1 Functions of Videoconference Client Transmitter
2 Reference Model of Videoconference Client Transmitter
3 Input and Output Data of Videoconference Client Transmitter
4 Functions of Videoconference Client Transmitter’s AI Modules
5 I/O Data of Videoconference Client Transmitter’s AI Modules
6 AIW, AIMs and JSON Metadata of Videoconference Client Transmitter
1 Functions of Client Transmitter
The function of a Client Transmitter is to:
- Receive from a Participant:
- Input Audio from the microphone.
- Input Visual from the camera.
- Participant’s Avatar Model.
- Participant’s language preferences (e.g., EN-US, IT-CH).
- Send to the Server:
- Speech Object (for Authentication).
- Face Object (for Authentication).
- Input Portable Avatars containing:
- Language preferences (at the start).
- Avatar Model (at the start).
- Speech.
- Avatar Descriptors.
2 Reference Model of Client Transmitter
Figure 1 gives the Reference Model of Client Transmitter AIW. Red text refers to data sent at meeting start.
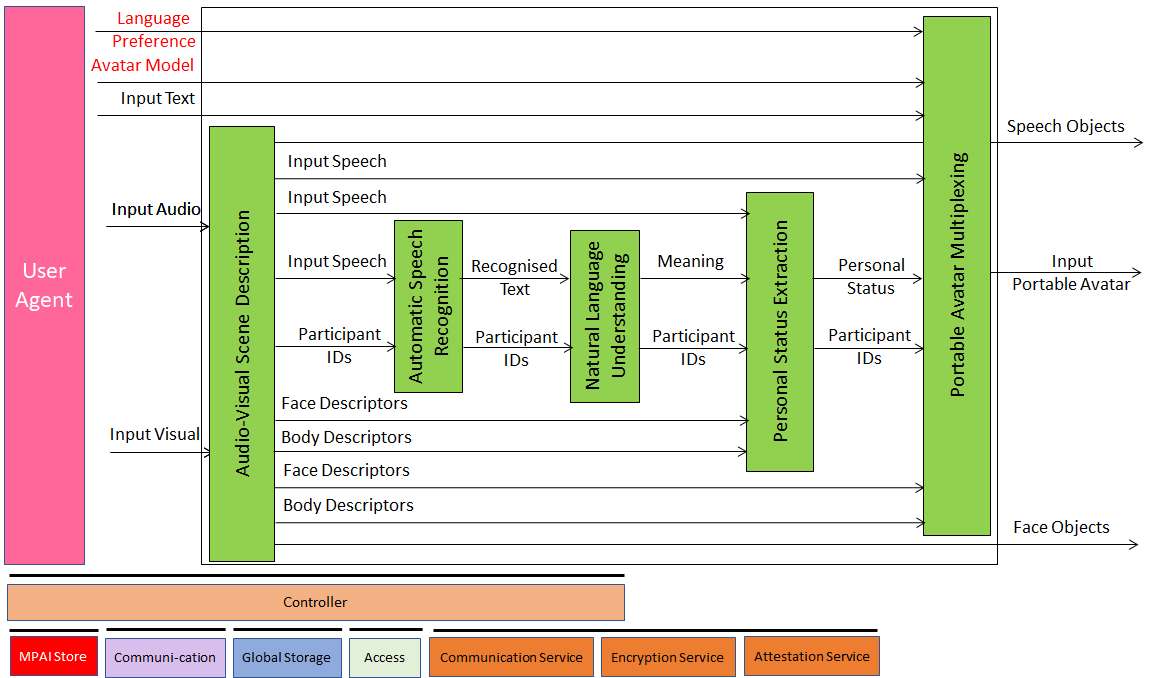
Figure 1 – Reference Model of Avatar
At the start, each participant sends to the Avatar Videoconference Server:
- Language preferences
- Avatar Model.
- Speech Object (for Authentication).
- Face Object (for Authentication).
During the videoconference the following AIMs of the Client Transmitter produce:
| AIM | Data produced |
| Audio-Visual Scene Description | Speech Objects, Face Descriptors, Body Descriptors, and Audio-Visual Scene Geometry |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Recognised Text |
| Input Face Description | Face Descriptors |
| Input Body Description | Body Descriptors |
| Natural Language Understanding | Meaning |
| Personal Status Extraction | Personal Status |
| Portable Avatar Description | Avatar Descriptors |
Videoconference Client Transmitters send Portable Avatars to Avatar Videoconference Server that the Server processes and re-distributes to Client Receivers.
3 Input and Output Data of Client Transmitter
Table 1 gives the input and output data of the Client Transmitter AIW:
Table 1 – Input and output data of Client Transmitter AIW
| Input | Description |
| Input Text | Chat text used by a human to communicate with Virtual Meeting Secretary or other participants |
| Language Preference | The language participant wishes to speak and hear. |
| Input Audio | Audio of Speech of participants in a meeting room. |
| Input Visual | Video of participants in a meeting room. |
| Avatar Model | The avatar model selected by the participant. |
| Output | Description |
| Speech Object | An utterance of a Participant used by Server for authentication. |
| Input Portable Avatar | Portable Avatar produced by Client Transmitter. |
| Face Object | Participant’s face used by Server for authentication. |
4 Functions of Client Transmitter’s AI Modules
Table 2 gives the functions of AI Modules of the Client Transmitter AIW.
Table 2 – AI Modules of Client Transmitter AIW
| AIM | Function |
| Audio-Visual Scene Description | 1. Receives Input Audio and Input Visual. 2. Provides Input Speech, Speech Object, Participant ID, Face Descriptors, Body Descriptors, Face Object. |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | 1. Receives Input Speech and Participant ID. 2. Provides Recognised Text and Participant ID. |
| Natural Language Understanding | 1. Receives Recognised Text, Participant ID. 2. Provides the Meaning of the Recognised Text. |
| Personal Status Extraction | 1. Receives Meaning, Speech, Face Descriptors, Body Descriptors, Participant ID. 2. Provides the Participant’s Personal Status, Participant ID. |
| Portable Avatar Multiplexing | 1. Receives Language Preference, Avatar Model, Input Text, Input Speech, Personal Status, Participant ID, Face Descriptors, Body Descriptors. 2. Provides the Portable Avatars of Participant with Participant ID. |
5 I/O Data of Client Transmitter’s AI Modules
Table 3 gives the AI Modules of Client Transmitter AIW.
Table 3 – AI Modules of Client Transmitter AIW
| AIM | Input | Output |
| Audio-Visual Scene Description | Input Audio Input Visual |
1. Input Speech 2. Speech Objects 3. Participant ID 4. Face Descriptors 5. Body Descriptors 6. Face Objects |
| Automatic Speech Recognition | Speech Objects | Recognised Text Participant ID |
| Natural Language Understanding | Recognised Text | Meaning Participant ID |
| Personal Status Extraction | Meaning Speech Face Object Body Object |
Personal Status Participant ID |
| Portable Avatar Multiplexing | Language Preference Avatar Model Input Text Input Speech Personal Status Participant ID |
Portable Avatars. |
6 AIW, AIM, and JSON Metadata of Videoconference Client Transmitter
Table 7 – AIMs and JSON Metadata
| AIW | AIMs | Name | JSON | |
| PAF-CTX | Videoconference Client Transmitter | X | ||
| OSD-AVS | Audio-Visual Scene Description | X | ||
| CAE-ASD | Audio Scene Description | X | ||
| CAE-AAT | Audio Analysis Transform | X | ||
| CAE-ASL | Audio Source Localisation | X | ||
| CAE-ASE | Audio Separation and Enhancement | X | ||
| CAE-AST | Audio Synthesis Transform | X | ||
| CAE-AMX | Audio Descriptor Multiplexing | X | ||
| OSD-VSD | Visual Scene Description | X | ||
| OSD-AVA | Audio-Visual Alignment | X | ||
| MMC-ASR | Automatic Speech Recognition | X | ||
| MMC-NLU | Natural Language Understanding | X | ||
| MMC-PSE | Personal Status Extraction | X | ||
| MMC-ITD | Input Text Description | X | ||
| MMC-ISD | Input Speech Description | X | ||
| PAF-IFD | Input Face Description | X | ||
| PAF-IBD | Input Body Description | X | ||
| MMC-PTI | PS-Text Interpretation | X | ||
| MMC-PSI | PS-Speech Interpretation | X | ||
| PAF-PFI | PS-Face Interpretation | X | ||
| PAF-PGI | PS-Gesture Interpretation | X | ||
| MMC-PMX | Personal Status Multiplexing | X | ||
| – | MMC-PMX | Personal Status Multiplexing | X | |

