| CAE | CAV | HMC | MMC | OSD | PAF |
| AI Workflows | AI Modules |
1 AI Workflows
1.1 Avatar Videoconference Server
PAF-AVS is a PAAI composed of collaborating PAAIs:
| Portable Avatar Demultiplexing | Makes available the components of all avatars received by PAF-AVS. |
| Text and Speech Translation | Translates the Speech Objects based on avatars’ Language preferences. |
| Service Participant Authentication | Uses participants’ speech and faces to authenticate a participant as a legitimate videoconference service user. |
| Portable Avatar Multiplexing | Combines into Portable Avatars dispatched to participants the following: – Modified avatar components. – Avatar IDs (at session start). – Scene descriptors (at session start) – Selected avatars’ Positions and Orientation (at session start). |
![]()
Figure 1 – Reference Model of Avatar Videoconference Server
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
- Portable Avatar Demultiplexing
- Text and Speech Translation
- Service Participant Authentication
- Portable Avatar Multiplexing
PAF-AVS performs Interpretation Level Operations (MMC-TST and PAF-SPA).
1.2 Videoconference Client Receiver
PAF-VCR is a PAAI composed of collaborating PAAIs performing the following operations:
| Portable Avatar Demultiplexing | Makes available the components of all avatars received by PAF-AVS. |
| Visual Scene Creation | Identifies the Spatial Attitude of the mouth of each avatar. |
| Audio Scene Creation | Adds the Speech Object to the mouth of each avatar. |
| Audio-Visual Scene Rendering | Renders the speech and visual component of the scene from a user-selected Point of View |
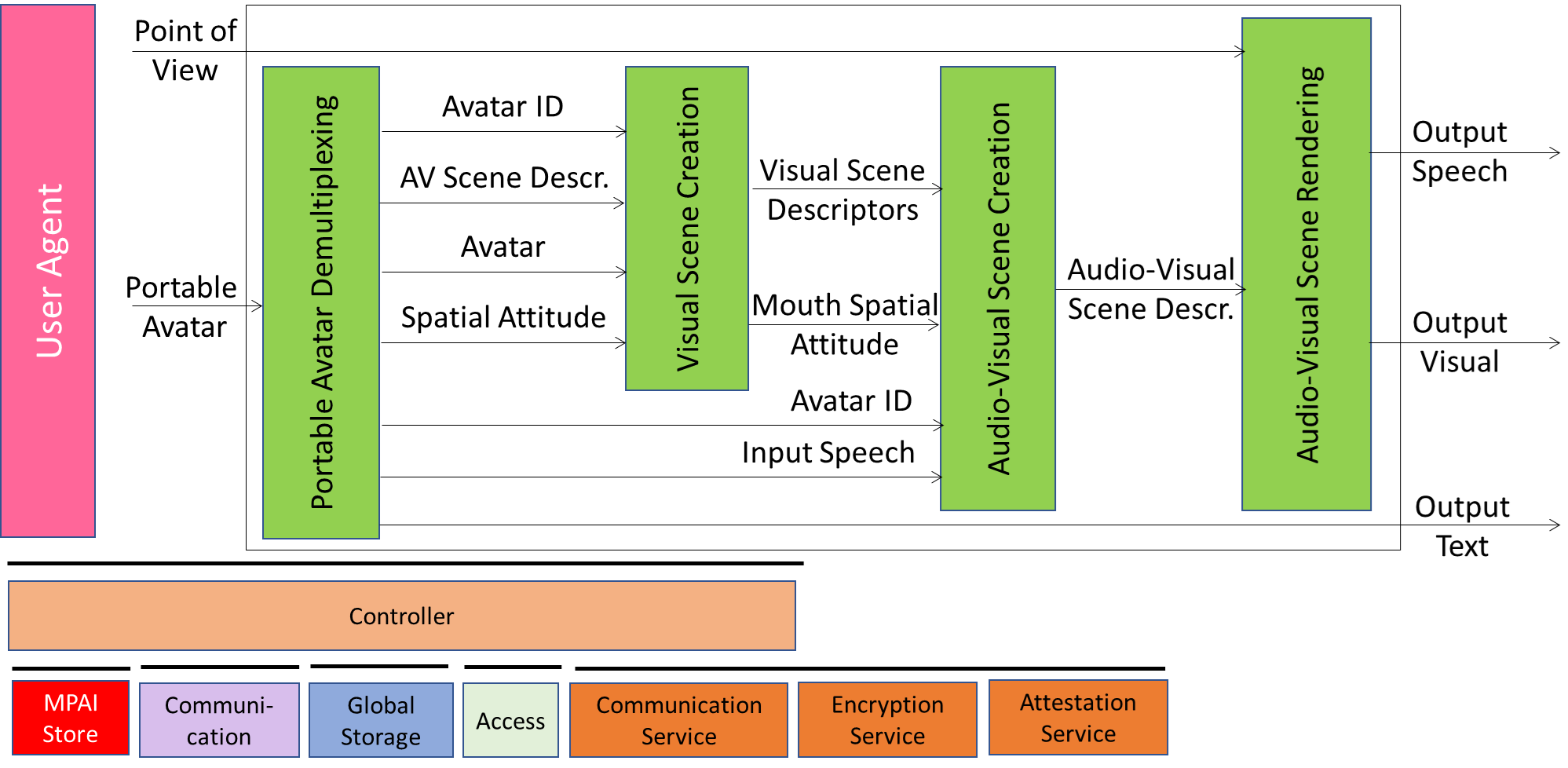
Figure 1 – Reference Model of Videoconference Client Receiver
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
- Portable Avatar Demultiplexing
- Visual Scene Creation
- Audio-Visual Scene Creation
- Audio-Visual Scene Rendering
PAF-VCT performs Descriptors Level Operations.
1.3 Videoconference Client Transmitter
PAF-VCT is a PAAI composed of the following collaborating PAAIs:
| AV Scene Description | Digitally represents the audio-visual scene removing the audio component and retaining the speech component. |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Converts the Input Speech into Text. |
| Personal Status Extraction | Extracts the Personal Status from input Text-Speech-Face-Gesture. |
| Personal Status Multiplexing | Uses Text and Personal Status to improve the quality of the produced Avatar and multiplexes Input Selector, Avatar Model, and Participant ID with other data internal to the AIW. |
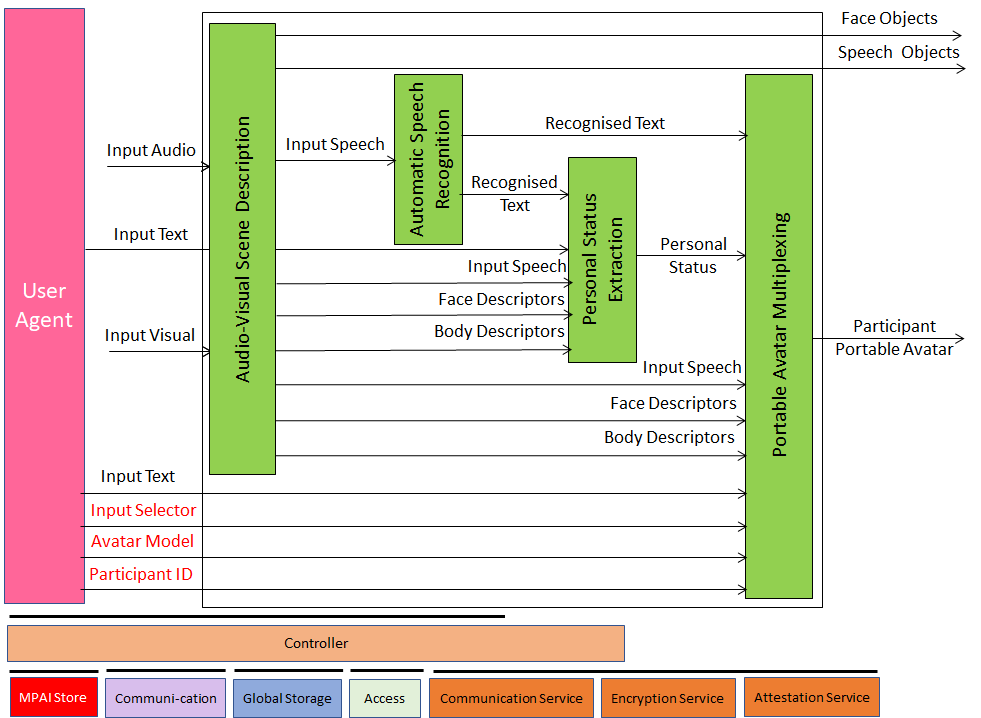
Figure 1 – Reference Model of Videoconference Client Transmitter (PAF-ABV)
The following links analyse the AI Modules:
- Audio-Visual Scene Description
- Automatic Speech Recognition
- Personal Status Extraction
- Portable Avatar Multiplexing
PAF-VCT performs Descriptors Level Operations.
2 AI Modules
2.1 Audio-Visual Scene Rendering
PAF-AVR:
| Receives | Point of View | To be used in rendering the scene and its objects. |
| AV Scene Descriptors | jointly with or alternatively with Portable Avatar (PA). | |
| Portable Avatar | Jointly with or alternatively to AV Scene Descriptors. | |
| Transforms | Portable Avatar | Into generic Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors if input is PA. |
| Produces | Output Speech | Resulting from the rendering of Speech Scene Descriptors from human-selected Point of View. |
| Output Audio | Resulting from the rendering of Audio Scene Descriptors from human-selected Point of View. | |
| Output Visual | Resulting from the rendering of Visual Scene Descriptors from human-selected Point of View. |
A PAF-AVR implementation requires graphic rendering capabilities to render the Audio-Visual Scene and the Avatar from the user-selected Point of View.
PAF-AVR performs Descriptors Level Operation.
2.2 Face Identity Recognition
PAF-FIR:
| Receives | Text Object | Text that is related with the Face to be identified. |
| Image Visual Object | Image containing Face to be identified. | |
| Face Time | Time when the face should be identified. | |
| Visual Scene Geometry | Of the scene where the Face is located. | |
| Finds | Bounding Boxes | That include Faces, using spatial information. |
| Applies | Face ID algorithm | That references a specific Face Taxonomy. |
| Finds | The best match | Between the Faces and those in a database. |
| Produces | Face Identities | Face Instance Identifiers. |
| Bounding Boxes | Bounding Boxes that include faces. |
PAF-FIR performs Descriptors (Bounding Boxes) and Interpretation (Face IDs) Level Operations.
2.3 Personal Status Display
PAF-PSD
| Receives | Machine ID | ID to be used to identify the Avatar in Portable Avatar. |
| Text Object | Text associated to Avatar in Portable Avatar. | |
| Personal Status | Personal Status associated to Avatar in Portable Avatar. | |
| Avatar Model | 3D Model associated to Avatar in Portable Avatar. | |
| Speech Model | Speech Model Associated to Avatar in Portable Avatar. | |
| Synthesises | Speech Object | Possibly through an input Speech Model. |
| Generates | Face Descriptors | Using Speech Object, input Avatar Model, and Face Personal Status. |
| Produces | Portable Avatar | Including Machine ID, Speech Model, Text Object, Avatar Model and internally generated Speech Object and Avatar |
| Enables | PAF-AVR | To render the Portable Avatar produced by PAF-PSD. |
PAF-PSD performs Descriptors Level Operation.
1.4 Service Participant Authentication
PAF-SPA
| Receives | Participant ID | ID of a Participant in a session of a Service. From an upstream AIM or another AIW. |
| Face Visual Object | Face of Participant. | |
| Speech Object | Speech segment of Participant. | |
| Recognises | Face ID | From Face Objects |
| Speech ID | From Speech Object | |
| Uses | Speech & Face ID | To search an Service ID database. |
| Produces | Subscriber ID | ID of Service Subscriber |
PAF-SPA can be implemented using Neural Networks.
PAF-SPA performs Interpretation Level Operation.

