights salient objects, normalised positions, proximity, and interaction cues. |
| Visual Action Status | Visual spatial constraints and scene anchoring from PGM-AUC. |
SubAIMs
Figure 2 gives the Reference Model of the Visual Spatial Reasoning (PGM-VSR) Composite AIM.
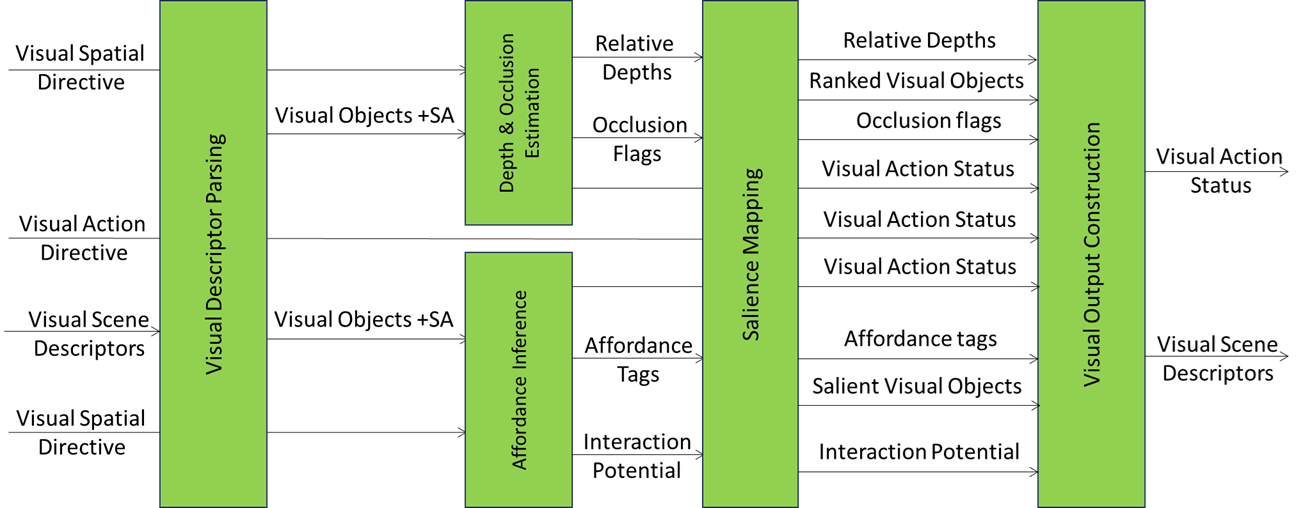 Figure 2 – Reference Model of Visual Spatial Reasoning (PGM-VSR) Composite AIM
Figure 2 – Reference Model of Visual Spatial Reasoning (PGM-VSR) Composite AIM
Table 3 specifies the Functions performed by PGM-VSP AIM’s SubAIMs in the current example partitioning in SubAIMs.
Table 3 – Functions performed by PGM-VSP AIM’s SubAIMs (example)
| VDP | Visual Descriptors Parsing | Purpose | Decompose initial VSD into structured components and validate scene integrity. |
| Tasks | • Extract Visual Objects (VIO) and Object Spatial Attitudes (OSA: position, orientation, scale).
• Normalize coordinates to A-User PointOfView. • Validate descriptor completeness and schema compliance. • Maintain references for multimodal fusion. |
||
| Output | • Structured VIO list with OSA metadata.
• Validation report with confidence and uncertainty flags. |
||
| DOE | Depth and Occlusion Estimation | Purpose | Compute relative depth and occlusion relationships among visual objects to support spatial reasoning and safe interaction planning. |
| Tasks | • Estimate object distance from PointOfView using depth maps, stereo disparity, or scene geometry.
• Normalize depth values across heterogeneous sources and align with A-User coordinates. • Detect occlusion relationships and compute occlusion ratios. • Attach visibility status (VISIBLE, PARTIAL, HIDDEN) and confidence scores. • Integrate proximity zones (near/mid/far) for salience and rendering decisions. |
||
| Output | • DepthProfile: {objectID, depthValue, confidence, proximityZone}.
• OcclusionMap: {objectID, occludedBy[], occlusionRatio, visibilityStatus}. • Metadata: PointOfView, EnrichmentTime, AIM ID. |
||
| AFI | Affordance Inference | Purpose | Determine actionable properties and interaction potential of objects. |
| Tasks | • Infer affordances (graspable, clickable, draggable) from geometry and semantics.
• Cross-check inferred affordances against Rights and Rules. • Attach confidence scores and safety flags. |
||
| Output | • AffordanceProfile per object: {actions[], constraints, safetyFlags, confidence}. | ||
| VSM | Visual Salience Mapping | Purpose | Rank objects by prominence and relevance for interaction. |
| Tasks | • Compute salience using visual cues (size, contrast, motion) and depth from DOE.
• Integrate User gaze/gesture and A-User Control directives. • Filter non-salient entities to optimize reasoning and rendering. |
||
| Output | • RankedVisualObjects list with salience scores and rationale. | ||
| VOC | Visual Output Construction | Purpose | Aggregate enriched visual data into a coherent VSD₁ for downstream AIMs. |
| Tasks | • Merge outputs from VDP, DOE, AFI, and VSM.
• Attach metadata: PointOfView, EnrichmentTime, AIM ID. • Serialize VSD₁ for interoperability with Domain Access. |
||
| Output | • VSD₁: enriched Visual Scene Descriptor ready for Domain Access. |
Table 4 gives the AIMs composing the Visual Spatial Reasoning (PGM-VSR) Composite AIM:
Table 4 – AIMs of the Visual Spatial Reasoning (PGM-VSR) Composite AIM
| AIM | AIMs | Names | JSON |
| PGM-VSR | Visual Spatial Reasoning | Link | |
| PGM-ADP | Visual Descriptors Parsing | Link | |
| PGM-DOE | Depth and Occlusion Estimation | Link | |
| PGM-AFI | Affordance Inference | Link | |
| PGM-SMP | Visual Salience Mapping | Link | |
| PGM-VOC | Visual Output Construction | Link |
Table 5 gives the input and output data of the PGM-VSR AIM.
Table 5 – Input and output data of the PGM-VSR AIM
| AIMs | Input | Output | To |
| Visual Descriptors Parsing | Visual Scene Descriptors | Visual Objects Spatial Attitude |
DOE, AFI, SMP, VOC |
| Depth and Occlusion Estimation | Visual Objects Spatial Attitude Visual Spatial Directive |
Relative Depths Occlusion Flags Visual Spatial Status |
SMP, VOC |
| Affordance Inference | Visual Objects Spatial Attitude Visual Action Directive |
Affordance Tags Interaction Potential Visual Spatial Status |
SMP, VOC |
| Salience Mapping | Relative Depths Occlusion Flags Affordance Tags Interaction Potential Visual Action Directive |
Relative Depths Occlusion Flags Ranked Visual Objects Affordance Tags Interaction Potential Salient Visual Objects Visual Spatial Status |
VOC |
| Visual Output Construction | Relative Depths Occlusion Flags Ranked Visual Objects Affordance Tags Interaction Potential Salient Visual Objects Visual Spatial Status |
Visual Scene Descriptors Visual Spatial Status |
— |
Table 6 specifies the External and Internal Data Types of the Visual Spatial Reasoning AIM.
Table 6 – External and Internal Data Types identified in Visual Spatial Reasoning AIM
| Data Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| VisualSceneDescriptors | – Final structured output containing all spatialised and semantically enriched visual data (input). – The product of the Composite AIM (output). |
| UserPointOfView | Contained in component Basic Visual Scene Descriptors. |
| VisualObjects | Structured list of Visual Objects extracted from the Visual Scene Descriptors. |
| SpatialAttitudes | Position, Orientation, and their first and second order D spatial attributes of each Visual Object, including . |
| DepthEstimates | Classification of each object’s relative depth (e.g., foreground, midground, background). |
| OcclusionFlags | Visibility classification of each object (e.g., fully visible, partially occluded, hidden). |
| AffordanceProfile | Actionable properties of visual objects (e.g., graspable, tappable, obstructive) and inferred interaction potential. |
| RankedVisualObject | Ordered list of visual objects prioritized by perceptual salience and interaction relevance. |
| FilteredSalientObjects | Subset of Ranked Visual Objects selected for inclusion in the OSD-VSD1. |
| VisualSpatialDirective | Dynamic modifier provided by Domain Access AIM. Injects constraints, priorities, and refinement logic into reasoning Sub-AIMs. |
| VisualSpatialStatus | Structured status report from directive-aware Sub-AIMs. Includes constraint satisfaction, override flags, and anchoring metadata. |
Tables 7 maps VSR Inputs/Outputs to Unified Messages.
Table 7 – VSR Inputs/Outputs mapped to Unified Messages
| VSR Data Name | Role | Origin / Destination | Unified Schema Mapping |
|---|---|---|---|
| Context | Input | From Context Capture (CXC) | Consumed by VSR as scene input; carried in Context; referenced via Envelope.CorrelationId; MUST include Trace.Origin and Trace.Timestamp. |
| Visual Scene Descriptors (modified) | Input | From Domain Access (DAC) | Directive → TargetAIM=VSR; constraints/priorities injected in Parameters/Constraints; correlation maintained. |
| Visual Action Directive | Input | From A‑User Control (AUC) | Directive → Operation for visual actions; scheduling via Priority; correlation via Envelope.CorrelationId. |
| Entity State | Input | From Context Capture (CXC) | If used by VSR: carried in Context, referenced as Entity State for posture/attention |
| Visual Scene Descriptors | Output | To DAC / PRC | Status → Result (structured scene representation: geometry, 3D positions, depth, occlusion, affordances); maintain Envelope.CorrelationId. |
| Visual Action Status | Output | To A‑User Control (AUC) | Status → State/Progress/Summary/Result; includes spatial constraints and anchoring; MUST include Trace.Origin and Trace.Timestamp. |
5. JSON Metadata
https://schemas.mpai.community/PGM1/V1.0/AIMs/VisualSpatialReasoning.json
6. Profiles
No Profiles

