| 1 Functions | 2 Reference Model | 3 I/O Data |
| 4 Functions of AI Modules | 5 I/O Data of AI Modules | 6 AIW, AIMs, and JSON |
| 7 Reference Software | 8 Conformance Testing | 9 Performance Assessment |
1 Functions of Motion Actuation Subsystem
The Motion Actuation Subsystem (MAS):
- Transmits spatial and weather information gathered from its sensors and mechanical subsystems to the Environment Sensing Subsystem (ESS).
- Receives AMS-MAS Messages from the Autonomous Motion Subsystem (AMS).
- Translates AMS-MAS Message into specific Commands to its own Brake, Motor, and Wheel mechanical subsystems.
- Receives Responses from its Brake, Motor, and Wheel mechanical subsystems.
- Packages Responses into and sends AMS-MAS Messages to Autonomous Motion Subsystem.
2 Reference Architecture of Motion Actuation Subsystem
Figure 1 represents the Reference Model of the Motion Actuation Subsystem (CAV-MAS) V1.1.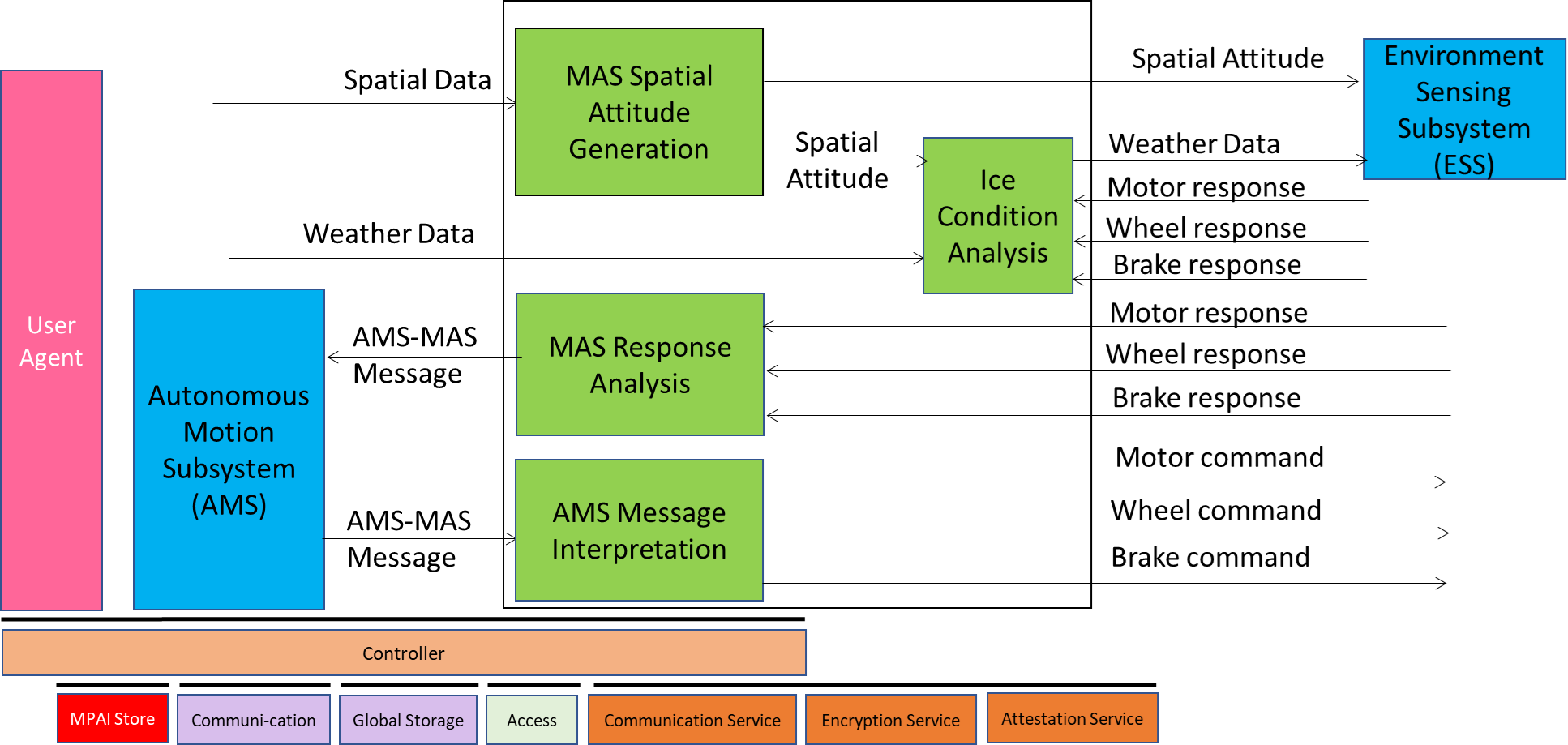 Figure 1 – Motion Actuation Subsystem Reference Model
Figure 1 – Motion Actuation Subsystem Reference Model
The operation of the Motion Actuation Subsystem unfolds as follows:
- AMS Command Interpretation
- Interprets the AMS-MAS Messages received from AMS and issues commands to the Brake, Motor, and Wheel mechanical subsystems.
- MAS Response Analysis
- Interprets the responses received from the Brake, Motor, and Wheel mechanical subsystems and sends AMS-MAS Messages to to AMS.
- MAS Spatial Attitude Generation
- Computes the initial Ego CAV’s Spatial Attitude Attitude using Spatial Data (Odometer, Speedometer, Accelerometer, and Inclinometer) Data
- Sends the initial Spatial Attitude Attitude to the ESS.
- Ice Condition Analysis
- Augments Weather Data analysing the responses of the Brake, Motor, and Wheel mechanical subsystems.
- Sends augmented Weather Data to ESS.
3 I/O Data of Motion Actuation Subsystem
Table 1 gives the input/output data of Motion Actuation Subsystem.
Table 1 – I/O data of Motion Actuation Subsystem
| Input | Comments |
| Spatial Data | Collection of distance, velocity, acceleration, and inclination data. |
| Weather Data | Data such as humidity, pressure, temperature. |
| AMS-MAS Message | Message including motion information. |
| Motor Response | Information on effects of applied motor force. |
| Wheel Response | Information on effects of applied Wheel rotation force. |
| Brake Response | Information on effects of applied brake force. |
| Output | Comments |
| Spatial Attitude | Position, Orientation and their velocity and acceleration vectors. |
| Weather Data | Data such as humidity, pressure, temperature, ice condition. |
| Motor Command | Applied motor torque. |
| Wheel Command | Applied wheel torque. |
| Brake Command | Applied brake deceleration. |
| AMS-MAS Message | Message including results of MAS Response analysis. |
4 Functions of Motion Actuation Subsystem’s AI Modules
Table 2 gives the AI Modules of Autonomous Motion Subsystem.
Table 2 – Functions of Motion Actuation Subsystem’s AI Modules
| AIM | Function |
| MAS Spatial Attitude Generation | Computes Ego CAV’s Spatial Attitude using Spatial Data. |
| AMS Command Interpretation | Receives, analyses, and actuates AMS-MAS Message into specific commands to Brakes, Wheels, and Motors. |
| MAS Response Analysis | Receives and analyses responses from Brakes, Wheel, and Motors and sends the MAS-AMS Response to AMS. |
| Ice Condition Analysis | Adds ice condition information to input Weather Data. |
5 I/O Data of Motion Actuation Subsystem’s AI Modules
Table 3 gives, for each AIM (1st column), the input data (2nd column) from which AIM (column) and the output data (3rd column).
Table 3 – I/O Data of Motion Actuation Subsystem’s AI Modules
6 AIW, AIMs, and JSON
| AIW | AIMs | AIM Names | JSON |
| CAV-MAS | Motion Actuation Subsystem | X | |
| CAV-MSG | MAS Spatial Attitude Generation | X | |
| CAV-AMI | AMS-MAS Message Interpretation | X | |
| CAV-MRA | MAS Response Analysis | X | |
| CAV-ICA | Ice Condition Analysis | X |
7 Reference Software
8 Conformance Testing

