<–Introduction Go to ToC General aspects of MPAI-CAV Architecture–>
The Technical Specification: Connected Autonomous Vehicle (MPAI-CAV) – Architecture specifies the architecture of a Connected Autonomous Vehicle, i.e., a physical system that:
- Converses with humans by understanding their utterances, e.g., a request to be taken to a destination.
- Acquires information with a variety of sensors on the physical environment where it is located or traverses like the one depicted in Figure 1.
- Plans a Route enabling the CAV to reach the requested destination.
- Autonomously reaches the destination by:
- Moving in the physical environment.
- Building Digital Representations of the Environment.
- Exchanging elements of such Representations with other CAVs and CAV-aware entities.
- Making decisions about how to execute the Route.
- Acting on the CAV motion actuation to implement the decisions.
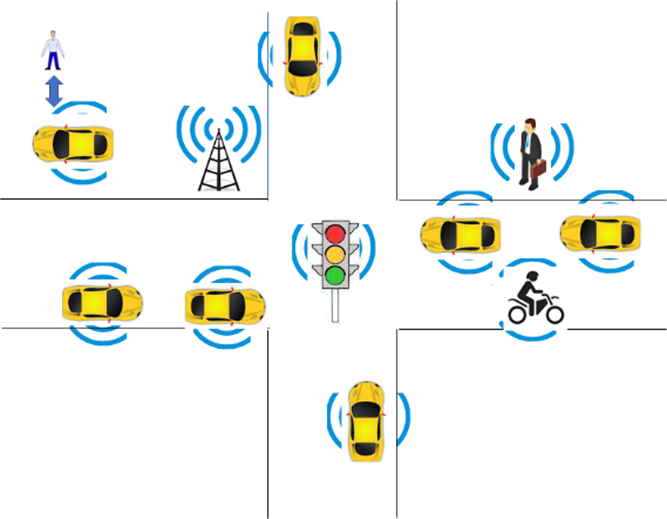
Figure 1 – An environment of CAV operation
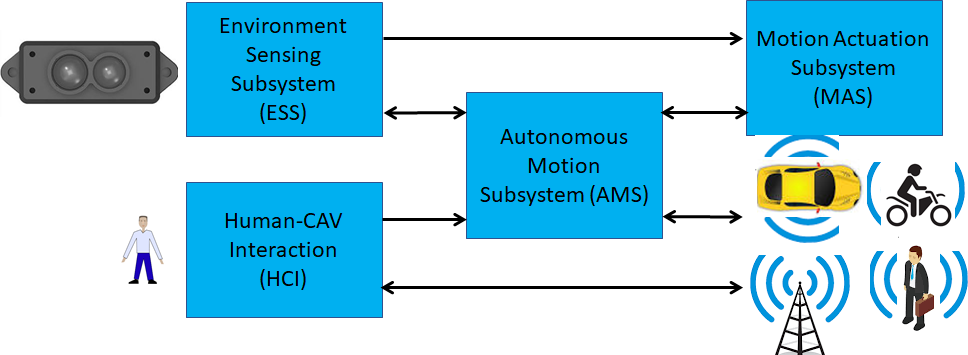
Figure 2 depicts the four Subsystems composing the MPAI-CAV Architecture. The arrows refer to the exchange of information between Subsystems and other CAVs or CAV-aware systems.
- Human-CAV Interaction (HCI).
- Environment Sensing Subsystem (ESS),
- Autonomous Motion Subsystem (AMS).
- Motion Actuation Subsystem (MAS).
This Technical Specification assumes that each Subsystem in implemented as an AI Workflow (AIW) as described in Annex 4 – Chapter 1. An AI Workflow is a combination of AI Modules (AIM) that are executed in the AI Framework (AIF).
Chapters 6-0-8-9 specify the four Subsystems. Each Chapter provides the following:
- The Function of the Subsystem (AI Workflow).
- The input/output data of the Subsystem.
- The topology of the Components (AI Modules) of the Subsystem.
- For each AI Module of the Subsystem:
- The Function.
- The input/output Data.
It is important to highlight the fact that:
- The input/output data have known semantics because CAVs should be explainable.
- Components can be merged into one if the external interfaces are preserved. Merged Components may have reduced Explainability.
- This specification specifies how certain CAV functions can be achieved. It does not mandate the support of any of these functions.
An additional Chapter includes the elements of the so-called Communication Device that enables a CAV to communicate with other CAVs.
This Technical Report has been developed by the Connected Autonomous Vehicle group of the Requirements Standing Committee. MPAI intends to publish a Technical Specification where the Functional Requirements of the I/O Data to/from the AIWs (Subsystems) and AIM and Data Formats are specified. Further Technical Specifications may follow.
<–Introduction Go to ToC General aspects of MPAI-CAV Architecture–>
© Copyright MPAI 2022-23. All rights reserved

