<- References Go to ToC Human-CAV Interaction->
1 Functions of Connected Autonomous Vehicle
2 Reference Architecture of Connected Autonomous Vehicle
3 I/O Data of Connected Autonomous Vehicle
1 Functions of Connected Autonomous Vehicle
A Connected Autonomous Vehicle is defined as a physical system that:
- Converses with humans by understanding their utterances, e.g., a request to be taken to a destination.
- Senses the environment where it is located or traverses like the one depicted in Figure 1.
- Plans a Route enabling the CAV to reach the requested destination.
- Autonomously reaches the destination by:
- Moving in the physical environment.
- Building Digital Representations of the Environment.
- Exchanging elements of such Representations with other CAVs and CAV-aware entities.
- Making decisions about how to execute the Route.
- Actuating the CAV motion to implement the decisions.
Figure 1 – An environment of CAV operation
2 Reference Architecture of Connected Autonomous Vehicle
The MPAI-CAV Reference Model is composed of four Subsystems:
- Human-CAV Interaction (HCI).
- Environment Sensing Subsystem (ESS),
- Autonomous Motion Subsystem (AMS).
- Motion Actuation Subsystem (MAS).
The Subsystems are represented in Figure 2 where the arrows refer to the exchange of information between Subsystems and between a Subsystem and other CAVs or CAV-aware systems. The sensing of the Environment and the Motion Actuation are represented by icons.
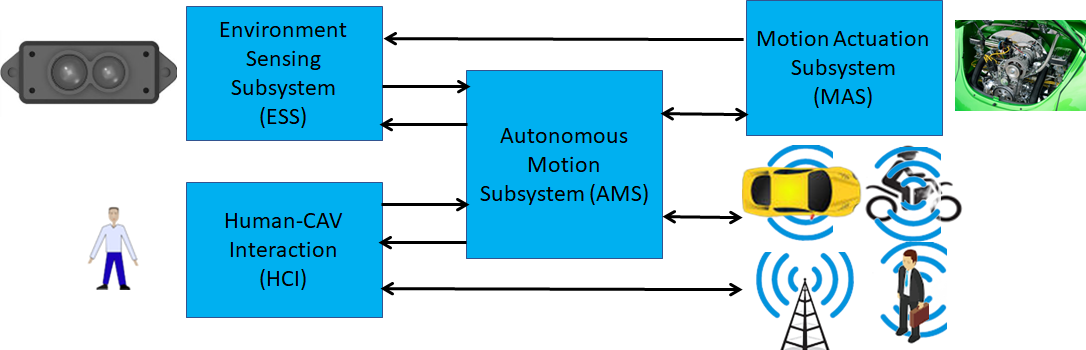
Figure 2 – The MPAI-CAV subsystems
The operation of a CAV unfolds according to the following workflow:
| Human | Requests the CAV, via HCI, to take the human to a destination. |
| HCI | 1. Authenticates humans. |
| 2. Interprets the request of humans. | |
| 3. Issues commands to the AMS. | |
| AMS | 1. Requests ESS to provide the current Pose. |
| ESS | 1. Computes and sends the Basic Environment Representation (BER) to AMS. |
| AMS | 1. Computes and sends Route(s) to HCI. |
| HCI | 1. Sends travel options to Human. |
| Human | 1. May integrate/correct their instructions. 2. Issues commands to HCI. |
| HCI | 1. Communicates Route selection to AMS. |
| AMS | 1. Sends the BER to the AMSs of other CAVs. 2. Computes the Full Environment Representation (FER). 3. Decides best motion to reach the destination. 4. Issues appropriate commands to MAS. |
| MAS | 1. Executes the Command. 2. Sends response to AMS. |
| Human | 1. Interacts and holds conversation with other humans on board and the HCI. 2. Issues commands to HCI. 3. Requests HCI to render the FER. 4. Navigates the FER. 5. Interacts with humans in other CAVs. |
| HCI | Communicates with HCIs of other CAVs on matters related to human passengers. |
1.3 I/O Data of Connected Autonomous Vehicle
Table 2 gives the input/output data of the Connected Autonomous Vehicle.
Table 2 – I/O data of Human-CAV Interaction
| Input data | From | Comment |
| Audio (Outdoor) | Environment | For User authentication, command, conversation, etc. |
| Audio (Indoor) | Cabin Passengers | User’s social life and commands/interaction with HCI |
| Visual (Outdoor) | Environment | Commands/interaction with HCI |
| Visual (Indoor) | Cabin Passengers | User’s social life and commands/interaction with HCI |
| LiDAR | Cabin Passengers | Commands/interaction with HCI |
| Inter HCI Information | Remote HCI | From Ego CAV and Remote CAV |
| RADAR | Environment | Captured Environment by RADAR |
| LiDAR Data | Environment | Captured Environment by LiDAR |
| Visual Data (2/D and 3D) | Environment | Captured Environment by cameras |
| Ultrasound Data | Environment | Captured Environment by Ultrasound |
| Audio Data | Audio (16 Hz-20 kHz) | Captured Environment by Microphone Array |
| Inter AMS Information | Remote AMS | From Ego CAV and Remote CAV |
| Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Data | ~1 & 1.5 GHz Radio | Various GNSS Data sources |
| Other Environment Data | Environment | Temperature, Air pressure, Humidity, etc. |
| Wheel Motor Response | Wheel Motor | Forces wheels rotation, gives feedback. |
| Steering Wheel Response | Steering Wheel | Moves wheels by an angle, gives feedback. |
| Brake Response | Brakes | Acts on brakes, gives feedback. |
| Output data | To | Comment |
| Inter HCI Information | Remote HCI | Ego CAV and Remote CAV |
| Machine Personal Avatar | Cabin Passengers | HCI’s avatar when conversing |
| Inter AMS Information | Remote AMS | To Ego CAV and Remote CAV |
| Wheel Motor Command | Wheel Motors | Activates/suspends wheels rotation, gives feedback. |
| Steering Wheel Command | Steering Wheel | Moves wheels by an angle, gives feedback. |
| Brake Command | Brakes | Acts on brakes, gives feedback. |

