<- References Go to ToC AI Modules ->
1 Functions
The CUI-CPP AIM receives Primary Risks (i.e., for which an AIM is available and conforms with the relevant regulations) and Secondary (i.e., for which an AIM is not available or does not conform with the relevant regulations) statements, Financial and Governance Descriptors and Prediction Horizon and provides information about the future performance of a company in terms of default and business discontinuity of the company and governance impact:
| Receives | Prediction Horizon | Number of months for which prediction is sought. |
| Primary Risk Descriptors | Descriptors provided by by the Company being assessed about the Risks for which compliant Machine Learning Modules are available and conforms with the relevant regulations. | |
| Governance Descriptors | A set of indices/parameters that are used to assess the adequacy of the organisational model. | |
| Financial Descriptors | Data produced based on a set of accounting principles driving maintenance and reporting of company accounts so that financial statements can be consistent, transparent, and comparable across companies. | |
| Secondary Risk Statements | Risk whose impact is estimated based on Prediction Result Perturbation processing because a trained AI model is not available or does not conform with the relevant regulations. | |
| Produces | Organisation Descriptors | The set of
|
| Primary Default Descriptors | The set of
|
|
| Primary Discontinuity Descriptors | The set of:
|
|
| Secondary Risk Probability | The probability of an interruption of the operations of a company for a period of time less than 2% of the Prediction Horizon. |
2 Reference Architecture
CUI-CPP V2.0 assumes that workflow is based on Technical Specification: AI Framework (MPAI-AIF) V2.2 specifying the standard AI Framework (AIF) that enables initialisation, execution, dynamic configuration, and control of AI Workflows (AIW) composed of interconnected AI Modules (AIM).
The CUI-CPP V2.0 AI-Workflow supersedes those specified by previous MPAI-CUI specifications. These can still be used if their version is explicitly indicated.
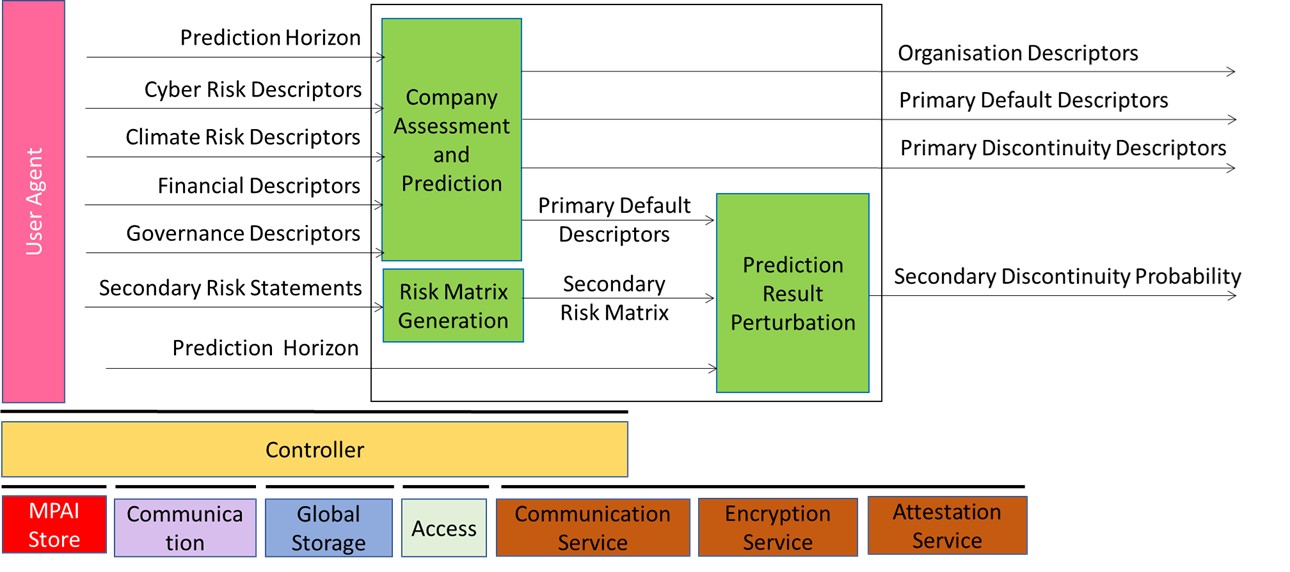
Figure 1 – Company Performance Prediction V2.0 Reference Model
The workflows operates as follows. First a Prediction Horizon must be se. The Descriptors of all Vertical Risks – currently, climate and cyber – that can be processed with an AIM that is compliant with relevant regulations are input to the Company Assessment and Prediction AIM together with Financial and Governance Descriptors. All the above-mentioned Descriptors are processed and Organisation Descriptors, Primary Default Descriptors and Primary Discontinuity Descriptors are provided.
Vertical Risks for which an AIM that is compliant with relevant regulations (called Secondary) are input as Secondary Risk Statements to the Risk Matrix Generation which is input to Prediction Result Perturbation together which Primary Default Descriptors. processed. The out of Prediction Result Perturbation is Secondary Discontinuity Probability.
3 I/O Data
Table 2 gives the input/output data of the CUI-CPP V2.0 AIW.
Table 1 – I/O data of CUI-CPP V2.0 AIW
| Input data | From | Description |
| Prediction Horizon | CUI-CPP user | Prediction time in months. |
| Primary Risk Descriptors | Company/ External source | Statements by the Company being assessed about the Risks for which compliant Machine Learning Modules are available in the CUI-CAP. |
| Governance Descriptors | Company | Statements by the Company being assessed about Company governance. |
| Financial Descriptors | Company | Statements by the Company being assessed about Company financial data. |
| Secondary Risk Statements | Company | Statements by the Company being assessed about the Company-perceived first level Risks of the Risk Taxonomy. |
| Output data | To | Description |
| Organisation Descriptors | User or App | A number and a vector of the most relevant elements of the Governance Descriptors affecting the assessment. |
| Primary Default Descriptors | User or App | The Primary Default Probability and a vector of the most relevant elements affecting the Primary Default Probability. |
| Primary Discontinuity Descriptors | User or App | The Primary Discontinuity Probability and a vector of the most relevant elements affecting the Primary Discontinuity Probability. |
| Secondary Discontinuity Probability | User or App | A number representing the probability the company is affected by a business discontinuity. |
4 Functions of AI Modules
Table 2 gives the functions of all CUI-CPP V2.0 AIMs. Each link provides the AIM function, reference model, Input/Output Data, and JSON metadata.
Table 2 – Functions of CUI-CPP V2.0 AIMs
| AIMs | Function |
| Risk Matrix Generation | Processes Secondary Risk Statements. Produces the Secondary Risk Matrix. |
| Company Assessment and Prediction | Processes Prediction Horizon, Primary Risk Statements, Governance Descriptors, and Financial Descriptors. Produces Organisation Descriptors, Primary Default Descriptors, and Primary Discontinuity Descriptors. |
| Prediction Result Perturbation | Processes Governance Descriptors, Financial Descriptors, Primary Default Descriptors, Secondary Risk Matrix, and Prediction Horizon. Produces Secondary Business Discontinuity Probability by perturbing the Governance Descriptors and Financial Descriptors. |
5 I/O Data of AI Modules
Table 3 provides the link to the specified AIMs.
Table 3 – I/O Data of CUI-CPP V2.0 AIMs
| Acronym | Input | Output |
| CUI-CAP | Primary Risk Descriptors | Primary Default Descriptors |
| Governance Descriptors | Organisation Descriptors | |
| Financial Descriptors | Primary Discontinuity Descriptors | |
| Prediction Horizon | ||
| CUI-RMG | Secondary Risk Statements | Secondary Risk Matrix |
| CUI-PRP | Primary Default Descriptors | Secondary Discontinuity Probability |
| Secondary Risk Matrix |
6 AIWs and JSON Metadata
Table 4 provides the links to the AIW and AIW specifications and to the JSON Metadata.
Table 4 – AIWs and JSON Metadata
| AIW | AIMs | Name | JSON |
| CUI-CPP | Company Performance Prediction | X | |
| CUI-CAP | Company Assessment and Prediction | X | |
| CUI-PRP | Prediction Result Perturbation | X | |
| CUI-RMG | Risk Matrix Generation | X |
7 Reference Software
As a rule, MPAI provides Reference Software implementing the AIWs released with the following disclaimers:
- The CUI-CPP V2.0 Reference Software Implementation, if in source code, is released with the BSD-3-Clause licence.
- The purpose of this Reference Software is to provide a working Implementation of CUI-CPP V2.0, not to provide a ready-to-use product.
- MPAI disclaims the suitability of the Software for any other purposes and does not guarantee that it is secure.
- Use of this Reference Software may require acceptance of licences from the respective copyright holders. Users shall verify that they have the right to use any third-party software required by this Reference Software.
Note that at this stage the CUI-CPP V2.0 does not include Reference Software.
8 Conformance Testing
An implementation of an AIW conforms with CUI-CPP V2.0 if it accepts as input _and_ produces as output Data and/or Data Objects (the combination of Data of a Data Type and its Qualifier) conforming with those specified by CUI-CPP V2.0.
The Conformance is expressed by one of the two statements
- “Data conforms with the relevant (Non-MPAI) standard” – for Data.
- “Data validates against the Data Type Schema” – for Data Object.
The latter statement implies that:
- Any Sub-Type of the Data conforms with the relevant Sub-Type specification of the applicable Qualifier.
- Any Content and Transport Format of the Data conform with the relevant Format specification of the applicable Qualifier.
- Any Attribute of the Data
- Conforms with the relevant (Non-MPAI) standard – for Data, or
- Validates against the Data Type Schema – for Data Object.
The method to Test the Conformance of an instance of Data or Data Object is specified in the Data Types chapter.
9 Performance Assessment
Performance is an umbrella term used to describe a variety of attributes – some specific of the application domain the Implementation intends to address. Therefore, Performance Assessment Specifications provide methods and procedures to measure how well an AIW or an AIM performs its function. Performance of an Implementation includes methods and procedures for all or a subset of the following characteristics:
- Quality – for instance, how well a Face Identity Recognition AIM recognises faces, how precise or error-free are the changes in a Visual Scene detected by a Visual Change Detection AIM, or how satisfactory are the responses provided by an Answer to Multimodal Question AIW.
- Robustness – for instance, how robust is the operation of an Implementation with respect to duration of operation, load scaling, etc.
- Extensibility – for instance, the degree of confidence a user can have in an Implementation when it deals with data outside of its stated application scope.
- Bias: – for instance, how dependent on specific features of the training data is the inference, as in Company Performance Prediction when the accuracy of the prediction may widely change based on the size or the geographic position of a Company; or face recognition in Television Media Analysis.
- Legality – for instance, in which jurisdictions the use of an AIM or an AIW complies with a regulation, e.g., the European AI Act.
- Ethics: may indicate the conformity of an AIM or AIW to a target ethical standard.
<- References Go to ToC AI Modules ->

