<-Operation Go to ToC Actions->
| 1. Inroduction | 2. App | 3. Device | 4. Service | 5. User |
1 Introduction
Process is the first of the constitutive elements of MMM’. It is an instance of a Program running in a device or in the computing platform underpinning an M-Instance specified by:
- The Functions it performs.
- Qualifiers.
- Metadata having the following extensible general form:
| ProcessID | The ID of the Process. |
| InRights | The list of Process Actions the Process can perform with their Levels. |
| OutRights | The list of Process Actions that another Process can request the Process to perform. |
| WalletID | The ID of the Wallet related to the Process. |
| DescrMdata | Any human-readable description of the Process. |
- Performs Actions on Items.
- May request other Processes to perform Actions (Inter-Process Protocol) by sending a Request-Action Item.
- Performs a request contained in a Request-Action if:
- The requesting Process holds the Rights that are required to perform the request.
- The requested Process holds Rights to perform the requested Action on the Item.
- May Perform, or request another Process to perform, Actions on Items even in the absence of Rights, if the Rules so allow.
- May send back a Response-Action after receiving a Request-Action.
Table 1 – Elements of Request-Action and Response-Action
| Request-Action | Response-Action | Details |
| Request-Action ID | Response-Action ID | Unique ID |
| Emission Time | Emission Time | Tine of Issuance |
| Source Process ID | Source Process ID | Requesting Process ID |
| Destination Process ID | Destination Process ID | Requested Process ID |
| InItems | OutItems | In/Output Items required by the Action |
| InLocations | Locations of InItems | |
| OutLocations | Locations of OutItems | |
| OutRights | Expected Rights on OutItems |
- May communicate to a Process in another M-Instance through an M-Instance’s Resolution Service (Inter M-Instance Protocol).
- To obtain conversion of the Format of an Item’s Data by calling a Conversion Service (see Figure 2).
- To specify their communication needs by:
- Requesting the needed maximum and average bitrate value.
- Reserving the needed bitrate for a time and a location.
- Requesting that the same simultaneous Experience be provided to a specified number of Devices.
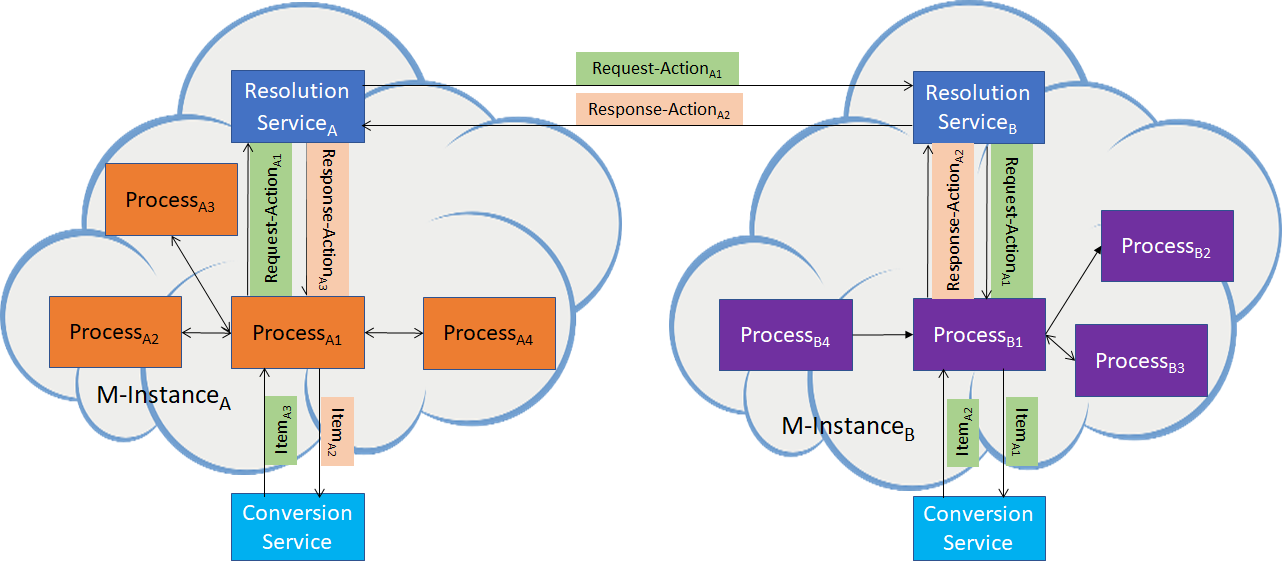
Figure 2 – Resolution and Conversion Services
There are four types of Process.
2 App
| Functions | An instance of an application-specific Program executed on a Device. |
| Functional Requirements | The Manager of the M-Instance in which an App will be deployed may request that the Device be subject to certification. |
3 Device
| Functions | A Device can: 1. UM-Capture Data from a U-Location 2. UM-Send Data and Metadata to a User and/or 1. MM-Send an Entity from an M-Location to the Device 2. MU-Render an Entity at a U-Location. |
| Functional Requirements | To connect and interoperate with an M-Instance, a Device needs to expose its Process Capabilities to the M-Instance. |
4 Service
| Purpose | A Process that provides specific Functionalities. |
| Functional Requirements | A Service may be: 1. One of the Services natively supported by an M-Instance. 2. Hosted by the M-Instance but provided by a third party. |
5 User
| Purpose | A Process representing a Registered human. |
| Functional Requirements | 1. A User may perform the following functions: 1.1. Act as the interface of the human with the M-Instance. 1.2. Render the User as a Persona UM-Animated by a Stream or MM-Animated by an autonomous agent. 2. Animation results from an MM-/UM-Animate Action and enabled by a Program run by the User. 3. The Animation Program may be part of the Processes registered by a human or provided by the M-Instance. |
<-Operation Go to ToC Actions->

