1 Scope of Television Media Analysis
2 Reference Model of Television Media Analysis
3 I/O Data of Television Media Analysis
4 Functions of AI Modules of Television Media Analysis
5 I/O Data of AI Modules of Television Media Analysis
6 AIMs and JSON Metadata of Television Media Analysis
1 Scope of Television Media Analysis
Television Media Analysis (OSD-TMA) gives Audio-Visual Event Descriptors in the form of a set of significant Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors with scene changes, IDs of speakers and faces with their spatial positions, and text from utterances of a video program provided as input.
2 Reference Model of Television Media Analysis
Figure 2 depicts the Reference Model of TV Media Analysis.
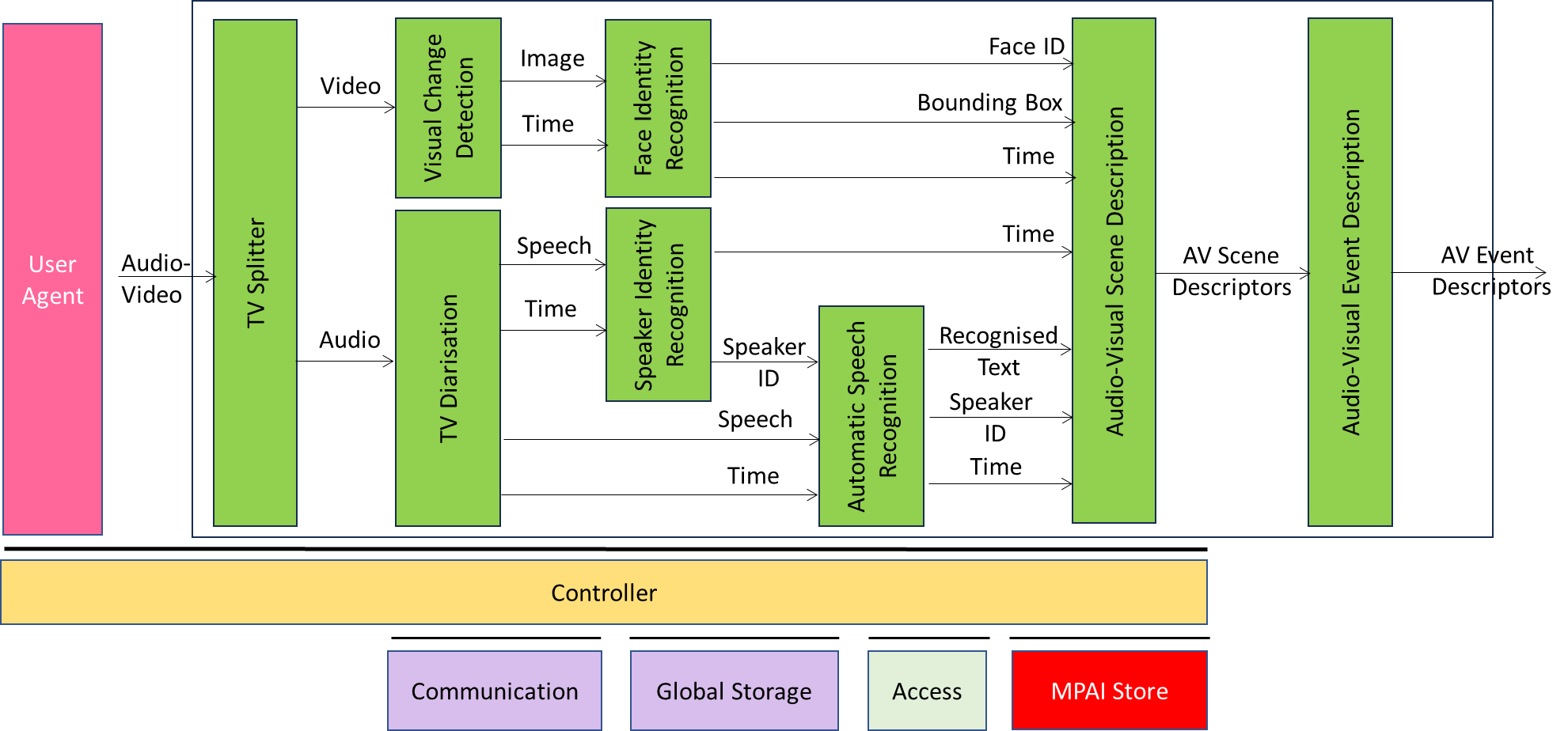
Figure 2 – Reference Model of OSD-TMA
Table 1 gives the names and acronyms of the AIMs.
Table 1 – Names and acronyms of the AIMs
| Acronyms | AIM Names |
| OSD-TVS | TV Splitter |
| OSD-SCD | Scene Change Detection |
| MMC-TVD | TV Diarisation |
| PAF-FIR | Face Identity Recognition |
| MMC-SIR | Speaker Identity Recognition |
| MMC-ASR | Automatic Speech Recognition |
| OSD-AVS | Audio-Visual Scene Description |
| OSD-AVE | Audio-Visual Event Description |
3 I/O Data of Television Media Analysis
Table 2 provides the input and output data of the TV Media Analysis Use Case:
Table 2 – I/O Data of TV Media Analysis
| Input | Descriptions |
| Input Audio-Video | Audio-Video to be analysed. |
| Input | Descriptions |
| AV Event Descriptors | Resulting analysis. |
4 Functions of AI Modules of Television Media Analysis
Table 3 provides the functions of the TV Media Analysis Use Case. Note that processing proceeds asynchronously, e.g., TV Splitter separates audio and video for the entire duration of the file and passes the entire audio and video files.
Table 3 – Functions of AI Modules of Conversation with Personal Status
| AIM | Function |
| TV Splitter | 1. Receives Audio-Visual
a. An audio-video file. b. Metadata (e.g., title, date). 2. Produces a. Video file b. Audio file 3. When the files of the full duration of the video are ready, AV Splitter informs the following AIMs. |
| Scene Change Detection | 1. Receives Video file.
2. Iteratively a. Looks for a video frame that conveys a scene changed from the preceding scene (depends on threshold). b. Assigns a video clip identifier to the video clip. c. Produces a set of images with StartTime and EndTime. i. An image ii. Time stamp |
| TV Diarisation | 1. Receives Audio file.
2. Iteratively detects speaker change. a. For each audio segment (from one change to the next): i. Becomes aware that there is speech. ii. Assigns a speech segment ID and anonymous speaker ID (i.e., the identity is unknown) in the segment. iii. Decides whether: 1. The existing speaker has stopped. 2. A new speaker has started a speech segment. iv. If a speaker has started a speech: 1. Assigns a new speech segment ID. 2. Check whether the speaker is new or old in the session. 3. If old retain old anonymous speaker ID. 4. If new assign a new anonymous speaker ID. b. Produces a series of audio sequences each of which contains: i. A speech segment. ii. Start and end time. iii. Anonymous Speaker ID. |
| Face Identity Recognition | 1. Receives a set of images per video clip.
2. For each image identifies the bounding boxes. 3. Extracts faces from the bounding boxes. 4. Extracts the embeddings that represent a face. 5. Compares the embeddings with those stored in the face recognition data base. 6. Associates the embeddings with a face ID. |
| Speaker Identity Recognition | 1. Receives a speech segment.
2. Extracts the embeddings that represent the speech segment. 3. Compares the embeddings with those stored in the speaker recognition data base. 4. Associates the embeddings with a Speaker ID. |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | 1. Receives a speech segments and SpeakerID.
2. Produces the transcription of the speech payload. 3. Attaches time stamps to specific portions of the transcription. |
| Audio-Visual Scene Description | 1. Receives
1. Bounding box coordinates, Face ID, and time stamps 2. Speaker ID and time stamps. 3. Reconciles Face ID and Speaker ID. 4. Text and time stamps 5. Produces a JSON multiplexing the input data. 2. Produces Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors |
| Audio-Visual Event Description | 1. Receives Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors
2. Produces Audio-Visual Event Descriptors |
5 I/O Data of AI Modules of Television Media Analysis
Table 4 provides the I/O Data of the AI Modules of the TV Media Analysis Use Case.
Table 4 – I/O Data of AI Modules of Conversation with Personal Status
| AIM | Receives | Produces |
| TV Splitter | Audio-Video | Audio
Video |
| Scene Change Detection | Video | Image |
| TV Diarisation | Audio | Speech Segments |
| Face Identity Recognition | Image | Face ID |
| Speaker Identity Recognition | Speech Segments | Speaker ID |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Speech Segments | Text |
| Audio-Visual Scene Description | 1. Bounding box coordinates
2. Face ID 3. Scene time stamps 4. Speaker ID 5. Speech time stamps. 6. Recognised Text from Speech Segments 7. Text and time stamps |
AV Scene Descriptors with reconciled Face and Speech IDs. |
| Audio-Visual Event Description | Audio-Visual Scene Descriptors | AV Event Descriptors |
6 AIMs and JSON Metadata of Television Media Analysis
Table 5 – AIMs and JSON Metadata
| AIW | AIM | Name |
| OSD-TMA | OSD-TVS | TV Splitter |
| OSD-VCD | Visual Change Detection | |
| MMC-TVD | TV Diarisation | |
| PAF-FIR | Face Identity Recognition | |
| MMC-SIR | Speaker Identity Recognition | |
| MMC-ASR | Automatic Speech Recognition | |
| OSD-AVS | Audio-Visual Scene Description | |
| OSD-AVE | Audio-Visual Event Description |

