<-Go to AI Workflows Go to ToC ->
| 1 Functions | 2 Reference Model | 3 I/O Data |
| 4 Functions of AI Modules | 5 I/O Data of AI Modules | 6 AIW, AIMs, and JSON Metadata |
| 7 Reference Software | 8 Conformance Testing | 9 Performance Assessment |
1 Functions
Enhanced Audioconference Experience addresses the situation where one or more speakers are active in a noisy meeting room and are trying to communicate with one or more interlocutors using speech over a network. In this situation, the user experience is very often far from satisfactory due to multiple competing speakers, non-ideal acoustical properties of the physical spaces that the speakers occupy and/or the background noise. These can lead to a reduction in speech intelligibility resulting in participants not fully understanding what their interlocutors are saying, a situation of distraction that may possibly lead to “o-called” audioconference fatigue. When microphone arrays are used to capture the speakers, most of the described problems can be resolved by appropriate processing of the captured signals. The speech signals from multiple speakers can be separated from each other, the non-ideal acoustics of the space can be improved, and background noise can be substantially suppressed.
CAE-EAE is concerned with extracting:
- The individual speakers’ speech signals from the microphone array as well as reducing the background noise and the reverberation that reduce speech intelligibility.
- The speakers’ Spatial Attitudes with respect to the position of the microphone array to facilitate the spatial representation of the speech signals at the receiver side if necessary.
Spatial Attitudes are represented in the Audio Scene Geometry format and further processes packaged for efficient delivery. Possible compression of the extracted speech signals as well as their reconstruction/representation at the receiver side are specified by the Qualifiers of the Speech Objects.
The Enhanced Audio Experience AIW:
| Receives | Audio Object | Composed of Audio Data and Qualifier. The latter describes the format of the Audio Data and Attributes such as Microphone Array Geometry and capturing device geometry. |
| Audio Source Model | A polynomial description of a simple acoustic source parameterised in terms of its direction with respect to the capture point. | |
| Produces | Audio Scene Descriptors | The description of the Audio Scene including individual Audio Objects and their Spatial Attitudes. Audio Objects include Data and Qualifiers. |
2 Reference Model
Figure 1 depicts the Reference Model for the CAE-EAE.
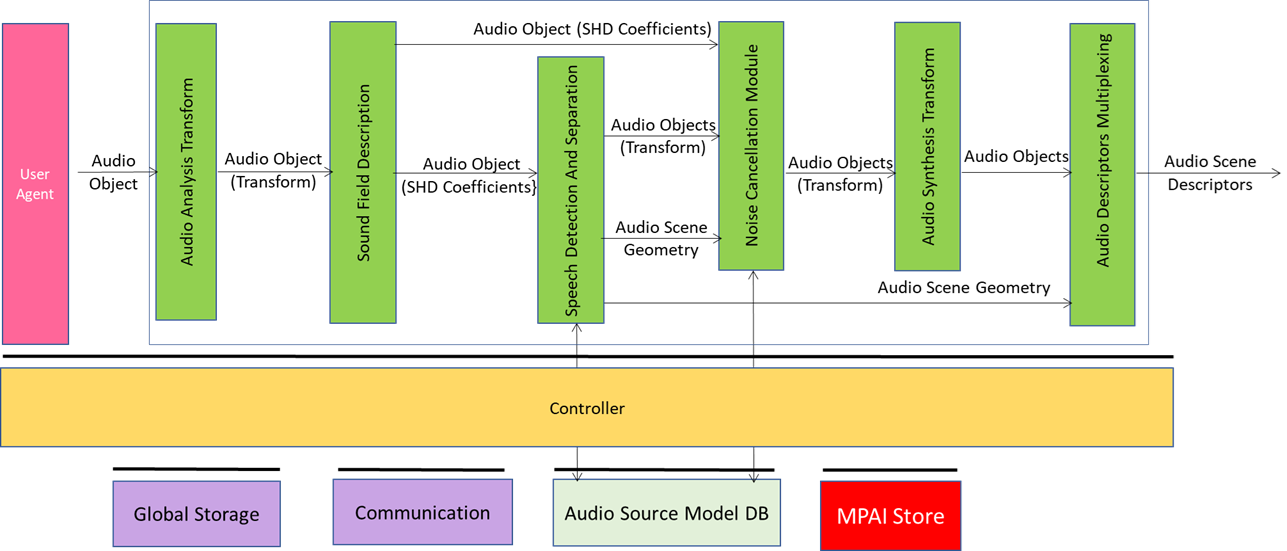
Figure 1 – Enhanced Audioconference Experience Reference Model
EAE receives An Audio Object which includes, Audio Data, Microphone Array Geometry and Device Geometry. Using this information, the system can detect the relative directions of the active speakers according to the microphone array and separate relevant audioconference speech sources from each other and from other spurious sounds. Since audio conferencing is a real-time application scenario, the use case operates on Audio Blocks.
The sequence of operations of the EAE use case is the following:
- Audio Analysis Transform transforms the Multichannel Audio into frequency bands via a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). The following operations are carried out in discrete frequency bands. When such a configuration is used a 50% overlap between subsequent audio blocks needs to be employed. The output is a data structure comprising complex valued audio samples in the frequency domain.
- Sound Field Description converts the output from the Analysis Transform AIM into the spherical frequency domain [20]. If the microphone array used in capturing the scene is a spherical microphone array, Spherical Fourier Transform (SFT) can be used to obtain the Spherical Harmonic Decomposition (SHD) coefficients that represent the captured sound field in the spatial frequency domain. For other types of arrays, more elaborate processing might be necessary. The output of this AIM is (M × (N+1)2) complex valued data frame comprising the SHD coefficients up to an order which depends on the number of individual microphones in the array.
- Speech Detection and Separation receives the SHD coefficients of the sound field to detect directions of active sound sources and to separate them. Each separated source can either be a speech or a non-speech signal. Speech detection is carried out on an Audio Block basis by using on each separated source an appropriate voice activity detector (VAD) that is a part of this AIM. This AIM will output speech as an (M × S) Audio Block comprising transform domain speech signals and block-by-block the Audio Scene Geometry in JSON format comprising auxiliary information which contains a (M × 1) binary mask indicating the channels of the transform domain SHD coefficients that would be used by the Noise Cancellation AIM for denoising. Speech Detection and Separation AIM uses the Source Model KB which contains discrete-time and discrete-valued simple acoustic source models that are used in source separation.
- Noise Cancellation Module eliminates background noise and reverberation which reduce the audio quality. If environmental conditions do not substantially add ambient noise to the desired speech, this AIM acts as a Passthrough AIM.
- It receives Transform Speech from Speech Detection and Separation AIM and Acoustic Scene Metadata which includes attributes pertaining to the Audio Block being processed for denoising, and SHD coefficients.
- It uses Source Model KB. The output of Noise Cancellation AIM is Denoised Transform Speech as an (M × S) complex-valued data structure which will in the next stage be processed through Synthesis Transform AIM to obtain Denoised Speech.
- Audio Synthesis Transform receives Denoised Transform Speech and outputs Denoised Transform Speech (F × S) by applying the inverse of the analysis transform.
- Audio Descriptors Multiplexing: produced the output Audio Scene Descriptors from Audio Objects and the Audio Scene Geometry.
3 I/O data of AI Workflow
Table 1 shows the input and output data for the Enhanced Audioconference Experience workflow.
Table 1 – I/O data of Enhanced Audioconference Experience
| Inputs | Comments |
| Audio Object | Audio Data and optional metadata regarding Sub-Types, Formats and Attributes of the Audio Data. |
| Audio Source Model | A polynomial description of a simple acoustic source parameterised in terms of its direction with respect to the capture point. |
| Outputs | Comments |
| Audio Scene Descriptors | A Data Type including the Audio Objects of a scene, their sub-scenes, and their arrangement in the scene. |
4 Functions of AI Modules
Table 2 gives the AIMs used by the Enhanced Audioconference Experience AIW.
Table 2 – AIMs of Enhanced Audioconference Experience
| AIM | Function |
| Audio Analysis Transform | Represents the input Multichannel Audio in a new form amenable to further processing by the subsequent AIMs in the architecture. |
| Sound Field Description | Produces Spherical Harmonic Decomposition Coefficients of the Transformed Multichannel Audio. |
| Speech Detection and Separation | Separates speech and non-speech signals in the Spherical Harmonic Decomposition producing Transform Speech and Audio Scene Geometry. |
| Noise Cancellation Module | Removes noise and/or suppresses reverberation in the Transform Speech producing Enhanced Transform Audio. |
| Audio Synthesis Transform | Effects inverse transform of Enhanced Transform Audio producing Enhanced Audio Objects ready for packaging. |
| Audio Descriptors Multiplexing | Multiplexes Enhanced Audio Objects and the Audio Scene Geometry. |
5 I/O Data of AI Modules
Table 3 specifies the I/O Data of CAE-EAE.
Table 3 – CAE-EAE AIMs and their data
| AIM | Input Data | Output Data |
| Audio Analysis Transform | Audio Object | Audio Object (Transform) |
| Sound Field Description | Audio Object (Transform) | Audio Object (SHD Coefficients) |
| Speech Detection and Separation | Audio Object (SHD Coefficients) Audio Source Model |
Audio Objects (Transform) Audio Scene Geometry |
| Noise Cancellation Module | Audio Object (SHD Coefficients) Audio Object (Transform) Audio Scene Geometry Audio Source Model |
Enhanced Audio Objects (Transform) |
| Audio Synthesis Transform | Enhanced Audio Objects (Transform) | Enhanced Audio Objects |
| Audio Description Packaging | Enhanced Audio Objects Audio Scene Geometry |
Audio Scene Descriptors |
6 AIW, AIMs, and JSON Metadata
Table 4 provides links to the AI Modules and JSON Metadata.
Table 4 – AIW, AIMs, and JSON Metadata
| AIW | AIMs | Names | JSON |
| CAE-EAE | Enhanced Audioconference Experience | File | |
| CAE-AAT | Audio Analysis Transform | File | |
| CAE-SFD | Sound Field Description | File | |
| CAE-SDS | Speech Detection and Separation | File | |
| CAE-NCM | Noise Cancellation Module | File | |
| CAE-AST | Audio Synthesis Transform | File | |
| CAE-ADP | Audio Descriptors Multiplexing | File |
7 Reference Software
The CAE-EAE Reference Software can be downloaded from the MPAI Git.
8 Conformance Testing
Table 2 provides the Conformance Testing Method for CAE-EAE AIW. Conformance Testing of the individual AIMs are given by the individual AIM Specification.
Table 2 – Conformance Testing Method for OSD-EAE AIW
| Receives | Audio Object | Shall validate against the Audio Object Schema. The Qualifier shall validate against the Audio Qualifier schema. |
| Audio Source Model | Shall validate against the Audio Source Model Schema. | |
| Produces | Audio Scene Descriptors | Shall validate against the Audio Scene Descriptors Schema. The Audio Objects shall validate against the Audio Object Schema. The Spatial Attitudes shall validate against the Spatial Attitudes Schemas. The Qualifier shall validate against the Audio Qualifier schema. |
9 Performance Assessment

