| 1 Functions | 2 Reference Model | 3 I/O Data |
| 4 Functions of AI Modules | 5 I/O Data of AI Modules | 6 AIW, AIMs, and JSON |
| 7 Reference Software | 8 Data Types | 9 Performance Assessment |
1 Functions
The Autonomous Motion Subsystem (AMS) provides on request by HCI routes to a destination, produces the Full Environment Descriptors that include subsets of Full Environment Descriptors from selected CAVs in range, issues message to and processes messages received from MAS, and stores data receives/produced in AMS Memory for future use.
2 Reference Model
Figure 1 gives the Autonomous Motion Subsystem Reference Model.
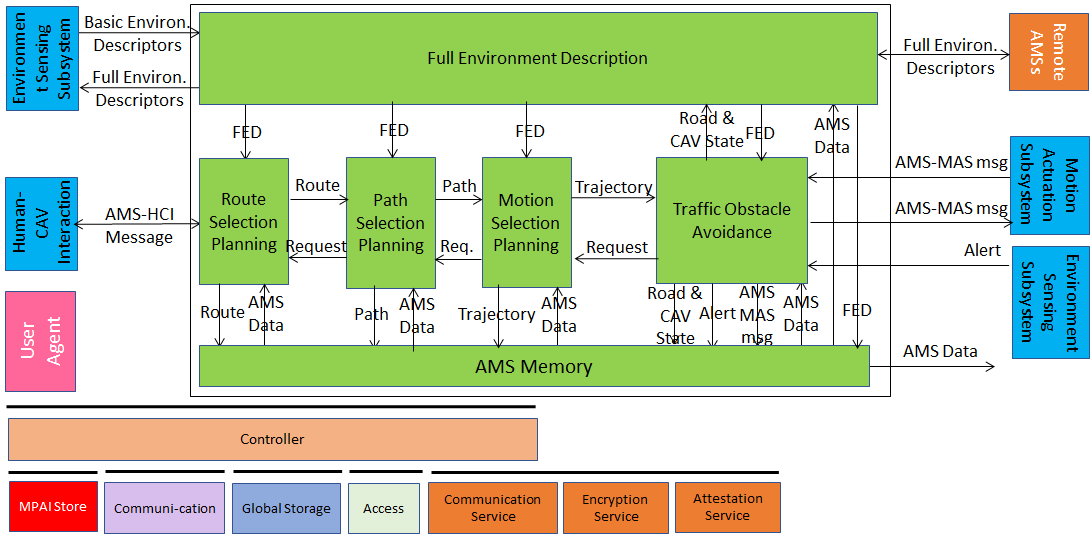
Figure 1 – Autonomous Motion Subsystem Reference Model
The operation of the Autonomous Motion Subsystem unfolds as follows:
- A human requests the Human-CAV Interaction to take them to a destination.
- HCI interprets request and passes the interpretation to the AMS.
- The AMS activates Route Planning to generate a set of Waypoints starting from the current Pose (obtained from the ESS) up to destination.
- The AMS
- Receives Basic Scene Descriptors from the ESS.
- Requests (subsets of) Remote AMSs’ Full Scene Descriptors and responds to similar requests from Remote AMSs.
- Integrates all sources of Environment Descriptors into Full Environment Descriptors
- The Route’s Waypoints cause the Path Selection Planning to generate a set of Positions to reach the next Waypoint.
- Motion Selection Planning generates a Trajectory to reach the next Position in each Path.
- Traffic Obstacle Avoidance receives the Trajectory and checks if an Alert was received.
- If an Alert was received, Traffic Obstacle Avoidance detects whether the Trajectory creates a collision.
- If a collision is detected, Traffic Obstacle Avoidance requests a new Trajectory from Motion Planner.
- If no collision is detected, Traffic Obstacle Avoidance issues an AMS-MAS Message to MAS.
- The MAS sends an AMS-MAS Message to AMS informing about the execution of the Command.
- The AMS, based on the received MAS-AMS Messages, may
- Discontinue the execution of the earlier AMS-MAS Message.
- Issue a new AMS-MAS Message.
- Inform Obstacle Avoidance and Full Environment Description.
- The decision of each element of the chain may be recorded in the AMS Memory (“black box”).
The Trajectory Planning and Decision (CAV-TPD) is a Composite AIM that includes the Path Selection Planning, Motion Selection Planning, and the Traffic Obstacle Avoidance AIMs
3 I/O Data
Table 1 gives the input/output data of Autonomous Motion Subsystem.
Table 1 – I/O data of Autonomous Motion Subsystem
| Input data | From | Comment |
| Basic Environment Descriptors | Environment Sensing Subsystem | CAV’s Environment representation from ESS. |
| Alert | Environment Sensing Subsystem | Critical information from an EST in ESS. |
| AMS-HCI Message | Human-CAV Interaction | Human commands, e.g., “take me home”. |
| Full Environment Descriptors | Remote AMSs | Other CAVs and vehicles, and roadside units. |
| AMS-MAS Message | Motion Actuation Subsystem | Message sent by the AMS to the MAS. |
| Ego-Remote AMS Message | Remote AMS | Remote AMS to Ego AMS message. |
| Output data | To | Comment |
| AMS-HCI Message | Human-CAV Interaction | AMS’s message to HCI-AMS. |
| AMS-MAS Message | Motion Actuation Subsystem | Message to MAS, e.g., “in 5s assume a given Spatial Attitude”. |
| Full Environment Descriptors | Remote AMSs | To Ego CAV’s ESS and to REmote CAVs. |
| Ego-Remote AMS Message | Remote AMSs | Ego AMS to Remote AMS message. |
| AMS Data | External Device | For offline analysis. |
4 Functions of AI Modules
Table 2 gives the AI Modules of the Autonomous Motion Subsystem.
Table 2 – Functions of Autonomous Motion Subsystem’s AI Modules
| AIM | Function |
| Full Environment Description | Creates an internal environment representation by fusing information received from ESS, Remote AMSs, and other CAV-aware entities. Updates the CAV State. |
| Route Selection Planning | Computes a set of possible Routes, through the road network, from the current to the target destination. |
| Path Selection Planning | Generates a set of Paths, considering: 1. Route. 2. Full Environment Descriptors (Spatial Attitude, Road State, etc.). 4. Traffic Rules. |
| Motion Selection Planning | Defines a Trajectory to reach a Goal using the Spatial Attitude considering: 1. CAV’s kinematic and dynamic constraints. 2. Full Environment Descriptors 3. Passengers’ comfort. |
| Traffic Obstacle Avoidance | Checks whether Trajectory is compatible with Alert information: if it is not, it requests a new Trajectory; if it is, it instructs the MAS to execute the Trajectory considering the Environment conditions and receives MAS-AMS Messages about the execution. Based on a Message, updated Road State and CAV State may be communicated to Obstacle Avoidance. |
| AMS Memory | Records decisions by Route Planning, Path Planning, Motion Planning, Obstacle Avoidance, Full Environment Description, and Command Issuance. |
5 I/O Data of AI Modules
Table 3 gives, for each AIM (1st column), the input data (2nd column) and the output data (3rd column) of Autonomous Motion Subsystem.
Table 3 – Autonomous Motion Subsystem’s data
| AIM | Input | Output |
| Full Environment Description | – Basic Environment Descriptors – Full Environment Descriptors – AMS Data – Road State – CAV State |
– Full Environment Descriptors |
| Route Selection Planning | – Full Environment Descriptors – AMS Data – AMS-HCI Message – Selected Route – Route ID – Request |
– AMS-HCI Message – Route |
| Path Selection Planning | – Full Environment Descriptors – AMS Data – Route |
– Paths |
| Motion Selection Planning | – Full Environment Descriptors – AMS Data – Paths – Request |
– Trajectory – Request |
| Traffic Obstacle Avoidance | – Full Environment Descriptors – Trajectory – AMS Data – Alert – AMS-MAS Message – Request |
– Full Environment Descriptors – AMS-MAS Message – Road State – CAV State – Alert |
| AMS Memory | – Full Environment Descriptors – Route – Path – Trajectory – Alert – Road State – CAV State – AMS-MAS Message |
– AMS Data |
6 AIW, AIMs, and JSON Metadata
| AIW | AIMs | Name | JSON |
| CAV-AMS | Autonomous Motion Subsystem | X | |
| CAV-FEV | Full Environment Description | X | |
| CAV-RSP | Route Selection Planning | X | |
| CAV-PSP | Path Selection Planning | X | |
| CAV-MSP | Motion Selection Planning | X | |
| CAV-TOA | Traffic Obstacle Avoidance | X | |
| CAV-AMM | AMS Memory | X |

