<–Architecture and Operation Go to ToC AI Modules–>
| Function | Reference Model | Input/Output Data |
| Functions of AI Modules | Input/output Data of AI Modules | AIW, AIMs, and JSON Metadata |
1 Function
An Autonomous User (A-User), having the functionalities specified by Technical Specification: MPAI Metaverse Model (MPAI-MMM) – Technologies (MMM-TEC) implemented with the AI Workflow of Technical Specification: AI Framework (MPAI-AIF), according to this PGM-AUA standard:
- Receives commands from a human responsible for it.
- Captures Perceptible Objects (Text Objects, Audio Objects, 3D Model Objects, and Visual Objects) from an Audio-Visual Scene in an M-Instance that includes the User it interacts with that can be another Autonomous or a Human User (H-User), i.e., a User that is under direct control of a human, and other objects.
- Processes the captured information.
- May produce a Speaking Avatar rendered in the M-Instance and perform Actions or Process Action Requests that accomplishes the results of the said processed information.
- Receives Process Action Responses produced by the M-Instance in response to the Process Action Requests.
2 Reference Model
Figure 1 gives the Reference Model of the AI Workflow implementing the Autonomous User.
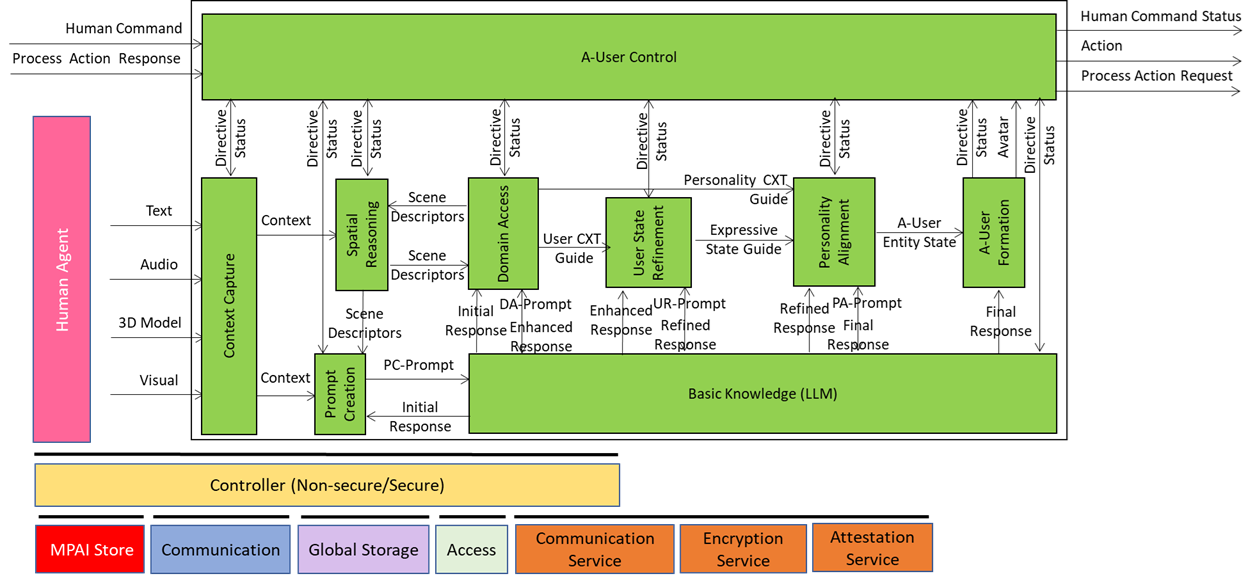
Figure 1 – Reference Model of Autonomous User Architecture (PGM-AUA)
2 Input/output data
Table 2 gives the Input/Output Data of the Autonomous User AIW.
Table 2 – Input/output data of the Autonomous User
| Input | Description |
| Human Command | A command from the responsible human overtaking or complementing the control of the A-User. |
| Process Action Response | Generated by the M-Instance Process sin response to the A-User’s Process Action Request |
| Text Object | User input as text. |
| Audio Object | The Audio component of the Scene where the User is embedded. |
| 3D Model Object | The 3DModel component of the Scene where the User is embedded. |
| Visual Object | The Visual component of the Scene where the User is embedded. |
| Output | Description |
| Human Command Status | |
| Action | Action performed by A-User. |
| Process Action Request | A-User’s Process Action Request. |
4 Functions of AI Modules
Table 3 gives the functions performed by PGM-AUA AIMs.
Table 3 – Functions of PGM-AUA AIMs
Note: The table does not analyse Directive/Status Data to and from A-User Control to PGM-AUA.
| Acronym | Name | Definition |
| PGM-AUC | A-User Control | The User Control AIM (PGM-USC) governs the operational lifecycle of the A-User though its AIMs and orchestrates its interaction with both the M-Instance and the human User. |
| PGM-CXT | Context Capture | Captures at least one of Text, Audio, 3D Model, and Visual, and produces Context, a representation of the User and the environment where the User is located. |
| PGM-ASR | Audio Spatial Reasoning | Transforms raw Audio Scene Descriptors and Audio cues into semantic outputs that Prompt Creation (PRC) uses to enhance User Text and to Domain Access (DAC) seeking additional information. |
| PGM-VSR | Visual Spatial Reasoning | Transforms raw Visual Scene Descriptors (objects, gesture vectors, and gaze cues) into semantic outputs that Prompt Creation (PRC) uses to enhance User Text and to Domain Access (DAC) seeking additional information. |
| PGM-PRC | Prompt Creation | Transforms into natural language prompts (PR-Prompts) to Basic Knowledge semantic inputs received from – Context Capture (CXC) – Audio and Visual Spatial Reasoning (SPR) and, – Domain Access (DAC) as responses provided to SPR (indirectly). |
| PGM-BKN | Basic Knowledge | A language model – not necessarily general-purpose – receiving the enriched texts from PC Prompt Creation (PCR), Domain Access (DAC), User State Refinement (USR), and Personality Alignment (PAL) and converts into responses used by the various AIMs to gradually produce the Final Response. |
| PGM-DAC | Domain Access | Performs the following main functions: – Interprets the Audio and Visual Spatial Outputs from Audio and Visual Space Reasoning and any User-related semantic inputs. – Selects and activates domain-specific behaviours to deal with specific inputs from SPR and BKN. – Produces semantically enhanced outputs to SPR and BKN. |
| PGM-USR | User State Refinement | Modulates the Enhanced Response from BKN into a User State and Context-aware UR-Prompt, which is then sent to BKN. |
| PGM-PAL | Personality Alignment | Modulates the Refined Response into an A-User Personality Profile-aware PA-Prompt, which is then sent to BKN. |
| PGM-AUR | A-User Formation | Receives the Final Response from BKN, A-User Personal Status from Personality Alignment (PAL), and Command from A-User Control and renders the A-User as a speaking Avatar. |
5 Input/output Data of AI Modules
Table 4 provides acronyms, names, and links to the specification of the AI modules composing the PGM-AUA AIW and their input/output data. The current specification is tentative but is expected to evolve from input from Responses to the Call for Technologies.
Table 4 – Input/output Data of AI Modules
6 AIW, AIMs, and JSON Metadata
Table 6 provides the links to the AIW and AIM specifications and to the JSON syntaxes.
Table 6 – AIW, AIMs, and JSON Metadata
| AIW | AIMs | Name | JSON |
| PGM-AUA | Autonomous User | X | |
| PGM-AUC | A-User Control | X | |
| PGM-CXT | Context Capture | X | |
| PGM-ASR | Audio Spatial Reasoning | X | |
| PGM-VSR | Visual Spatial Reasoning | X | |
| PGM-PRC | Prompt Creation | X | |
| PGM-BKN | Basic Knowledge | X | |
| PGM-DAC | Domain Access | X | |
| PGM-USR | User State Refinement | X | |
| PGM-PAL | Personality Alignment | X | |
| PGM-AUR | A-User Formation | X |

