The Text and Speech Translation Composite AIM is specified in the following six sections.
1 Functions of Text and Speech Translation
2 Reference Architecture of Text and Speech Translation
3 I/O Data of Text and Speech Translation
4 I/O Data of AI Modules of Text and Speech Translation
5 I/O Data of AI Modules of Text and Speech Translation
6 JSON Metadata of Text and Speech Translation and its AIMs
1 Functions of Text and Speech Translation
Text and Speech Translation (MMC-STT):
- Receives:
- Input Selection determining whether the input is provided as text or speech. If the desired output is speech, the user can specify whether their speech features (voice colour, emotional charge, etc.) should be preserved in the translated speech.
- Target language.
- Input Text.
- Input Speech.
- Produces Translated Text or Translated Speech Objects in the target language.
2 Reference Architecture of Text and Speech Translation
Figure 1 depicts the Reference Architecture of the Text-and-Speech Translation Composite AIM.
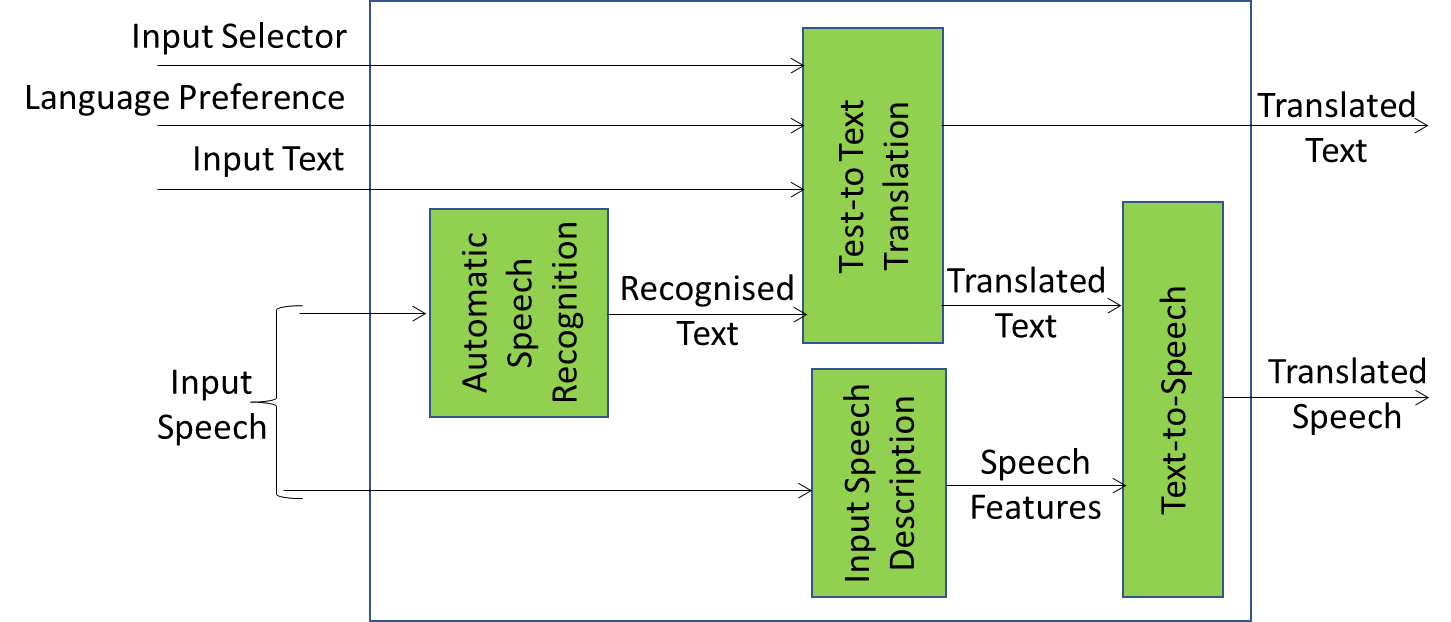
Figure 1 – The Text-and-Speech Translation Composite AIM
3 I/O Data of Text and Speech Translation
Table 1 provides the list of the I/O Data of the Text and Speech Translation Composite AIM.
Table 1 – I/O Data of Text and Speech Translation
| Input | Semantics |
| Input Selector | Determines whether: 1. The input will be in Text or Speech 2. The Input Speech features are preserved in the Output Speech. |
| Language Preferences | User-specified input Language (A) and output Language (B). |
| Input Speech | Speech produced in Language A by a human desiring translation into language B. |
| Input Text | Alternative textual source information to be translated into and pronounced in language B depending on the value of Input Selection. |
| Output | Description |
| Translated Speech | Input Speech in language A translated into language B preserving the Input Speech features in the Output Speech, depending on the value of Input Selection. |
| Translated Text | Text of Input Speech or Input Text translated into language B, depending on the value of Input Selection. |
4 I/O Data of AI Modules of Text and Speech Translation
Table 2 gives the functions of Text-and-Speech Translation AIMs.
Table 2 – Functions of Text-and-Speech Translation AI Modules
| AIM | Functions |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Recognises Input Speech. |
| Text-to-Text Translation | Translates Recognised Text into Translated Text. |
| Input Speech Description | Extracts Speech Descriptors (a.k.a. Features) from Input Speech. |
| Text-to-Speech (Features) | Synthesises Translated Text adding Speech Features |
5 I/O Data of AI Modules of Text and Speech Translation
The AI Modules of Text-and-Speech Translation are given in Table 3.
Table 3 – AI Modules of Text-and-Speech Translation
| AIM | Receives | Produces |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Input Speech | Recognised Text |
| Text-to-Text Translation | 1. Input Text 2. Recognised Text (Based on Input Selector) |
Translated Text |
| Input Speech Description | Input Speech | Speaker-specific Speech Descriptors |
| Text-to-Speech (Features) | 1. Translated Text 2. Speech Descriptors (Based on Input Selection) |
Produces Output Speech. |
6 Specification of Text and Speech Translation AIMs, and JSON Metadata
Table 4 – AIMs and JSON Metadata
| AIM | Name | JSON |
| MMC-TST | Text and Speech Translation | X |
| – MMC-ASR | Automatic Speech Recognition | X |
| – MMC-TTT | Text-to-Text Translation | X |
| – MMC-ISD | Input Speech Description | X |
| – MMC-TTS | Text-to-Speech | X |

