| 1 Functions | 2 Reference Model | 3 I/O Data |
| 4 Functions of AI Modules | 5 I/O Data of AI Modules | 6 AIW, AIMs, and JSON |
| 7 Reference Software | 8 Conformance Testing | 9 Performance Assessment |
1 Functions of Motion Actuation Subsystem
The Motion Actuation Subsystem (MAS) transmits spatial and weather information gathered from its sensors and mechanical subsystems to the Environment Sensing Subsystem (ESS), receives messages from the Autonomous Motion Subsystem (AMS), translates messages into specific Commands to its own Brake, Motor, and Wheel mechanical subsystems, receives and packages, and sends responses from its Brake, Motor, and Wheel mechanical subsystems to AMS.
2 Reference Architecture of Motion Actuation Subsystem
Figure 1 represents the Reference Model of the Motion Actuation Subsystem (CAV-MAS).
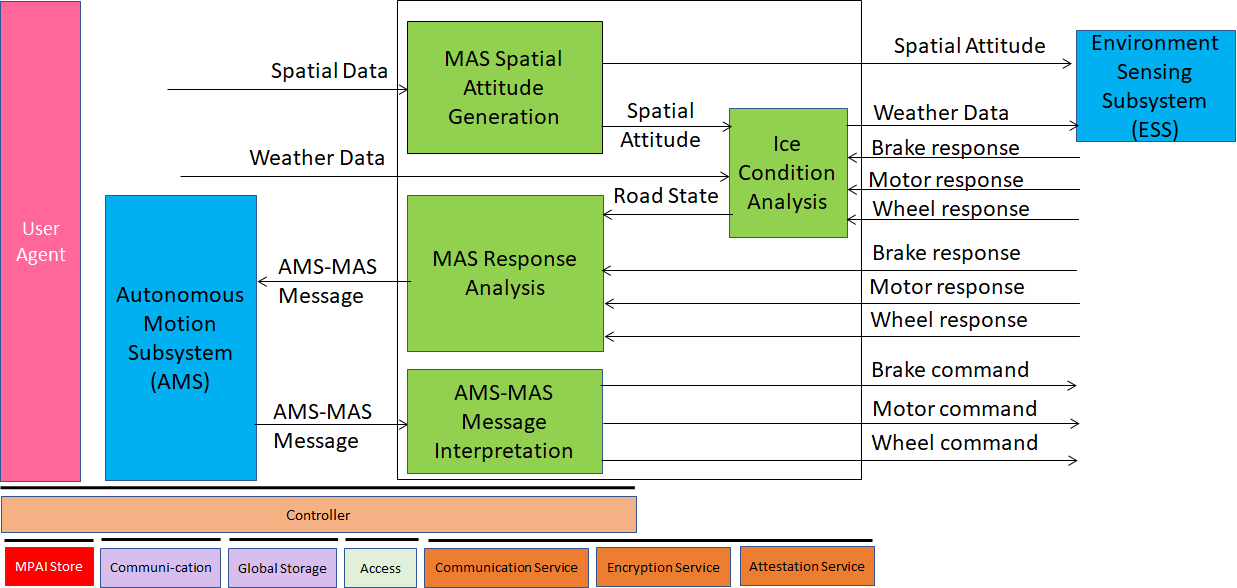 Figure 1 – Motion Actuation Subsystem Reference Model
Figure 1 – Motion Actuation Subsystem Reference Model
The operation of the Motion Actuation Subsystem unfolds as follows:
- AMS Command Interpretation
- Interprets the AMS-MAS Messages received from AMS and issues commands to the Brake, Motor, and Wheel mechanical subsystems.
- MAS Response Analysis
- Interprets the responses received from the Brake, Motor, and Wheel mechanical subsystems and sends AMS-MAS Messages to AMS.
- MAS Spatial Attitude Generation
- Computes the initial Ego CAV’s Spatial Attitude Attitude using Spatial Data (Odometer, Speedometer, Accelerometer, and Inclinometer) Data
- Sends the initial Spatial Attitude to the ESS.
- Ice Condition Analysis
- Augments Weather Data analysing the responses of the Brake, Motor, and Wheel mechanical subsystems.
- Sends augmented Weather Data to ESS.
3 I/O Data of Motion Actuation Subsystem
Table 1 gives the input/output data of Motion Actuation Subsystem.
Table 1 – I/O data of Motion Actuation Subsystem
| Input | Comments |
| Spatial Data | Collection of distance, velocity, acceleration, and inclination data. |
| Weather Data | Data such as humidity, pressure, temperature. |
| AMS-MAS Message | Message including motion information. |
| Motor Response | Information on effects of applied motor force. |
| Wheel Response | Information on effects of applied Wheel rotation force. |
| Brake Response | Information on effects of applied brake force. |
| Output | Comments |
| Spatial Attitude | Position, Orientation and their velocity and acceleration vectors. |
| Weather Data | Data such as humidity, pressure, temperature, ice condition. |
| Motor Command | Applied motor torque. |
| Wheel Command | Applied wheel torque. |
| Brake Command | Applied brake deceleration. |
| AMS-MAS Message | Message including results of MAS Response analysis. |
4 Functions of Motion Actuation Subsystem’s AI Modules
Table 2 gives the AI Modules of Autonomous Motion Subsystem.
Table 2 – Functions of Motion Actuation Subsystem’s AI Modules
| AIM | Function |
| MAS Spatial Attitude Generation | Computes Ego CAV’s Spatial Attitude using Spatial Data. |
| AMS Message Interpretation | Receives, analyses, and actuates AMS-MAS Message into specific commands to Brakes, Wheels, and Motors. |
| MAS Response Analysis | Receives and analyses responses from Brakes, Wheel, and Motors and sends the MAS-AMS Response to AMS. |
| Ice Condition Analysis | Adds ice condition information to input Weather Data. |
5 I/O Data of Motion Actuation Subsystem’s AI Modules
Table 3 gives, for each AIM (1st column), the input data (2nd column) from which AIM (column) and the output data (3rd column).
Table 3 – I/O Data of Motion Actuation Subsystem’s AI Modules
6 AIW, AIMs, and JSON
| AIW | AIMs | AIM Names | JSON |
| CAV-MAS | Motion Actuation Subsystem | X | |
| CAV-MSG | MAS Spatial Attitude Generation | X | |
| CAV-AMI | AMS-MAS Message Interpretation | X | |
| CAV-MRA | MAS Response Analysis | X | |
| CAV-ICA | Ice Condition Analysis | X |
7 Reference Software
8 Conformance Testing

